Presynaptic alpha2delta-3 is required for synaptic morphogenesis independent of its Ca2+-channel functions
- PMID: 19820706
- PMCID: PMC2996863
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2417
Presynaptic alpha2delta-3 is required for synaptic morphogenesis independent of its Ca2+-channel functions
Abstract
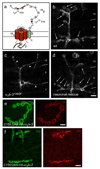
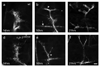
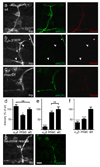
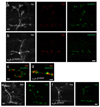
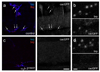
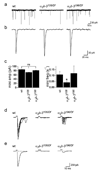
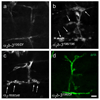
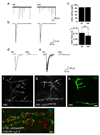
Synaptogenesis involves the transformation of a growth cone into synaptic boutons specialized for transmitter release. In Drosophila embryos lacking the alpha(2)delta-3 subunit of presynaptic, voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels, we found that motor neuron terminals failed to develop synaptic boutons and cytoskeletal abnormalities arose, including the loss of ankyrin2. Nevertheless, functional presynaptic specializations were present and apposed to clusters of postsynaptic glutamate receptors. The alpha(2)delta-3 protein has been thought to function strictly as an auxiliary subunit of the Ca(2+) channel, but the phenotype of alpha(2)delta-3 (also known as stj) mutations cannot be explained by a channel defect; embryos lacking the pore-forming alpha(1) subunit cacophony formed boutons. The synaptogenic function of alpha(2)delta-3 required only the alpha(2) peptide, whose expression sufficed to rescue bouton formation. Our results indicate that alpha(2)delta proteins have functions that are independent of their roles in the biophysics and localization of Ca(2+) channels and that synaptic architecture depends on these functions.
Figures
References
-
- Lardi-Studler B, Fritschy JM. Matching of pre- and postsynaptic specializations during synaptogenesis. Neuroscientist. 2007;13:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Robitaille R, Adler EM, Charlton MP. Strategic location of calcium channels at transmitter release sites of frog neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1990;5:773–779. - PubMed
-
- Wolf M, Eberhart A, Glossmann H, Striessnig J, Grigorieff N. Visualization of the domain structure of an L-type Ca2+ channel using electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 2003;332:171–182. - PubMed
-
- Nishimune H, Sanes JR, Carlson SS. A synaptic laminin-calcium channel interaction organizes active zones in motor nerve terminals. Nature. 2004;432:580–587. - PubMed
-
- De Waard M, Gurnett CA, Campbell KP. Structural and functional diversity of voltage-activated calcium channels. Ion Channels. 1996;4:41–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

