Catalytic activities of NifEN: implications for nitrogenase evolution and mechanism
- PMID: 19805110
- PMCID: PMC2761346
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907872106
Catalytic activities of NifEN: implications for nitrogenase evolution and mechanism
Abstract
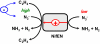
NifEN is a key player in the biosynthesis of nitrogenase MoFe protein. It not only shares a considerable degree of sequence homology with the MoFe protein, but also contains clusters that are homologous to those found in the MoFe protein. Here we present an investigation of the catalytic activities of NifEN. Our data show that NifEN is catalytically competent in acetylene (C(2)H(2)) and azide (N(3)(-)) reduction, yet unable to reduce dinitrogen (N(2)) or evolve hydrogen (H(2)). Upon turnover, C(2)H(2) gives rise to an additional S = 1/2 signal, whereas N(3)(-) perturbs the signal originating from the NifEN-associated FeMoco homolog. Combined biochemical and spectroscopic studies reveal that N(3)(-) can act as either an inhibitor or an activator for the binding and/or reduction of C(2)H(2), while carbon monoxide (CO) is a potent inhibitor for the binding and/or reduction of both N(3)(-) and C(2)H(2). Taken together, our results suggest that NifEN is a catalytic homolog of MoFe protein; however, it is only a "skeleton" version of the MoFe protein, as its associated clusters are simpler in structure and less versatile in function, which, in turn, may account for its narrower range of substrates and lower activities of substrate reduction. The resemblance of NifEN to MoFe protein in catalysis points to a plausible, sequential appearance of the two proteins in nitrogenase evolution. More importantly, the discrepancy between the two systems may provide useful insights into nitrogenase mechanism and allow reconstruction of a fully functional nitrogenase from the "skeleton" enzyme, NifEN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decoding the nitrogenase mechanism: the homologue approach.Acc Chem Res. 2010 Mar 16;43(3):475-84. doi: 10.1021/ar900254x. Acc Chem Res. 2010. PMID: 20030377 Free PMC article.
-
NifEN: a versatile player in nitrogenase assembly, catalysis and evolution.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2025 Mar;30(2):135-149. doi: 10.1007/s00775-024-02086-6. Epub 2024 Dec 12. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 39663240 Review.
-
Dual functions of NifEN: insights into the evolution and mechanism of nitrogenase.Dalton Trans. 2010 Mar 28;39(12):2964-71. doi: 10.1039/b922555b. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Dalton Trans. 2010. PMID: 20221527 Free PMC article.
-
Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenases containing altered MoFe proteins with substitutions in the FeMo-cofactor environment: effects on the catalyzed reduction of acetylene and ethylene.Biochemistry. 2000 Mar 21;39(11):2970-9. doi: 10.1021/bi992092e. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10715117
-
Nitrogenase structure and function: a biochemical-genetic perspective.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:335-66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.002003. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8561464 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitrogenase and homologs.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015 Mar;20(2):435-45. doi: 10.1007/s00775-014-1225-3. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015. PMID: 25491285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP-dependent substrate reduction at an [Fe8S9] double-cubane cluster.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 20;115(12):2994-2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720489115. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29507223 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the nitrogenase mechanism: the homologue approach.Acc Chem Res. 2010 Mar 16;43(3):475-84. doi: 10.1021/ar900254x. Acc Chem Res. 2010. PMID: 20030377 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of nitrogen fixation and nitrogenase-like sequences amongst microbial genomes.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 3;13:162. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-162. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22554235 Free PMC article.
-
NifEN: a versatile player in nitrogenase assembly, catalysis and evolution.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2025 Mar;30(2):135-149. doi: 10.1007/s00775-024-02086-6. Epub 2024 Dec 12. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 39663240 Review.
References
-
- Burgess BK, Lowe DJ. Mechanism of molybdenum nitrogenase. Chem Rev. 1996;96:2983–3012. - PubMed
-
- Barney BM, et al. Breaking the N2 triple bond: Insights into the nitrogenase mechanism. Dalton Trans. 2006;19:2277–2284. - PubMed
-
- Einsle O, et al. Nitrogenase MoFe-protein at 1.16 Å resolution: A central ligand in the FeMo-cofactor. Science. 2002;297:1696–1700. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Fay AW, Lee CC, Yoshizawa J, Ribbe MW. Assembly of nitrogenase MoFe protein. Biochemistry. 2008;47:3973–3981. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin PJ, et al. The Azotobacter vinelandii NifEN complex contains two identical [4Fe-4S] clusters. Biochemistry. 1998;37:10420–10428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

