Curcumin induces apoptosis-independent death in oesophageal cancer cells
- PMID: 19809435
- PMCID: PMC2778521
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605308
Curcumin induces apoptosis-independent death in oesophageal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Oesophageal cancer incidence is increasing and survival rates remain extremely poor. Natural agents with potential for chemoprevention include the phytochemical curcumin (diferuloylmethane). We have examined the effects of curcumin on a panel of oesophageal cancer cell lines.
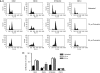
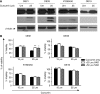
Methods: MTT (3-(4,5-dimethyldiazol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assays and propidium iodide staining were used to assess viability and DNA content, respectively. Mitotic catastrophe (MC), apoptosis and autophagy were defined by both morphological criteria and markers such as MPM-2, caspase 3 cleavage and monodansylcadaverine (MDC) staining. Cyclin B and poly-ubiquitinated proteins were assessed by western blotting.
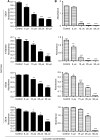
Results: Curcumin treatment reduces viability of all cell lines within 24 h of treatment in a 5-50 muM range. Cytotoxicity is associated with accumulation in G2/M cell-cycle phases and distinct chromatin morphology, consistent with MC. Caspase-3 activation was detected in two out of four cell lines, but was a minor event. The addition of a caspase inhibitor zVAD had a marginal or no effect on cell viability, indicating predominance of a non-apoptotic form of cell death. In two cell lines, features of both MC and autophagy were apparent. Curcumin-responsive cells were found to accumulate poly-ubiquitinated proteins and cyclin B, consistent with a disturbance of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. This effect on a key cell-cycle checkpoint regulator may be responsible for the mitotic disturbances and consequent cytotoxicity of this drug.
Conclusion: Curcumin can induce cell death by a mechanism that is not reliant on apoptosis induction, and thus represents a promising anticancer agent for prevention and treatment of oesophageal cancer.
Figures




References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Kumar A, Bharti AC (2003) Anticancer potential of curcumin: preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res 23: 363–398 - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Takada Y, Banerjee S, Newman RA, Bueso-Ramos CE, Price JE (2005) Curcumin suppresses the paclitaxel-induced nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in breast cancer cells and inhibits lung metastasis of human breast cancer in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 11: 7490–7498 - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4: 807–818 - PubMed
-
- Aoki H, Takada Y, Kondo S, Sawaya R, Aggarwal BB, Kondo Y (2007) Evidence that curcumin suppresses the growth of malignant gliomas in vitro and in vivo through induction of autophagy: role of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol Pharmacol 72: 29–39 - PubMed
-
- Biederbick A, Kern HF, Elsasser HP (1995) Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol 66: 3–14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

