Apoptosis and expression of AQP5 and TGF-beta in the irradiated rat submandibular gland
- PMID: 19809564
- PMCID: PMC2757666
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2009.41.3.145
Apoptosis and expression of AQP5 and TGF-beta in the irradiated rat submandibular gland
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of X-ray irradiation on apoptosis and change of expression of aquaporin 5 (AQP5) and transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) in the rat submandibular gland (SMG).
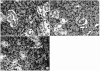
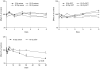
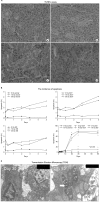
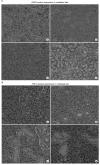
Materials and methods: SMGs of 120 male Sprague-Dawley rats were irradiated with a single X-ray dose (3, 10, 20, or 30 Gy). At the early and late post-irradiation phase, apoptosis was measured by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) method, and expression of AQP5 and TGF-β was determined by immunohistochemical staining.
Results: At the late post-irradiation phase, increased apoptosis was evident and marked decreases of expression of AQP5 expression by acinar cells and TGF-β expression by ductal cells were evident.
Conclusion: Apoptosis after X-ray irradiation develops relatively late in rat SMG. Irradiation reduces AQP5 and TGF-β expression in different SMG cell types.
Keywords: AQP5; Apoptosis; Radiation; Submandibular gland; TGF-β.
Figures
References
-
- Taylor JC, Terrell JE, Ronis DL, Fowler KE, Bishop C, Lambert MT, et al. Disability in patients with head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130:764–769. - PubMed
-
- Konings AW, Coppes RP, Vissink A. On the mechanism of salivary gland radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62:1187–1194. - PubMed
-
- Abok K, Brunk U, Jung B, Ericsson J. Morphologic and histochemical studies on the differing radiosensitivity of ductular and acinar cells of the rat submandibular gland. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45:443–460. - PubMed
-
- Peter B, Van Waarde MA, Vissink A, s-Gravenmade EJ, Konings AW. The role of secretory granules in the radiosensitivity of rat salivary gland acini--a morphological study. Radiat Res. 1994;140:419–428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

