Blood pressure lowering in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease for prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia
- PMID: 19821318
- PMCID: PMC7163274
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub3
Blood pressure lowering in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease for prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia
Update in
-
Pharmacological treatment of hypertension in people without prior cerebrovascular disease for the prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;5(5):CD004034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34028812 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: This is an update of a previous review (McGuinness 2006).Hypertension and cognitive impairment are prevalent in older people. Hypertension is a direct risk factor for vascular dementia (VaD) and recent studies have suggested hypertension impacts upon prevalence of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Therefore does treatment of hypertension prevent cognitive decline?
Objectives: To assess the effects of blood pressure lowering treatments for the prevention of dementia and cognitive decline in patients with hypertension but no history of cerebrovascular disease.
Search strategy: The Specialized Register of the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group, The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL, LILACS as well as many trials databases and grey literature sources were searched on 13 February 2008 using the terms: hypertens$ OR anti-hypertens$.
Selection criteria: Randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trials in which pharmacological or non-pharmacological interventions to lower blood pressure were given for at least six months.
Data collection and analysis: Two independent reviewers assessed trial quality and extracted data. The following outcomes were assessed: incidence of dementia, cognitive change from baseline, blood pressure level, incidence and severity of side effects and quality of life.
Main results: Four trials including 15,936 hypertensive subjects were identified. Average age was 75.4 years. Mean blood pressure at entry across the studies was 171/86 mmHg. The combined result of the four trials reporting incidence of dementia indicated no significant difference between treatment and placebo (236/7767 versus 259/7660, Odds Ratio (OR) = 0.89, 95% CI 0.74, 1.07) and there was considerable heterogeneity between the trials. The combined results from the three trials reporting change in Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) did not indicate a benefit from treatment (Weighted Mean Difference (WMD) = 0.42, 95% CI 0.30, 0.53). Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels were reduced significantly in the three trials assessing this outcome (WMD = -10.22, 95% CI -10.78, -9.66 for systolic blood pressure, WMD = -4.28, 95% CI -4.58, -3.98 for diastolic blood pressure). Three trials reported adverse effects requiring discontinuation of treatment and the combined results indicated no significant difference (OR = 1.01, 95% CI 0.92, 1.11). When analysed separately, however, more patients on placebo in Syst Eur 1997 were likely to discontinue treatment due to side effects; the converse was true in SHEP 1991. Quality of life data could not be analysed in the four studies. Analysis of the included studies in this review was problematic as many of the control subjects received antihypertensive treatment because their blood pressures exceeded pre-set values. In most cases the study became a comparison between the study drug against a usual antihypertensive regimen.
Authors' conclusions: There is no convincing evidence from the trials identified that blood pressure lowering in late-life prevents the development of dementia or cognitive impairment in hypertensive patients with no apparent prior cerebrovascular disease. There were significant problems identified with analysing the data, however, due to the number of patients lost to follow-up and the number of placebo patients who received active treatment. This introduced bias. More robust results may be obtained by conducting a meta-analysis using individual patient data.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

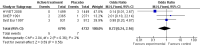
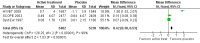
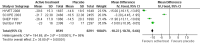
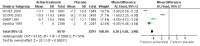
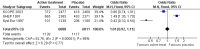
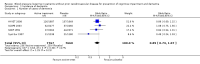





Update of
-
The effects of blood pressure lowering on development of cognitive impairment and dementia in patients without apparent prior cerebrovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD004034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD004034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub3. PMID: 16625595 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
HYVET 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bulpitt C, Fletcher A, Beckett N, Coope J, Gil‐Extremera B, Fore tte F, et al. Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial (HYVET): protocol for the main trial . Drugs & Aging 2001 ; 18 :151‐164. - PubMed
