Comparison between contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and Selvester QRS scoring system in estimating changes in infarct size between the acute and chronic phases of myocardial infarction
- PMID: 19804513
- PMCID: PMC6932321
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2009.00327.x
Comparison between contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and Selvester QRS scoring system in estimating changes in infarct size between the acute and chronic phases of myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: The Selvester QRS score was developed as a method to estimate infarct size (IS) using the ECG and has been validated during the prereperfusion era. Few comparisons exist with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (ceMRI) in reperfused patients. This study evaluates the ability of the Selvester QRS score to estimate serial changes in IS during the acute and chronic phases of the infarct evolution in patients who have received reperfusion therapy.
Methods: Thirteen patients with acute myocardial infarction underwent serial ceMRI studies in the acute (<1 week) and chronic phase (>2 months) after their initial myocardial infarction. QRS scoring was performed on the corresponding ECGs. The correlation between ceMRI measurement and QRS score estimation of IS was determined at both time points and for the difference between the two phases.
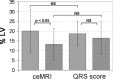
Results: The mean IS was 20.1 +/- 11.0% of total left ventricular mass (% LV) in the acute phase and 13.3 +/- 6.4% LV in the chronic phase ceMRI. The mean IS estimated by Selvester QRS score in the acute and chronic phases were 18.7 +/- 8.2% and 16.4 +/- 8.5% LV, respectively. A modest correlation was found for the acute (r = 0.57) and chronic phase IS (r = 0.54). However, there was no correlation for the difference in IS between the acute and chronic phases.
Conclusions: In this pilot study, the Selvester QRS score correlates modestly to IS by ceMRI during both the acute and chronic phases of the infarction process. The serial changes over time in the Selvester QRS score and IS by ceMRI show no correlation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of the correlation of the Selvester QRS scoring system with cardiac contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging-measured acute myocardial infarct size in patients with and without thrombolytic therapy.J Electrocardiol. 2009 Mar-Apr;42(2):139-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2008.12.004. Epub 2009 Jan 20. J Electrocardiol. 2009. PMID: 19159901 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of infarct size changes with delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and electrocardiogram QRS scoring during the 6 months after acutely reperfused myocardial infarction.J Electrocardiol. 2008 Nov-Dec;41(6):609-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2008.06.011. Epub 2008 Sep 14. J Electrocardiol. 2008. PMID: 18790502
-
Comparison of serial measurements of infarct size and left ventricular ejection fraction by contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and electrocardiographic QRS scoring in reperfused anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction.J Electrocardiol. 2010 May-Jun;43(3):230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2010.01.003. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Electrocardiol. 2010. PMID: 20116803 Clinical Trial.
-
Consideration of QRS complex in addition to ST-segment abnormalities in the estimation of the "risk region" during acute anterior or inferior myocardial infarction.J Electrocardiol. 2014 Jul-Aug;47(4):535-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 18. J Electrocardiol. 2014. PMID: 24813354 Review.
-
Electrocardiographic evaluation of reperfusion therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 1996 Feb;43(1):68-85. Dan Med Bull. 1996. PMID: 8906982 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of electrocardiographic criteria for identifying left ventricular dysfunction in patients with previous myocardial infarction.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021 Mar;26(2):e12812. doi: 10.1111/anec.12812. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021. PMID: 33124739 Free PMC article.
-
Selvester QRS score and total perfusion deficit calculated by quantitative gated single-photon emission computed tomography in patients with prior anterior myocardial infarction in the coronary intervention era.Heart Vessels. 2017 Apr;32(4):369-375. doi: 10.1007/s00380-016-0884-0. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Heart Vessels. 2017. PMID: 27488118
-
Simple indices of infarct size post ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) provides similar risk stratification to cardiac MRI.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 21;19(11):e0311157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311157. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39570931 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the Selvester QRS score after primary PCI strategy and conservative treatment for STEMI patients with negative T waves.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019 Nov;24(6):e12684. doi: 10.1111/anec.12684. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019. PMID: 31368226 Free PMC article.
-
Decreases in electrocardiographic R-wave amplitude and QT interval predict myocardial ischemic infarction in Rhesus monkeys with left anterior descending artery ligation.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e71876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071876. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levy D, Thom TJ. Death rates from coronary disease—progress and a puzzling paradox. N Engl J Med 1998;339:915–917. - PubMed
-
- Ribichini F, Ferrero V, Wijns W. Reperfusion treatment of ST‐elevation acute myocardial infarction. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2004;47:131–157. - PubMed
-
- Hochman JS, Choo H. Limitation of myocardial infarct expansion by reperfusion independent of myocardial salvage. Circulation 1987;75:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Ertl G, Frantz S. Healing after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 2005;66:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Sobel BE, Bresnahan GF, Shell WE, et al Estimation of infarct size in man and its relation to prognosis. Circulation 1972;46:640–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

