Cigarette smoking among university students in Greece: a comparison between medical and other students
- PMID: 19802656
- PMCID: PMC2824102
- DOI: 10.1007/s12199-009-0110-0
Cigarette smoking among university students in Greece: a comparison between medical and other students
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of the study was to investigate the smoking habits of medical and other students and to explore the most important factors associated with students' smoking.
Methods: University students were surveyed in late spring 2006 regarding their smoking status and additional health- and behavior-related characteristics.
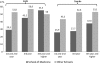
Results: A total of 1205 (269 medical and 936 nonmedical) students participated in the study. Of these 47% reported being current smokers (35% among medical students), and 30% of the smokers had already started smoking at the age of 16 years. Smokers reported a significantly higher prevalence of cough and respiratory infections and a decrease in physical fitness. The most important factor associated with smoking prevalence was friendship with smokers and maternal smoking. A better knowledge of harmful effects showed a strong association with nonsmokers. Although nonmedical students exhibited a greater possibility to be a smoker, awareness of harmful effects among medical students was not as significant as factor against smoking compared with among nonmedical students.
Conclusions: This study shows that smoking prevalence among medical and other students in Greece is extremely high. A lack of effective education against smoking in medical students was evident and this underlines the need to identify the factors to be included in planning effective antismoking programs.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO): Facts and figures about tobacco. http://www.who.int/tobacco/fctc/cop/en/index.html (2006). Accessed 21 May 2009.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2008: the MPOWER package. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Rundall TG, Bruvold WH. A meta-analysis of school-based smoking and alcohol use prevention programs. Health Educ. 1988;15:317–334. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources