Identification and treatment of metabolic complications in pediatric obesity
- PMID: 19809879
- PMCID: PMC5504917
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-009-9115-7
Identification and treatment of metabolic complications in pediatric obesity
Abstract
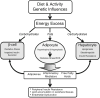
Metabolic consequences of obesity including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver infiltration are rapidly emerging in the pediatric population. Identifying effective strategies for identifying and treating these obesity related comorbidities in children are crucial to the prevention of future cardiovascular disease and poor health outcomes.This review discusses the pathophysiologic connections between obesity, metabolic disease and cardiovascular risk. Current evidence and recommendations for screening and treatment for the metabolic consequences of pediatric obesity are reviewed.
Figures
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–55. - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D, Bell RA, D’Agostino RB, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, et al. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA. 2007;297:2716–24. - PubMed
-
- Marra F, Bertolani C. Adipokines in liver diseases. Hepatology. 2009;50:957–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

