Carbonic anhydrase II-based metal ion sensing: Advances and new perspectives
- PMID: 19818877
- PMCID: PMC2818387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.09.031
Carbonic anhydrase II-based metal ion sensing: Advances and new perspectives
Abstract
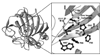
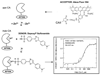
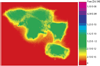
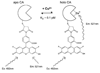
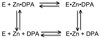
Carbonic anhydrases are archetypical zinc metalloenzymes and as such, they have been developed as the recognition element of a family of fluorescent indicators (sensors) to detect metal ions, particularly Zn(2+) and Cu(2+). Subtle modification of the structure of human carbonic anhydrase II isozyme (CAII) alters the selectivity, sensitivity, and response time for these sensors. Sensors using CAII variants coupled with zinc-dependent fluorescent ligands demonstrate picomolar sensitivity, unmatched selectivity, ratiometric fluorescence signal, and near diffusion-controlled response times. Recently, these sensors have been applied to measuring the readily exchangeable concentrations of zinc in the cytosol and nucleus of mammalian tissue culture cells and concentrations of free Cu(2+) in seawater.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Revisiting zinc coordination in human carbonic anhydrase II.Inorg Chem. 2012 Oct 15;51(20):11098-105. doi: 10.1021/ic301645j. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Inorg Chem. 2012. PMID: 23030313 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the role of metal ions in carbonic anhydrase catalysis.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 11;11(1):4557. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18425-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32917908 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of cytosolic/tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II, IX, and XII with Schiff's bases incorporating chromone and aromatic sulfonamide moieties, and their zinc complexes.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 15;15(12):3096-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.04.055. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005. PMID: 15908204
-
Analyzing free zinc(II) ion concentrations in cell biology with fluorescent chelating molecules.Metallomics. 2015 Feb;7(2):202-11. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00230j. Metallomics. 2015. PMID: 25362967 Review.
-
Fluorescence-based biosensing of zinc using carbonic anhydrase.Biometals. 2001 Sep-Dec;14(3-4):205-22. doi: 10.1023/a:1012980628412. Biometals. 2001. PMID: 11831457 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Zinc (Zn (2+) ) and Glutamate Receptors in the Processes Underlying Neurodegeneration.Neural Plast. 2015;2015:591563. doi: 10.1155/2015/591563. Epub 2015 May 27. Neural Plast. 2015. PMID: 26106488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Techniques for measuring cellular zinc.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Dec 1;611:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27580940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase CDCA1 in marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii.Mar Drugs. 2015 Mar 25;13(4):1688-97. doi: 10.3390/md13041688. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25815892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent sensors for measuring metal ions in living systems.Chem Rev. 2014 Apr 23;114(8):4564-601. doi: 10.1021/cr400546e. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24588137 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Renal Tubular Acidosis: H+/Base and Ammonia Transport Abnormalities and Clinical Syndromes.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018 Jul;25(4):334-350. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2018.05.005. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 30139460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A. Counting the zinc-proteins encoded in the human genome. J Proteome Res. 2006;5:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Coleman JE. Zinc proteins: Enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1992;61:897–946. - PubMed
-
- Christianson DW. Structural biology of zinc. Advances in Protein Chemistry. 1991;42:281–355. - PubMed
-
- Vallee BL, Auld DS. Zinc coordination, function, and structure of zinc enzymes and other proteins. Biochemistry. 1990;29:5647–5659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

