Spontaneous autoimmune myocarditis and cardiomyopathy in HLA-DQ8.NODAbo transgenic mice
- PMID: 19811893
- PMCID: PMC3574900
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2009.09.005
Spontaneous autoimmune myocarditis and cardiomyopathy in HLA-DQ8.NODAbo transgenic mice
Abstract
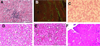
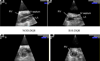
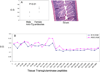
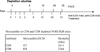
Most individuals have viral infections at some point in their life, however, only few develop autoreactivity to cardiac myosin following infection suggesting a genetic predisposition. Population studies have shown that among all the genetic factors linked with autoimmune disease development, MHC class II genes are the most significant genetic factors. Experimental autoimmune myocarditis resembling human Dilated cardiomyopathy can be induced in susceptible mice by infection with coxsackie virus as well as immunization with purified foreign and murine cardiac specific a-myosin. We generated transgenic mice lacking endogenous class II molecules, HLA-DR3.Abo and HLA-DQ8.Abo transgenic mice in NOD and HLA-DQ8.Abo in B10 background, to study the role of MHC in spontaneous autoimmunity. The HLA molecules in these mice are expressed on cell surface and can positively select CD4+ T cells expressing various Vb T cell receptors. NOD.DQ8 female mice spontaneously developed myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Histopathology of heart revealed mononuclear infiltrate consisting of CD4 and Mac-1+ cells and myocyte necrosis. NOD.DQ8 mice showed cellular and humoral autoreactive response to self cardiac myosin.. Depletion of CD8 and CD4 + cells suggested that CD8 T cells may act as regulatory cells while CD4 cells are required as effector cells. NOD.DR3 and B10.DQ8 mice did not develop any cardiac pathology suggesting DQ8 is required for predisposition to the spontaneous autoreactivity while NOD background influences onset and progression of disease. Thus these mice provide powerful tools to understand the role of HLA class II molecules in predisposition and onset of human diseases and to develop immunotherapy.
Figures

References
-
- Kim KS, Hufnagel G, Chapman NM, Tracy S. The group B coxsackieviruses and myocarditis. Reviews in medical virology. 2001;11:355–368. - PubMed
-
- Olinde KD, O'Connell JB. Inflammatory heart disease: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and treatment of myocarditis. Annual review of medicine. 1994;45:481–490. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, Herskowitz A, Neumann DA, Neu N. Autoimmune myocarditis: a paradigm of post-infection autoimmune disease. Immunology today. 1988;9:117–120. - PubMed
-
- Maisch B, Bauer E, Cirsi M, Kochsiek K. Cytolytic cross-reactive antibodies directed against the cardiac membrane and viral proteins in coxsackievirus B3 and B4 myocarditis. Characterization and pathogenetic relevance. Circulation. 1993;87:IV49–IV65. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, Neumann DA, Herskowitz A, Traystman MD, Beisel KW. Genetics of susceptibility to viral myocarditis in mice. Pathology and immunopathology research. 1988;7:266–278. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

