UBE2S elongates ubiquitin chains on APC/C substrates to promote mitotic exit
- PMID: 19820702
- PMCID: PMC2875106
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1983
UBE2S elongates ubiquitin chains on APC/C substrates to promote mitotic exit
Abstract
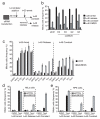
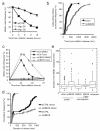
The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C), a ubiquitin ligase, is the target of the spindle-assembly checkpoint (SAC), and it ubiquitylates protein substrates whose degradation regulates progress through mitosis. The identity of the ubiquitin-conjugating (E2) enzymes that work with the APC/C is unclear. In an RNA interference (RNAi) screen for factors that modify release from drug-induced SAC activation, we identified the E2 enzyme UBE2S as an APC/C auxiliary factor that promotes mitotic exit. UBE2S is dispensable in a normal mitosis, but its depletion prolongs drug-induced mitotic arrest and suppresses mitotic slippage. In vitro, UBE2S elongates ubiquitin chains initiated by the E2 enzymes UBCH10 and UBCH5, enhancing the degradation of APC/C substrates by the proteasome. Indeed, following release from SAC-induced mitotic arrest, UBE2S-depleted cells neither degrade crucial APC/C substrates, nor silence this checkpoint, whereas bypassing the SAC through BUBR1 depletion or Aurora-B inhibition negates the requirement for UBE2S. Thus, UBE2S functions with the APC/C in a two-step mechanism to control substrate ubiquitylation that is essential for mitotic exit after prolonged SAC activation, providing a new model for APC/C function in human cells.
Figures



References
-
- Musacchio A, Salmon ED. The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:379–393. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Lin DP, Matsumoto S, Kitazono A, Matsumoto T. Fission yeast Slp1: an effector of the Mad2-dependent spindle checkpoint. Science. 1998;279:1045–1047. - PubMed
-
- Pines J. Mitosis: a matter of getting rid of the right protein at the right time. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Peters JM. The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:644–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

