FTY720 (fingolimod) in Multiple Sclerosis: therapeutic effects in the immune and the central nervous system
- PMID: 19814729
- PMCID: PMC2782328
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00451.x
FTY720 (fingolimod) in Multiple Sclerosis: therapeutic effects in the immune and the central nervous system
Abstract
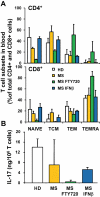
FTY720 (fingolimod) is a first-in-class sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator that was highly effective in Phase II clinical trials for Multiple Sclerosis (MS). FTY720 is phosphorylated in vivo by sphingosine kinase-2 to form the active moiety FTY720-phosphate that binds to four of the five G protein-coupled S1P receptor subtypes. Studies using conditional S1P1 receptor-deficient and sphingosine kinase-deficient mice showed that the egress of lymphocytes from lymph nodes requires signalling of lymphocytic S1P1 receptors by the endogenous ligand S1P. The S1P mimetic FTY720-phosphate causes internalization and degradation of cell membrane-expressed S1P1, thereby antagonizing S1P action at the receptor. In models of human MS and demyelinating polyneuropathies, functional antagonism of lymphocytic S1P1 slows S1P-driven egress of lymphocytes from lymph nodes, thereby reducing the numbers of autoaggressive TH17 cells that recirculate via lymph and blood to the central nervous system and the sciatic/ischiatic nerves. Based on its lipophilic nature, FTY720 crosses the blood-brain barrier, and ongoing experiments suggest that the drug also down-modulates S1P1 in neural cells/astrocytes to reduce astrogliosis, a phenomenon associated with neurodegeneration in MS. This may help restore gap-junctional communication of astrocytes with neurons and cells of the blood-brain barrier. Additional effects may result from (down-) modulation of S1P3 in astrocytes and of S1P1 and S1P5 in oligodendrocytes. In conclusion, FTY720 may act through immune-based and central mechanisms to reduce inflammation and support structural restoration of the central nervous system parenchyma. Beyond the autoimmune indications, very recent studies suggest that short-term, low-dose administration of FTY720 could help treat chronic (viral) infections. Differential effects of the drug on the trafficking of naïve, central memory and effector memory T cell subsets are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Albert R, Hinterding K, Brinkmann V, Guerini D, Mueller-Hartwieg C, Knecht H, et al. Novel immunomodulator FTY720 is phosphorylated in rats and humans to form a single stereoisomer. identification, chemical proof, and biological characterization of the biologically active species and its inactive enantiomer. J Med Chem. 2005;48:5373–77. - PubMed
-
- Allende ML, Yamashita T, Proia RL. G-protein-coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood. 2003;102:3665–3667. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez SE, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007;18:300–307. - PubMed
-
- Antel J, Miron V. Central nervous system effects of current and emerging multiple sclerosis-directed immuno-therapies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008;110:951–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