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Nunes M, Fletcher A, Forette F, Bulpitt C. A substudy protocol of the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial assessing cognitive decline and dementia incidence (HYVET‐COG): an ongoing randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial . Drugs Aging 2006 ; 23 :83‐92. - PubMed
-
- Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, Dumiterscu D, et al. for the HYVET Study Group. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. NEJM 2008;358:1887‐1898. - PubMed
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Forette F, Tuomilehto J, Clarke R, Ritchie C, et al. for the HYVET investigators. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET‐COG): a double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7:683‐689. - PubMed
SCOPE 2003 {published data only}
-
- Degl'Innocenti A, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A, Wiklund I. Health‐related quality of life during treatment of elderly patients with hypertension: results from the Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of Human Hypertension 2004;18(4):239‐45. - PubMed
-
- Lithell H, Hansson L, Skoog I, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. The Study of COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE); outcomes in patients not receiving add‐on therapy after randomization. Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(8):1605‐12. - PubMed
-
- Lithell H, Hansson L, Skoog I, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. The Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE): principal results of a randomised double‐blind intervention trial. Journal of Hypertension 2003;21:875‐886. - PubMed
-
- Papademetriou V, Farsang C, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. Stroke Prevention With the Angiotension II Type‐1 Receptor Blocker Candesartan in Elderly Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension. The Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2004;44(6):1175‐80. - PubMed
-
- Skoog I, Lithell H, Hansson L, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, et al. for the SCOPE Study Group. Effect of baseline cognitive function and antihypertensive treatment on cognitive and cardiovascular outcomes: Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). American Journal of Hypertension 2005; Vol. 18:1052‐1059. - PubMed
SHEP 1991 {published data only}
-
- Applegate WB, Pressel S, Wittes J, Luhr J, Shekelle RB, Camel GH, et al. Impact of the Treatment of Isolated Systolic Hypertension on Behavioral Variables. Results From the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program. Arch Intern Med 1994;154:2154‐2160. - PubMed
-
- Bari M, Pahor M, Franse LV, Shorr RI, Wan JY, Ferrucci L, et al. Dementia and Disability Outcomes in Large Hypertension Trials: Lessons Learned from the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) Trial. American Journal of Epidemiology 2001;153:72‐8. - PubMed
-
- SHEP Cooperative Research Group. Prevention of Stroke by Antihypertensive Drug Treatment in Older Persons With Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Final Results of the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP). JAMA 1991;265:3255‐64. - PubMed
-
- The Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) Cooperative Research Group. Rationale and Design of a Randomized Clinical Trial on Prevention of Stroke in Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1988;41:1197‐1208. - PubMed
Syst Eur 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Amery A, Birkenhager W, Bulpitt CJ, Clement D, Leeuw P, Dollery CT, et al. Syst‐Eur. A multicentre trial on the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: Objectives, protocol, and organization. Aging Clin Exp Res 1991;3:287‐302. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher AE, Bulpitt CJ, Thijs L, Toumilehto J, Antikainen R, Bossini A, et al. Quality of life on randomised treatment for isolated hypertension: results from the Syst‐Eur Trial. Journal of Hypertension 2002;20:2069‐2079. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher AE, Bulpitt CJ, Tuomilehto J, Browne J, Bossini A, Kawecka‐Jaszcz K, et al. Quality of life of elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: baseline data from the Syst‐Eur Trial. Journal of Hypertension 1988;16:1117‐1124. - PubMed
-
- Forette F, Seux M‐L, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Babarskiene M‐R, Babeanu S, et al. The Prevention of Dementia With Antihypertensive Treatment. New Evidence From the Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst‐Eur) Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2002;162:2046‐2052. - PubMed
-
- Forette F, Seux ML, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Birkenhager WH. Reduction of dementia by calcium‐antagonist‐based antihypertensive treatment. European Heart Journal Supplements 2000;2:D17‐D19.
