Long-term improvement in mdx cardiomyopathy after therapy with peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers
- PMID: 19815563
- PMCID: PMC2802205
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp335
Long-term improvement in mdx cardiomyopathy after therapy with peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers
Abstract
Aims: The cardiomyopathy found in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is responsible for death due to heart failure in approximately 30% of patients and additionally contributes to many DMD morbidities. Strategies to bypass DMD-causing mutations to allow an increase in body-wide dystrophin have proved promising, but increasing cardiac dystrophin continues to be challenging. The purpose of this study was to determine if therapeutic restoration of cardiac dystrophin improved the significant cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction identified in X-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) dystrophin-null mouse due to a truncation mutation over time after treatment.
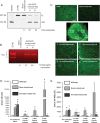
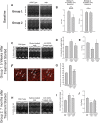
Methods and results: Mice lacking dystrophin due to a truncation mutation (mdx) were given an arginine-rich, cell-penetrating, peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PPMO) that delivered a splice-switching oligonucleotide-mediated exon skipping therapy to restore dystrophin in mdx mice before the development of detectable cardiomyopathy. PPMO successfully restored cardiac dystrophin expression, preserved cardiac sarcolemma integrity, and prevented the development of cardiac pathology that develops in mdx-null mice over time. By echocardiography and Doppler analysis of the mitral valve, we identified that PPMO treatment of mdx mice prevented the cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction identified in sham-treated, age-matched mdx mice, characteristic of DMD patients early in the disease process, in as little as 5-6 weeks after the initiation of treatment. Surprisingly, despite the short-term replacement of cardiac dystrophin (<1% present after 12 weeks by immunodetection), PPMO therapy also provided a durable cardiac improvement in cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction for up to 7 months after the initiation of treatment.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate for the first time that PPMO-mediated exon skipping therapy early in the course of DMD may effectively prevent or slow down associated cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction with significant long-term impact.
Figures


Comment in
-
Exon skipping with morpholino oligomers: new treatment option for cardiomyopathy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy?Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Feb 1;85(3):409-10. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp397. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20008475 No abstract available.
References
-
- Monaco AP, Bertelson CJ, Liechti-Gallati S, Moser H, Kunkel LM. An explanation for the phenotypic differences between patients bearing partial deletions of the DMD locus. Genomics. 1988;2:90–95. - PubMed
-
- van Deutekom JC, Janson AA, Ginjaar IB, Frankhuizen WS, Aartsma-Rus A, Bremmer-Bout M, et al. Local dystrophin restoration with antisense oligonucleotide PRO051. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2677–2686. - PubMed
-
- Dunckley MG, Manoharan M, Villiet P, Eperon IC, Dickson G. Modification of splicing in the dystrophin gene in cultured Mdx muscle cells by antisense oligoribonucleotides. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1083–1090. - PubMed
-
- Wilton SD, Lloyd F, Carville K, Fletcher S, Honeyman K, Agrawal S, et al. Specific removal of the nonsense mutation from the mdx dystrophin mRNA using antisense oligonucleotides. Neuromuscul Disord. 1999;9:330–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

