A TGFbeta-responsive gene signature is associated with a subset of diffuse scleroderma with increased disease severity
- PMID: 19812599
- PMCID: PMC3867816
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2009.318
A TGFbeta-responsive gene signature is associated with a subset of diffuse scleroderma with increased disease severity
Abstract
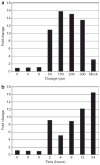
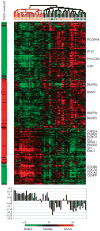
Systemic sclerosis is a complex disease with widespread skin fibrosis and variable visceral organ involvement. Since transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) has been implicated in driving fibrosis in systemic sclerosis, a mechanism-derived gene expression signature was used to assay TGFbeta-responsive gene expression in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc). Primary dermal fibroblasts from patients with diffuse SSc (dSSc) and healthy controls were treated with TGFbeta, and the genome-wide gene expression was measured on DNA microarrays over a time course of 24 hours. Eight hundred and ninety-four probes representing 674 uniquely annotated genes were identified as TGFbeta responsive. Expression of the TGFbeta-responsive signature was examined in skin biopsies from 17 dSSc, seven limited SSc (lSSc), three morphea patients, and six healthy controls. The TGFbeta-responsive signature was expressed in 10 out of 17 dSSc skin biopsies, but was not found in lSSc, morphea, or healthy control biopsies. Expression of dSSC the TGFbeta-responsive signature stratifies patients into two major groups, one of which corresponds to the "diffuse-proliferation" intrinsic subset that showed higher modified Rodnan skin score and a higher likelihood of scleroderma lung disease. The TGFbeta-responsive signature is found in only a subset of dSSc patients who could be targeted by specific therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
ML Whitfield has filed a patent application for gene expression biomarkers in scleroderma. This intellectual property has been licensed to a startup company, Celdara Medical, LLC, that is aiming to translate the discovery into clinical use. Dr Whitfield holds an interest in this company. The remaining authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Akhmet-shina A, Dees C, Pileckyte M, Maurer B, Axmann R, Jungel A, et al. Dual inhibition of c-abl and PDGF receptor signaling by dasatinib and nilotinib for the treatment of dermal fibrosis. FASEB J. 2008;22:2214–22. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AJ, Miller MH, Littlejohn GO. A survival study of patients with scleroderma diagnosed over 30 years (1953–1983): the value of a simple cutaneous classification in the early stages of the disease. J Rheumatol. 1988b;15:276–83. - PubMed
-
- Baroni SS, Santillo M, Bevilacqua F, Luchetti M, Spadoni T, Mancini M, et al. Stimulatory autoantibodies to the PDGF receptor in systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2667–76. - PubMed
-
- Chambers RC, Leoni P, Kaminski N, Laurent GJ, Heller RA. Global expression profiling of fibroblast responses to transforming growth factor-beta1 reveals the induction of inhibitor of differentiation-1 and provides evidence of smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. Am J Pathol. 2003;162:533–46. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

