Preserving fertility during cancer treatment
- PMID: 19812566
- PMCID: PMC3124896
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1009-1124
Preserving fertility during cancer treatment
Abstract
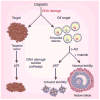
Imatinib (trade name Gleevec) preserves fertility in female mice treated with the common chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin. Imatinib seems to block an apoptotic pathway activated by cisplatin in ovarian germ cells (pages 1179– 1185). The findings could lead to new ways to protect germ cells from the damaging effects of cancer treatment.
Figures
Comment on
-
Inhibition of the c-Abl-TAp63 pathway protects mouse oocytes from chemotherapy-induced death.Nat Med. 2009 Oct;15(10):1179-85. doi: 10.1038/nm.2033. Epub 2009 Sep 27. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19783996
References
-
- von Wolff M, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:1547–1553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