References to studies excluded from this review
ALLHAT 2003 {published data only}
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Diuretic Versus Alpha‐Blocker as First‐Step Antihypertensive Therapy. Final Results From the Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Hypertension 2003;42:239‐246. - PubMed
ASCOT 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dahlof B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, Wedel H, Beevers DG, Caulfield M, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo‐Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial‐Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT‐BPLA): a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2005;366:895‐906. - PubMed
Black 2001 {published data only}
-
- Black HR, Elliott WJ, Weber MA, Frishman WH, Strom JA, Liebson PR, et al. One‐Year Study of Felodipine or Placebo for Stage 1 Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Hypertension 2001;38:1118‐1130. - PubMed
Framingham 1993 {published data only}
-
- Elias MF, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Cobb J, White LR. Untreated Blood Pressure Level is Inversely Related to Cognitive Functioning: The Framingham Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 1993;138:353‐364. - PubMed
-
- Farmer ME, White LR, Abbott RD, Kittner SJ, Kaplan E, Wolz MM, et al. Blood Pressure and Cognitive Performance. The Framingham Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 1987;126:1103‐1114. - PubMed
Hofman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hofman A, Ott A, Breteler MMB, Bots ML, Slooter AJC, Harskamp F, et al. Atherosclerosis, apolipoprotein E, and prevalence of dementia and Alzheimer's disease in the Rotterdam Study. The Lancet 1997;349:151‐54. - PubMed
HOT 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, Dahlof B, Elmfeldt D, Julius S, et al. Effects of intensive blood‐pressure lowering and low‐dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. The Lancet 1998;351:1755‐62. - PubMed
Hsieh 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hsieh M‐H, Chan P, Sue Y‐M, Liu J‐C, Liang TH, Huang T‐Y, et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Oral Stevioside in Patients with Mild Essential Hypertension: A Two‐Year, Randomised, Placebo‐Controlled Study. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25:2797‐2808. - PubMed
Kilander 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kilander L, Nyman H, Boberg M, Hansson L, Lithell H. Hypertension is Related to Cognitive Impairment. A 20‐Year Follow‐up of 999 men. Hypertension 1998;31:780‐786. - PubMed
Lasser 1989 {published data only}
-
- Lasser NL, Nash J, Lasser VI, Hamill SJ, Batey DM. Effects of antihypertensive therapy on blood pressure control, cognition and reactivity. A placebo‐controlled comparison of prazosin, propranolol, and hydrochlorothiazide. Am J Med 1989;86:98‐103. - PubMed
Launer 1995 {published data only}
-
- Launer LJ, Masaki K, Petrovitch H, Foley D, Havlik RJ. The Association Between Midlife Blood Pressure Levels and Late‐Life Cognitive Function. The Honolulu‐Asia Aging Study. JAMA 1995;274:1846‐1851. - PubMed
-
- Syme SL, Marmot MG, Kagan A, Kato H, Rhoads G. Epidemiologic Studies of Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke in Japanese Men Living in Japan, Hawaii and California: Introduction. American Journal of Epidemiology 1975;102:477‐480. - PubMed
LOMIR‐MCT‐IL {published data only}
-
- Amir M, Cristal N, Bar‐On D, Loidl A. Does the Combination of ACE Inhibitor and Calcium Antagonist Control Hypertension and Improve Quality of Life? The LOMIR‐MCT‐IL Study Experience. Blood Pressure 1994;3(Suppl 1):40‐42. - PubMed
-
- Bar‐On D, Amir M. Reexamining the Quality of Life of Hypertensive Patients. A New Self‐Structured Measure. American Journal of Hypertension 1993;6:62S‐66S. - PubMed
-
- Yodfat Y, Cristal N. A Multicenter, Double‐Blind, Randomized, Placebo‐Controlled Study of Isradipine and Methyldopa as Monotherapy or in Combination With Captopril in the Treatment of Hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1993;6:57S‐61S. - PubMed
