Overexpression of several Arabidopsis histone genes increases agrobacterium-mediated transformation and transgene expression in plants
- PMID: 19820187
- PMCID: PMC2782275
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.070607
Overexpression of several Arabidopsis histone genes increases agrobacterium-mediated transformation and transgene expression in plants
Abstract
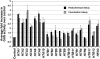
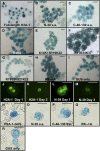
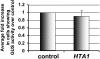
The Arabidopsis thaliana histone H2A-1 is important for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation. Mutation of HTA1, the gene encoding histone H2A-1, results in decreased T-DNA integration into the genome of Arabidopsis roots, whereas overexpression of HTA1 increases transformation frequency. To understand the mechanism by which HTA1 enhances transformation, we investigated the effects of overexpression of numerous Arabidopsis histones on transformation and transgene expression. Transgenic Arabidopsis containing cDNAs encoding histone H2A (HTA), histone H4 (HFO), and histone H3-11 (HTR11) displayed increased transformation susceptibility, whereas histone H2B (HTB) and most histone H3 (HTR) cDNAs did not increase transformation. A parallel increase in transient gene expression was observed when histone HTA, HFO, or HTR11 overexpression constructs were cotransfected with double- or single-stranded forms of a gusA gene into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) protoplasts. However, these cDNAs did not increase expression of a previously integrated transgene. We identified the N-terminal 39 amino acids of H2A-1 as sufficient to increase transient transgene expression in plants. After transfection, transgene DNA accumulates more rapidly in the presence of HTA1 than with a control construction. Our results suggest that certain histones enhance transgene expression, protect incoming transgene DNA during the initial stages of transformation, and subsequently increase the efficiency of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Constitutive expression exposes functional redundancy between the Arabidopsis histone H2A gene HTA1 and other H2A gene family members.Plant Cell. 2006 Jul;18(7):1575-89. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.039719. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16751347 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Arabidopsis histone H2A-1 gene correlates with susceptibility to Agrobacterium transformation.Plant J. 2002 Nov;32(3):285-98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01425.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12410808
-
Perturbation of H3K27me3-Associated Epigenetic Processes Increases Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017 Jan;30(1):35-44. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-16-0250-R. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017. PMID: 27926813
-
[T-DNA integration patterns in transgenic plants mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens].Yi Chuan. 2011 Dec;33(12):1327-34. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.01327. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 22207378 Review. Chinese.
-
Integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA into the Plant Genome.Annu Rev Genet. 2017 Nov 27;51:195-217. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-035320. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Annu Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28853920 Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis RETICULON-LIKE3 (RTNLB3) and RTNLB8 Participate in Agrobacterium-Mediated Plant Transformation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 24;19(2):638. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020638. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29495267 Free PMC article.
-
Biofortification of rice with lysine using endogenous histones.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Feb;87(3):235-48. doi: 10.1007/s11103-014-0272-z. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25512028 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic histone H4 replacement in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals a role for H4R17 in regulating flowering time.Plant Cell. 2022 Sep 27;34(10):3611-3631. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac211. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 35879829 Free PMC article.
-
cDNA Library Screening Identifies Protein Interactors Potentially Involved in Non-Telomeric Roles of Arabidopsis Telomerase.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Nov 12;6:985. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00985. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26617625 Free PMC article.
-
Agrobacterium expressing a type III secretion system delivers Pseudomonas effectors into plant cells to enhance transformation.Nat Commun. 2022 May 11;13(1):2581. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30180-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35546550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand, A., Zarir, V., Ryu, C.M., Kang, L., del-Pozo, O., Martin, G.B., and Mysore, K.S. (2007). Identification of plant genes involved in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation by using virus induced gene silencing as a functional genomics tool. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 20 41–52. - PubMed
-
- Baake, M., Doenecke, D., and Albig, W. (2001). Characterisation of nuclear localisation signals of the four human core histones. J. Cell. Biochem. 81 333–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

