Life in the inflamed intestine, Salmonella style
- PMID: 19819699
- PMCID: PMC3235402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.08.008
Life in the inflamed intestine, Salmonella style
Abstract
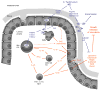
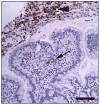
The lower gastrointestinal tract is densely populated with resident microbial communities (microbiota), which do not elicit overt host responses but rather provide benefit to the host, including niche protection from pathogens. However, introduction of bacteria into the underlying tissue evokes acute inflammation. Non-typhoidal Salmonella serotypes (NTS) elicit this stereotypic host response by actively penetrating the intestinal epithelium and surviving in tissue macrophages. Initial responses generated by bacterial host cell interaction are amplified in tissue through the interleukin (IL)-18/interferon-gamma and IL-23/IL-17 axes, resulting in the activation of mucosal barrier functions against NTS dissemination. However, the pathogen is adapted to survive antimicrobial defenses encountered in the lumen of the inflamed intestine. This strategy enables NTS to exploit inflammation to outcompete the intestinal microbiota, and promotes the Salmonella transmission by the fecal/oral route.
Figures
References
-
- Rabsch W, et al. Non-typhoidal salmonellosis: emerging problems. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Zhou D, Galan J. Salmonella entry into host cells: the work in concert of type III secreted effector proteins. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:1293–1298. - PubMed
-
- Abrahams GL, Hensel M. Manipulating cellular transport and immune responses: dynamic interactions between intracellular Salmonella enterica and its host cells. Cellular microbiology. 2006;8:728–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076246/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076246/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI032738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI079173/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI050553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI079173/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

