LC/MS analysis of cellular RNA reveals NAD-linked RNA
- PMID: 19820715
- PMCID: PMC2842606
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.235
LC/MS analysis of cellular RNA reveals NAD-linked RNA
Abstract
We developed a general method to detect cellular small molecule-RNA conjugates that does not rely on the reactivity of the small molecule. This technique revealed NAD-linked RNA in Escherichia coli and Streptomyces venezuelae. Subsequent characterization showed that NAD is a 5' modification of RNA, cannot be installed in vitro through aberrant transcriptional initiation, is only found among smaller cellular RNAs and is present at a surprisingly high abundance of approximately 3,000 copies per cell.
Figures


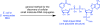
References
-
- Hoagland MB, Stephenson ML, Scott JF, Hecht LI, Zamecnik PC. A soluble ribonucleic acid intermediate in protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958;231:241–57. - PubMed
-
- Repoila F, Darfeuille F. Small regulatory non-coding RNAs in bacteria: physiology and mechanistic aspects. Biol Cell. 2009;101:117–31. - PubMed
-
- Szostak JW, Bartel DP, Luisi PL. Synthesizing life. Nature. 2001;409:387–90. - PubMed
-
- Visser CM, Kellogg RM. Bioorganic chemistry and the origin of life. J Mol Evol. 1978;11:163–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

