Uncovering pathways in DNA oligonucleotide hybridization via transition state analysis
- PMID: 19815517
- PMCID: PMC2759370
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904721106
Uncovering pathways in DNA oligonucleotide hybridization via transition state analysis
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 8;106(49):21007
Abstract
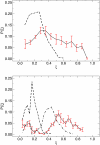
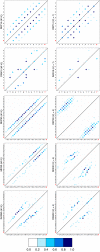
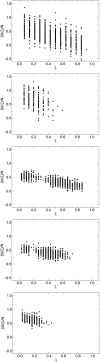
DNA hybridization plays a central role in biology and, increasingly, in materials science. Yet, there is no precedent for examining the pathways by which specific single-stranded DNA sequences interact to assemble into a double helix. A detailed model of DNA is adopted in this work to examine such pathways and to determine the role of sequence, if any, on DNA hybridization. Transition path sampling simulations reveal that DNA rehybridization is prompted by a distinct nucleation event involving molecular sites with approximately four bases pairing with partners slightly offset from those involved in ideal duplexation. Nucleation is promoted in regions with repetitive base pair sequence motifs, which yield multiple possibilities for finding complementary base partners. Repetitive sequences follow a nonspecific pathway to renaturation consistent with a molecular "slithering" mechanism, whereas random sequences favor a restrictive pathway involving the formation of key base pairs before renaturation fully ensues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Voet D, Voet JG, Pratt CW. Fundamentals of Biochemistry. New York: Wiley; 1999. pp. 751–930.
-
- Saiki RK, et al. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988;239:487–491. - PubMed
-
- Rothemund PWK. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature. 2006;404:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Freifelder D. Principles of Physical Chemistry with Applications to the Biological Sciences. Boston: Jones and Bartlett; 1985. pp. 513–517.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

