Novel expression signatures identified by transcriptional analysis of separated leucocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis
- PMID: 19815495
- PMCID: PMC2935323
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.108043
Novel expression signatures identified by transcriptional analysis of separated leucocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis
Abstract
Objective: To optimise a strategy for identifying gene expression signatures differentiating systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis that provide insight into disease pathogenesis and identify biomarkers.
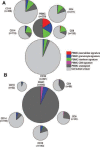
Methods: 44 vasculitis patients, 13 SLE patients and 25 age and sex-matched controls were enrolled. CD4 and CD8 T cells, B cells, monocytes and neutrophils were isolated from each patient and, together with unseparated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), were hybridised to spotted oligonucleotide microarrays.
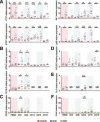
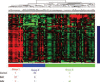
Results: Using expression data obtained from purified cells a substantial number of differentially expressed genes were identified that were not detectable in the analysis of PBMC. Analysis of purified T cells identified a SLE-associated, CD4 T-cell signature consistent with type 1 interferon signalling driving the generation and survival of tissue homing T cells and thereby contributing to disease pathogenesis. Moreover, hierarchical clustering using expression data from purified monocytes provided significantly improved discrimination between the patient groups than that obtained using PBMC data, presumably because the differentially expressed genes reflect genuine differences in processes underlying disease pathogenesis.
Conclusion: Analysis of leucocyte subsets enabled the identification of gene signatures of both pathogenic relevance and with better disease discrimination than those identified in PBMC. This approach thus provides substantial advantages in the search for diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in autoimmune disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, et al. Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 1999;286:531–7 - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000;403:503–11 - PubMed
-
- van't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002;415:530–6 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, et al. Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet 2005;365:671–9 - PubMed
-
- Lossos IS. Molecular pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:6351–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