MRC 1996 {published data only}
-
- Peart S. Results of MRC (UK) trial of drug therapy for mild hypertension. Clin Invest Med 1987;10:616‐20. - PubMed
-
- Prince M, Lewis G, Bird A, Blizard R, Mann A. A longitudinal study of factors predicting change in cognitive test scores over time, in an older hypertensive population. Psychological Medicine 1996;26:555‐568. - PubMed
Murray 2002 {published data only}
-
- Murray MD, Lane KA, Sujuan G, Evans RM, Unverzagt FM, Hall KS, Hendrie H. Preservation of Cognitive Function With Antihypertensive Medications: A Longitudinal Analysis of a Community‐Based Sample of African Americans Preservation of Cognitive Function With Antihypertensive Medications: A Longitudinal Analysis of a Community‐Based Sample of African Americans. Archives of Internal Medicine 2002;162(18):2090‐2096. - PubMed
PROGRESS 2003 {published data only}
-
- The PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Effects of Blood Pressure Lowering With Perindopril and Indapamide Therapy on Dementia and Cognitive Decline in Patients With Cerebrovascular Disease. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:1069‐1075. - PubMed
Richards 2000 {published data only}
-
- Richards SS, Emsley CL, Roberts J, Murray MD, Hall K, Sujuan G, Hendrie HC. The Association Between Vascular Risk Factor‐Mediating Medications and Cognition and Dementia Diagnosis in a Community‐Based Sample of African‐Americans. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48:1035‐1041. - PubMed
Skoog 1996 {published data only}
-
- Skoog I, Lernfelt B, Landahl S, Palmertz B, Andreasson LA, Nilsson L, et al. 15‐year longitudinal study of blood pressure and dementia. The Lancet 1996;347:1141‐45. - PubMed
Starr 1996 {published data only}
-
- Starr JM, Whalley LJ, Deary IJ. The Effects of Antihypertensive Treatment on Cognitive Function: Results from the HOPE Study. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1996;44:411‐415. - PubMed
STOP 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dahlof B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Schersten B, Ekbom T, Wester P‐O. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOP Hypertension). Lancet 1991;338:1281‐85. - PubMed
Syst China 1998 {published data only}
-
- Liu L, Wang JG, Gong L, Liu G, Staessen JA. Comparison of active treatment and placebo in older Chinese patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16:1823‐1829. - PubMed
VALUE 2004 {published data only}
-
- Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M, Brunner HR, Ekman S, Hansson L, et al. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomised trial. Lancet 2004;363:2022‐31. - PubMed
Additional references
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington DC: APA, 1987.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . 4th Edition. Washington DC : APA , 1994 .
Birns 2006
-
- Birns J, Morris R, Donaldson N, Kalra L. The effects of blood pressure reduction on cognitive function: a review of effects based on pooled data from clinic al trials . Journal of Hypertension 2006 ; 24 :1907‐1914. - PubMed
Brayne 1998
-
- Brayne C, Gill C, Huppert FA, et al. Vascular risk s and incident dementia :results from a cohort study of the very old . Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 1998 ; 9 :175‐180. - PubMed
Chalmers 1983
-
- Chalmers TC, Celano P, Sacks HS, Smith H Junior. Bias in Treatment Assignment in Controlled Clinical Trials. N Eng J Med 1983;309:1358‐61. - PubMed
Degl'Innocenti 2004
-
- Degl'Innocenti A, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A, Wiklund I. Health‐related quality of life during treatment of elderly patients with hypertension: results from the Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of Human Hypertension 2004;18(4):239‐45. - PubMed
Di Bari 2001
-
- Bari M, Pahor M, Franse LV, Shorr RI, Wan JY, Ferrucci L, Somes GW, Applegate WB. Dementia and disability outcomes in large hypertension trials: lessons learned from the systolic hypertension in the elderly program (SHEP) trial. American Journal of Epidemiology 2001;153(1):72‐8. - PubMed
Elias 1993
