An 8-oxo-guanine repair pathway coordinated by MUTYH glycosylase and DNA polymerase lambda
- PMID: 19820168
- PMCID: PMC2775316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907280106
An 8-oxo-guanine repair pathway coordinated by MUTYH glycosylase and DNA polymerase lambda
Abstract
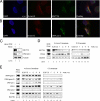
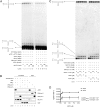
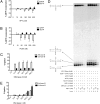
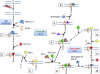
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) interact with DNA, frequently generating highly mutagenic 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxo-G) lesions. Replicative DNA polymerases (pols) often misincorporate adenine opposite 8-oxo-G. The subsequent repair mechanism allowing the removal of adenine and formation of C:8-oxo-G base pair is essential to prevent C:G to A:T transversion mutations. Here, we show by immunofluorescence experiments, in cells exposed to ROS, the involvement of MutY glycosylase homologue (MUTYH) and DNA pol lambda in the repair of A:8-oxo-G mispairs. We observe specific recruitment of MUTYH, DNA pol lambda, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) and DNA ligases I and III from human cell extracts to A:8-oxo-G DNA, but not to undamaged DNA. Using purified human proteins and a DNA template, we reconstitute the full pathway for the faithful repair of A:8-oxo-G mispairs involving MUTYH, DNA pol lambda, FEN1, and DNA ligase I. These results reveal a cellular response pathway to ROS, important to sustain genomic stability and modulate carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

