The role of low endothelial shear stress in the conversion of atherosclerotic lesions from stable to unstable plaque
- PMID: 19809311
- PMCID: PMC10926252
- DOI: 10.1097/HCO.0b013e328331630b
The role of low endothelial shear stress in the conversion of atherosclerotic lesions from stable to unstable plaque
Abstract
Purpose of review: Local hemodynamic factors are major determinants of the natural history of individual atherosclerotic plaque progression in coronary arteries. The purpose of this review is to summarize the role of low endothelial shear stress (ESS) in the transition of early, stable plaques to high-risk atherosclerotic lesions.
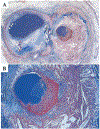
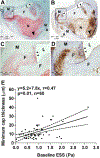
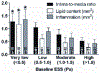
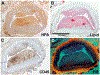
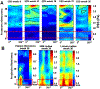
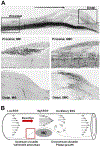
Recent findings: Low ESS regulates multiple pathways within the atherosclerotic lesion, resulting in intense vascular inflammation, progressive lipid accumulation, and formation and expansion of a necrotic core. Upregulation of matrix-degrading proteases promotes thinning of the fibrous cap, severe internal elastic lamina fragmentation, and extracellular matrix remodeling. In the setting of plaque-induced changes of the local ESS, coronary regions persistently exposed to very low ESS develop excessive expansive remodeling, which further exacerbates the proinflammatory low ESS stimulus. Recent studies suggest that the effect of recognized cardioprotective medications may be mediated by attenuation of the proinflammatory effect of the low ESS environment in which a plaque develops.
Summary: Low ESS determines the severity of vascular inflammation, the status of the extracellular matrix, and the nature of wall remodeling, all of which synergistically promote the transition of stable lesions to thin cap fibroatheromata that may rupture with subsequent formation of an occlusive thrombus and result in an acute coronary syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prediction of the localization of high-risk coronary atherosclerotic plaques on the basis of low endothelial shear stress: an intravascular ultrasound and histopathology natural history study.Circulation. 2008 Feb 26;117(8):993-1002. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.695254. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18250270
-
Role of endothelial shear stress in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling: molecular, cellular, and vascular behavior.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007 Jun 26;49(25):2379-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.059. Epub 2007 Jun 8. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17599600 Review.
-
Thin-capped atheromata with reduced collagen content in pigs develop in coronary arterial regions exposed to persistently low endothelial shear stress.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jul;33(7):1494-504. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300827. Epub 2013 May 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23640495 Free PMC article.
-
Risk stratification of individual coronary lesions using local endothelial shear stress: a new paradigm for managing coronary artery disease.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007 Nov;22(6):552-64. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0b013e3282f07548. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17921744 Review.
-
Natural history of experimental coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling in relation to endothelial shear stress: a serial, in vivo intravascular ultrasound study.Circulation. 2010 May 18;121(19):2092-101. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901678. Epub 2010 May 3. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 20439786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Calcium-Binding Protein S100A4 Is Upregulated in Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaques and Contributes to Expansive Remodeling.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Sep 15;9(18):e016128. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016128. Epub 2020 Sep 11. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32914661 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of half-turned truncal switch and conventional operations.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021 Jun 28;33(1):101-109. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivab035. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33667315 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Coronary Blood Flow Velocity and Wall Shear Stress Estimation Using Ultrasound in an Ex Vivo Porcine Heart.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024 Feb;15(1):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s13239-023-00697-9. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024. PMID: 37962814 Free PMC article.
-
Short Communication: Carotid Artery Plaque Burden in HIV Is Associated with Soluble Mediators and Monocytes.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2020 Dec;36(12):1020-1023. doi: 10.1089/AID.2020.0075. Epub 2020 Sep 28. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2020. PMID: 32862657 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation in stable angina pectoris: a narrative review on current evidence and underlying physiological mechanisms.Neth Heart J. 2024 Jan;32(1):23-30. doi: 10.1007/s12471-023-01830-y. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Neth Heart J. 2024. PMID: 37982981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Falk E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:C7–12 - PubMed
-
- Chatzizisis YS, Coskun AU, Jonas M, et al. Role of endothelial shear stress in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling: molecular, cellular and vascular behavior. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:2379–2393. - PubMed
-
- Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Farb A, et al. Healed plaque ruptures and sudden coronary death: evidence that subclinical rupture has a role in plaque progression. Circulation 2001;103:934–40. - PubMed
-
- Asakura T, Karino T. Flow patterns and spatial distribution of atherosclerotic lesions in human coronary arteries. Circ Res 1990;66: 1045–1066. - PubMed
-
-
Tanaka A, Imanishi T, Kitabata H, et al. Distribution and frequency of thin-capped fibroatheromas and ruptured plaques in the entire culprit coronary artery in patients with acute coronary syndrome as determined by optical coherence tomography. Am J Cardiol 2008;102:975–979
* This clinical, optical coherence tomography study demonstrated in-vivo the proximal distribution of TCFAs.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