-
- Elias MF, Wolf PA, Agostino RBD, Cobb J, White LR. Untreated blood pressure is inversely related to cognitive functioning: the Framingham Study. Journal of Epidemiology 1993;138(6):352‐64. - PubMed
Elias 2004
-
- Elias PK, Elias M F, Robbins MA, Budge MM. Blood pressure related cognitive decline: does age make a difference? . Hypertension 2004 ; 44 :631‐636. - PubMed
Feigin 2005
-
- Feigin V, Ratnasabapathy Y, Anderson C. Does blood pressure lowering treatment prevent deme ntia or cognitive decline in patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease? . Journal of the N eurological Sciences 2005 ; 229 :151‐155. - PubMed
Fogari 2004
-
- Fogari R, Mu gellini A, Zoppi A, et al. Effects of valsartan compared with enalapril on blood pressure and cognitive function in elderly patients with essential hypertension . European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2004 ; 59 :863‐868. - PubMed
Forette 2002
-
- Forette F, Seux M‐L, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Babarskiene M‐R, Babeanu S, et al. The Prevention of Dementia With Antihypertensive Treatment. New Evidence From the Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst‐Eur) Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2002;162:2046‐2052. - PubMed
Guo 1996
Guo 1999
-
- Guo Z, Fratiglioni L, Zhu L, Fastborn J, Wi nblad B, Viitanen M. Occurence and progression of dementia in a community population aged 75 years and older: relationship of antihypertensive medication use . Archives of Neurology 1999 ; 56 :991‐996. - PubMed
Hebert 2004
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bennet DA, et al. Blood pressure and late‐life cognitive function change: a biracial longitudinal population study . Neurology 2004 ; 62 :2021‐202 4. - PubMed
in't Veld 2001
-
- in't Veld BA, Ruitenberg A, Hofman A, Stricker BHC, Breteler MMB. Antihypertensive drugs and incidence of dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Neurobiology of Aging 2001;22:407‐412. - PubMed
Kennelly 2009
-
- Kennelly SP, Lawlor BA, Kenny RA. Blood pressure and the risk for dementia ‐ a d ouble edged sword . Ageing Research Reviews 2009 ; 8 :61‐70. - PubMed
Khachaturian 2006
-
- Khachaturian AS, Zandi PP, Lyketsos CG, Hayden KM, Skoog I, Norton MC, Tschanz, Mayer LS, Welsh‐Bohmer KA, Breitner JCS. Antihypertensive medic ation use and incident Alzheimer disease: the Cache County Study . Archives of Neurology 2006 ; 63 :686‐692. - PubMed
Kilander 2000
-
- Kilander L, Nyman H, Boberg M, Lithell H. The association b etween low diastolic blood pressure in middle age and cognitive function in old age: a population based study . Age Ageing 2000 ; 29 :243‐248. - PubMed
Kivipelto 2001
Launer 2000
-
- Launer LJ, Ross GW, Petrovich H, Masaki K, Foley D, White LR, Havlik RJ. Midlife blood pressure and dementia: the Honolulu‐Asia aging study . N eurobiology of Aging 2000 ; 21 :49‐55. - PubMed
Lindsay 2002
-
- Lindsay J, Laurin D, Verreault R, et al. Risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: a prospe ctive analysis from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging . American Journal of Epidemiology 2002 ; 156 :445‐453. - PubMed
Lithell 2004
-
- Lithell H, Hansson L, Skoog I, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, Trenkwalder P and Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. The Study of COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE); outcomes in patients not receiving add‐on therapy after randomization. Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(8):1605‐12. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;4:939‐44. - PubMed
Morris 2001
-
- Morris MC, Scherr PA, Hebert LE, Glynn RJ, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Association of incident Alzheimer disease and blood pressure measured from 13 years before to 2 years after diagnosis in a large community study . Archives of Neurology 2001 ; 58 :1640‐1646. - PubMed
Mulrow 1997
-
- Mulrow CD, Oxman AD (editors). Cochrane Collaboration Handbook, The Cochrane Library [database on disc and CDROM ]. Vol. Issue 1, Oxford: Update Software, 1997.
