A comprehensive analysis of the peroxiredoxin reduction system in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 reveals that all five peroxiredoxins are thioredoxin dependent
- PMID: 19820102
- PMCID: PMC2786602
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00831-09
A comprehensive analysis of the peroxiredoxin reduction system in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 reveals that all five peroxiredoxins are thioredoxin dependent
Abstract
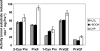
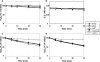
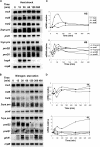
Cyanobacteria perform oxygenic photosynthesis, which gives rise to the continuous production of reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide anion radicals and hydrogen peroxide, particularly under unfavorable growth conditions. Peroxiredoxins, which are present in both chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, constitute a class of thiol-dependent peroxidases capable of reducing hydrogen peroxide as well as alkyl hydroperoxides. Chloroplast peroxiredoxins have been studied extensively and have been found to use a variety of endogenous electron donors, such as thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, or cyclophilin, to sustain their activities. To date, however, the endogenous reduction systems for cyanobacterial peroxiredoxins have not been systematically studied. We have expressed and purified all five Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 peroxiredoxins, which belong to the classes 1-Cys Prx, 2-Cys Prx, type II Prx (PrxII), and Prx Q, and we have examined their capacities to interact with and receive electrons from the m-, x-, and y-type thioredoxins from the same organism, which are called TrxA, TrxB, and TrxQ, respectively. Assays for peroxidase activity demonstrated that all five enzymes could use thioredoxins as electron donors, whereas glutathione and Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 glutaredoxins were inefficient. The highest catalytic efficiency was obtained for the couple consisting of PrxII and TrxQ thioredoxin. Studies of transcript levels for the peroxiredoxins and thioredoxins under different stress conditions highlighted the similarity between the PrxII and TrxQ thioredoxin expression patterns.
Figures




References
-
- Apel, K., and H. Hirt. 2004. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55:373-399. - PubMed
-
- Baier, M., and K. J. Dietz. 1997. The plant 2-Cys peroxiredoxin BAS1 is a nuclear-encoded chloroplast protein: its expressional regulation, phylogenetic origin, and implications for its specific physiological function in plants. Plant J. 12:179-190. - PubMed
-
- Bernroitner, M., M. Zamocky, P. G. Furtmuller, G. A. Peschek, and C. Obinger. 2009. Occurrence, phylogeny, structure, and function of catalases and peroxidases in cyanobacteria. J. Exp. Bot. 60:423-440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

