Patterns of divergence in the vCXCL and vGPCR gene clusters in primate cytomegalovirus genomes
- PMID: 19818982
- PMCID: PMC2846823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.002
Patterns of divergence in the vCXCL and vGPCR gene clusters in primate cytomegalovirus genomes
Abstract
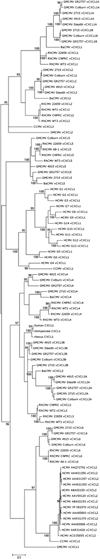
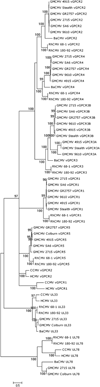
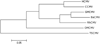
Primate cytomegalovirus (CMV) genomes contain tandemly repeated gene clusters putatively encoding divergent CXC chemokine ligand-like proteins (vCXCLs) and G protein-coupled receptor-like proteins (vGPCRs). In human, chimpanzee and rhesus CMVs, respectively, the vCXCL cluster contains two, three and six genes, and the vGPCR cluster contains two, two and five genes. We report that (i) green monkey CMV strains fall into two groups, containing either eight and five genes or seven and six genes in the respective clusters, and (ii) owl monkey CMV has two and zero genes. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that the vCXCL cluster evolved from a CXCL chemokine gene (probably GRO-alpha) that was captured in an incompletely spliced form by an ancestor of Old and New World primate CMVs, and that the vGPCR cluster evolved from a GPCR gene captured by an Old World primate CMV. Both clusters appear to have evolved via complex duplication and deletion events.
Figures





References
-
- Arav-Boger R, Foster CB, Zong JC, Pass RF. Human cytomegalovirus-encoded α-chemokines exhibit high sequence variability in congenitally infected newborns. J. Infect. Dis. 2006;193:788–791. - PubMed
-
- Bodaghi B, Jones TR, Zipeto D, Vita C, Sun L, Laurent L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Virelizier J-L, Michelson S. Chemokine sequestration by viral chemoreceptors as a novel viral escape strategy: withdrawal of chemokines from the environment of cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188:855–866. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang Y-N, Jeang K-T, Lietman T, Hayward GS. Structural organization of the spliced immediate-early gene complex that encodes the major acidic nuclear (IE1) and transactivator (IE2) proteins of African green monkey cytomegalovirus. J. Biomed. Sci. 1995;2:105–130. - PubMed
-
- Chee MS, Bankier AT, Beck S, Bohni R, Brown CM, Cerny R, Hornsnell T, Hutchinson CA, III, Kouzarides T, Martignetti JA, Preddie E, Satchwell SC, Tomlinson P, Weston KM, Barrell BG. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1990;154:126–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