Papademetriou 2004
-
- Papademetriou V, Farsang C, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. Stroke Prevention With the Angiotension II Type‐1 Receptor Blocker Candesartan in Elderly Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension. The Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2004;44(6):1175‐80. - PubMed
Peters 2008
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Forette F, Tuomilehto J, Clarke R, Ritchie C, et al. for the HYVET investigators. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET‐COG): a double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7:683‐689. - PubMed
Prince 1996
-
- Prince M, Lewis G, Bird A, Blizard R, Mann A. A longitudinal study of factors predicting change in cognitive test scores over time, in an older hypertensive population. Psychological Medicine 1996;26(3):555‐68. - PubMed
Prince 1996a
Qiu 2003
-
- Qiu C, Strauss E, Fastbom J, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Low blood pressure and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen project : a 6‐year follow‐up study . Archives of Neurology 2003 ; 60 :223‐228. - PubMed
Qiu 2003a
-
- Qiu C, Winblad B, Fastbom J, Fratiglioni L. Combined effects of APOE genotype, blood pressure and antihypertensive drug use on incident AD . Neurology 2003 ; 61 :655‐660. - PubMed
Qiu 2004
-
- Qiu C, Strauss E, W inblad B, Fratiglioni L. Decline in blood pressure over time and risk of dementia: a longitudi nal study from the Kungsholmen Project . Stroke 2004 ;35 :1810‐1815. - PubMed
Qui 2005
-
- Qui C, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. The age‐dependent relation of blood pressure to cognitive function and dementia. Lancet Neurology 2005;4:487‐99. - PubMed
Ratnasabapathy 2003
-
- Ratnasabapathy Y, Chi‐Lun Lee A, Feigin V, Anderson C. Blood pressure lowering interventions for preventing dementia in patients with cerebrovascular disease (Protocol). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2 Art. No.: CD004130.. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858] - DOI
Ruitenberg 2001
-
- Ruitenberg A, Skoog I, Ott A, et al. Blood pressure and risk of dementia: results from the Rotterdam Study and the Gothenburg H‐70 S tudy . Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2001 ; 12 :33‐39. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Starr 1992
-
- Starr JM, Whalley LJ. Senile hypertension and cognitive impairment: an overview. Journal of Hypertension 1992;10(2):S31‐42. - PubMed
Swan 1998
-
- Swan GE, DeCarli C, Miller BL, et al. Associa tion of midlife blood pressure to late‐life cognitive decline and brain morphology . Neurology 1998 ; 51 :986‐993. - PubMed
Tervo 2004
-
- Tervo S, Kivipelto M, Hänninen T, et al. Incidence and risk factors for mild cognitive impairment: a population based three‐year follow‐up study of cognitively healthy elderly subjects . Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Dis orders 2004 ; 17 :196‐203. - PubMed
Verghese 2003
-
- Verghese J, Lipton RB, Hall CB, Kuslansky G, Matz MJ. Low blood pressure and the risk of dementia in very old individuals . Neurology 2003 ; 61 :1667‐1672. - PubMed
Wang 2003
-
- Wang JG, Staessen JA, Birkenhä ger, WH. Antihypertensive treatment and prevention of stroke and dementia . Seminars in Cerebrovascular Diseases and Stroke 2003 ; 3 :155‐164.
Whitmer 2005
-
- Whitmer RA, Sidney S, Selby J, Johnston SC, Yaffe K. Midlife cardiovascular risk factors and risk of dementia in late life . Neurology 2005 ; 64 :277‐281. - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organisation. The ICD‐10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: WHO, 1992.
Wu 2003
-
- Wu C, Zhou D, Wen C, Zhang I, Como P, Qiao Y. Relationship between blood pressure and Alzheimer's disease in Linxian county . Life Science 2003 ; 72 :1125‐1133. - PubMed
Yamada 2003
-
- Yamada M, Kasagi F, Sasaki H, Maunari N, Mimori Y, Suzuki G. Association between dementia and midlife risk factors: the radiation effects research foundation adult health study . Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003 ; 51 :410‐414. - PubMed
Yasar 2005
-
- Yasar S, Cor rada M, Brookmeyer R, Kawas C. Calcium channel blockers and risk of AD: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging . Neurobiology of Aging 2005 ; 26 :157‐163. - PubMed
Yoshitake 1995
-
- Yoshitake T, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, et al. Incidence and risk factors of vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease in a defined elderly Japanese study: the Hisayama Study . Neurology 1995 ; 45 :1161‐1168. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
McGuinness 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

