Excoecarianin, Isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea, Inhibits Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Infection through Inactivation of Viral Particles
- PMID: 19808846
- PMCID: PMC3136347
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nep157
Excoecarianin, Isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea, Inhibits Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Infection through Inactivation of Viral Particles
Abstract
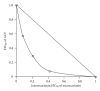
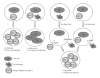
Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea (Euphorbiaceae) is one of the traditional medicinal plants widely used by oriental people to treat various diseases. We have previously demonstrated that the acetone extract of P. urinaria inhibits herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) but not HSV-1 infection. In a continuing effort to clarify the antiviral mechanisms of P. urinaria, we isolated the pure compound excoecarianin from the whole plant of P. urinaria through acetone extraction, and investigated its anti-HSV-1 and HSV-2 activities. Our results indicated that excoecarianin protected Vero cells from HSV-2 but not HSV-1 infection, and its 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) was 1.4 ± 0.1 μM. The antiviral effective concentration of excoecarianin did not affect the viability or the morphology of Vero cells. Although excoecarianin inhibited HSV-2 infection, the inhibitory effect, however, was most prominent when excoecarianin was concurrently added with the virus. Pretreatment of Vero cells with excoecarianin with removal of the drug prior to infection did not yield any antiviral effects, and the same observation was made for post viral entry treatment. Subsequent studies revealed that excoecarianin inactivated HSV-2 virus particles to prevent viral infection. A synergistic antiviral effect against HSV-2 was also observed when Vero cells were treated with a combination of acyclovir (ACV) and excoecarianin. These results suggested that excoecarianin merits to be further explored as an entry inhibitor against HSV-2 and could potentially be investigated for combinatorial drug treatment with nucleoside analogues such as ACV in therapeutic management of HSV-2 infection.
Figures

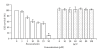


References
-
- Kleymann G, Fischer R, Betz UAK, et al. New helicase-primase inhibitors as drug candidates for the treatment of herpes simplex disease. Nature Medicine. 2002;8(4):392–398. - PubMed
-
- Liuzzi M, Deziel R, Moss N, et al. A potent peptidomimetic inhibitor of HSV ribonucleotide reductase with antiviral activity in vivo . Nature. 1994;372(6507):695–698. - PubMed
-
- Wathen MW. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of herpesviruses. Reviews in Medical Virology. 2002;12(3):167–178. - PubMed
-
- de Clercq E. Molecular targets for antiviral agents. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2001;297(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Naesens L, de Clercq E. Recent developments in herpesvirus therapy. Herpes. 2001;8(1):12–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

