The emerging role of HP1 in the DNA damage response
- PMID: 19805510
- PMCID: PMC2786877
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01048-09
The emerging role of HP1 in the DNA damage response
Abstract
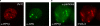
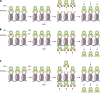
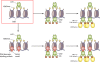
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) family members are versatile proteins involved in transcription, chromatin organization, and replication. Recent findings now have implicated HP1 proteins in the DNA damage response as well. Cell-biological approaches showed that reducing the levels of all three HP1 isoforms enhances DNA repair, possibly due to heterochromatin relaxation. Additionally, HP1 is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage, which was suggested to initiate the DNA damage response. These findings have led to the conclusion that heterochromatic proteins are inhibitory to repair and that their dissociation from heterochromatin may facilitate repair. In contrast with an inhibitory role, a more active role for HP1 in DNA repair also was proposed based on the finding that all HP1 isoforms are recruited to UV-induced lesions, oxidative lesions, and DNA breaks. The loss of HP1 renders nematodes highly sensitive to DNA damage, and mice lacking HP1beta suffer from genomic instability, suggesting that the loss of HP1 is not necessarily beneficial for repair. These findings raise the possibility that HP1 facilitates DNA repair by reorganizing chromatin, which may involve interactions between phosphorylated HP1 and other DNA damage response proteins. Taken together, these studies illustrate an emerging role of HP1 proteins in the response to genotoxic stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterochromatin protein 1 is recruited to various types of DNA damage.J Cell Biol. 2009 May 18;185(4):577-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810035. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19451271 Free PMC article.
-
The changing faces of HP1: From heterochromatin formation and gene silencing to euchromatic gene expression: HP1 acts as a positive regulator of transcription.Bioessays. 2011 Apr;33(4):280-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.201000138. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21271610 Review.
-
An HP1 isoform-specific feedback mechanism regulates Suv39h1 activity under stress conditions.Epigenetics. 2017 Feb;12(2):166-175. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2016.1278096. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 28059589 Free PMC article.
-
Human heterochromatin protein 1 isoforms HP1(Hsalpha) and HP1(Hsbeta) interfere with hTERT-telomere interactions and correlate with changes in cell growth and response to ionizing radiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8363-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8363-8376.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14585993 Free PMC article.
-
The heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) family: put away a bias toward HP1.Mol Cells. 2008 Sep 30;26(3):217-27. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18664736 Review.
Cited by
-
Biology and Physics of Heterochromatin-Like Domains/Complexes.Cells. 2020 Aug 11;9(8):1881. doi: 10.3390/cells9081881. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32796726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Epigenetics and Genetics in Cancer.Genomics Inform. 2013 Dec;11(4):164-73. doi: 10.5808/GI.2013.11.4.164. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Genomics Inform. 2013. PMID: 24465226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HP1β-dependent recruitment of UBF1 to irradiated chromatin occurs simultaneously with CPDs.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014 Dec 30;7(1):39. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-7-39. eCollection 2014. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014. PMID: 25587355 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation: a new target for protein degradation in cancer.Trends Cancer. 2025 Apr;11(4):403-420. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2025.01.013. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Trends Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40055119 Review.
-
A Systematic Analysis of Factors Localized to Damaged Chromatin Reveals PARP-Dependent Recruitment of Transcription Factors.Cell Rep. 2015 Jun 9;11(9):1486-500. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.053. Epub 2015 May 21. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26004182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aucott, R., J. Bullwinkel, Y. Yu, W. Shi, M. Billur, J. P. Brown, U. Menzel, D. Kioussis, G. Wang, I. Reisert, J. Weimer, R. K. Pandita, G. G. Sharma, T. K. Pandita, R. Fundele, and P. B. Singh. 2008. HP1-beta is required for development of the cerebral neocortex and neuromuscular junctions. J. Cell Biol. 183:597-606. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayoub, N., A. D. Jeyasekharan, J. A. Bernal, and A. R. Venkitaraman. 2008. HP1-beta mobilization promotes chromatin changes that initiate the DNA damage response. Nature 453:682-686. - PubMed
-
- Bartek, J., and J. Lukas. 2007. DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19:238-245. - PubMed
-
- Camenisch, U., R. Dip, S. B. Schumacher, B. Schuler, and H. Naegeli. 2006. Recognition of helical kinks by xeroderma pigmentosum group A protein triggers DNA excision repair. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13:278-284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
