Evidence for a founder mutation in the cathepsin C gene in three families with Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome
- PMID: 19816003
- PMCID: PMC2813799
- DOI: 10.1159/000245341
Evidence for a founder mutation in the cathepsin C gene in three families with Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome
Abstract
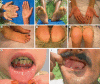
Background: Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome (PLS; OMIM 245000) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Clinically, PLS is characterized by hyperkeratosis involving the palms, soles, elbows and knees which is followed later on by periodontitis, destruction of alveolar bone and loss of primary and permanent teeth. The condition is caused by mutations in the cathepsin C (CTSC) gene.
Methods: We analyzed the DNA of members from 3 consanguineous families for mutations in the CTSC gene by direct sequencing analysis. We then performed haplotype analysis.
Results: We identified an identical recurrent missense mutation, R272P, in all 3 families. Microsatellite marker analysis around the CTSC gene revealed the same haplotype on the mutation-carrying allele in all 3 families.
Conclusion: The presence of this common mutation in families from 2 different geographical areas provides evidence for a founder effect for CTSC mutations in PLS.
Copyright 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Nakajima K, Nakano H, Takiyoshi N, Rokunohe A, Ikenaga S, Aizu T, Kaneko T, Mitsuhashi Y, Sawamura D. Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome and malignant melanoma: a high incidence of melanoma development in Japanese palmoplantar keratoderma patients. Dermatology. 2008;217:58–62. - PubMed
-
- Rao NV, Rao GV, Hoidal JR. Human dipeptidyl-peptidase I: gene characterization, localization, and expression. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:10260–10265. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JG, Kadziola A, Lauritzen C, Pedersen J, Larsen S, Dahl SW. Tetrameric dipeptidyl peptidase I directs substrate specificity by use of the residual pro-part domain. FEBS Lett. 2001;506:201–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

