Single dose oral rofecoxib for acute postoperative pain in adults
- PMID: 19821329
- PMCID: PMC4171390
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004604.pub3
Single dose oral rofecoxib for acute postoperative pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Editor's note: The anti-inflammatory drug rofecoxib (Vioxx) was withdrawn from the market at the end of September 2004 after it was shown that long-term use (greater than 18 months) could increase the risk of heart attack and stroke in a study of secondary prevention of adenoma recurrence. Further information is available at www.vioxx.com.Rofecoxib is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor previously licensed for treating acute and chronic pain; it was associated with fewer gastrointestinal adverse events than conventional NSAIDs. An earlier Cochrane review (Barden 2005) showed that rofecoxib is at least as effective as conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for postoperative pain.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of rofecoxib in single oral doses for moderate and severe postoperative pain.
Search strategy: We searched Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Oxford Pain Relief Database for studies to June 2009.
Selection criteria: Randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled trials of single dose orally administered rofecoxib in adults with moderate to severe acute postoperative pain.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. Pain relief or pain intensity data were extracted and converted into the dichotomous outcome of number of participants with at least 50% pain relief over 4 to 6 hours, from which relative risk and number needed to treat to benefit (NNT) were calculated. Numbers of participants using rescue medication over specified time periods, and time to use of rescue medication, were sought as additional measures of efficacy. Information on adverse events and withdrawals was collected.
Main results: Twenty new studies and seven from the earlier review met the inclusion criteria. Twenty-four studies were in dental surgery and three in other types of surgery. In total, 2636 participants were treated with rofecoxib 50 mg, 20 with rofecoxib 500 mg, and 1251 with placebo. The NNT for at least 50% pain relief over 4 to 6 hours with rofecoxib 50 mg was 2.2 (2.0 to 2.3) in all studies combined, 1.9 (1.8 to 2.0) in dental studies, and 6.8 (4.6 to 13) in other types of surgery. The median time to use of rescue medication was 14 hours for rofecoxib 50 mg and 2 hours for placebo. Significantly fewer participants used rescue medication following rofecoxib 50 mg than with placebo. Adverse events did not differ from placebo.
Authors' conclusions: Rofecoxib 50 mg (two to four times the standard daily dose for chronic pain) is an effective single dose oral analgesic for acute postoperative pain in adults, with a relatively long duration of action.
Conflict of interest statement
Current review: RAM and HJM have undertaken research/consultants for various pharmaceutical companies. RAM and HJM have received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies for presentations on analgesics research and other healthcare interventions. RAM, HJM, and SD have received research support from charities, government and industry sources at various times; no such support was received for the preparation of this systematic review.
Previous review: JR received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies for presentations on analgesics research and other healthcare interventions. JR and JB received research support from charities, government and industry sources at various times; no such support was received for the preparation of the systematic review.
Figures

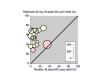



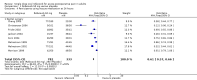


Update of
-
Single dose oral rofecoxib for postoperative pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;(1):CD004604. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004604.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD004604. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004604.pub3. PMID: 15674955 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Chang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chang DJ, Fricke JR, Bird SR, Bohidar NR, Dobbins TW, Geba GP. Rofecoxib versus codeine/acetaminophen in postoperative dental pain: a double blind, randomised, placebo‐ and active‐ comparator controlled clinical trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(9):1446‐55. - PubMed
Chang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chang DJ, Desjardins PJ, Chen E, Polis AB, et al. Comparison of the analgesic efficacy of rofecoxib and enteric‐coated diclofenac sodium in the treatment of postoperative dental pain: a randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2002;24(4):490‐502. - PubMed
Chang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chang DJ, Desjardins PJ, Bird SR, Black P, Chen E, Petruschke RA, et al. Comparison of rofecoxib and a multidose oxycodone/ acetaminophen regimen for the treatment of acute pain following oral surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2004;20(6):939‐49. - PubMed
Chang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chang DJ, Bird SR, Bohidar NR, King T. Analgesic efficacy of rofecoxib compared with codeine/acetaminophen using a model of acute dental pain. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radioliology and Endodontics 2005;100(4):e74‐80. - PubMed
Chelly 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chelly JE, Nissen CW, Rodgers AJ, Smugar SS, Tershakovec AM. The efficacy of rofecoxib 50 mg and hydrocodone/acetaminophen 7.5/750 mg in patients with post‐arthroscopic pain. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2007;23(1):195‐206. - PubMed
Christensen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Christensen KS, Cawkwell GD. Valdecoxib versus rofecoxib in acute postsurgical pain: results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2004;27(5):460‐70. - PubMed
Daniels 2006 {published data only}
-
- Daniels SE, Desjardins PJ, Bird SR, Smugar SS, Tershakovec AM. Rofecoxib 50 mg and valdecoxib 20 or 40 mg in adults and adolescents with postoperative pain after third molar extraction: results of two randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, single‐dose studies. Clinical Therapeutics 2006;28(7):1022‐34. - PubMed
Desjardins 2004 {published data only}
-
- Desjardins PJ, Black PM, Daniels S, Bird SR, Fitzgerald BJ, Petruschke RA, et al. A randomized controlled study comparing rofecoxib, diclofenac sodium, and placebo in post‐bunionectomy pain. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2004;20(10):1523‐37. - PubMed
Desjardins 2007 {published data only}
-
- Desjardins PJ, Black PM, Daniels SE, Bird SR, Petruschke RA, Chang DJ, Smugar SS, et al. A double‐blind randomized controlled trial of rofecoxib and multidose oxycodone/acetaminophen in dental impaction pain. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007;65(8):1624‐32. - PubMed
Edwards 2004 {published data only}
Ehrich 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ehrich EW, Dallob A, Lepeleire I, Hecken A, Riendeau D, Yuan W, et al. Characterisation of rofecoxib as a cyclooxygenase‐2 isoform inhibitor and demonstration of analgesia in the dental pain model. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1999;65:336‐47. - PubMed
Fricke 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fricke J, Varkalis J, Zwillich S, Adler R, Forester E, Recker DP, et al. Valdecoxib is more efficacious than rofecoxib in relieving pain associated with oral surgery. American Journal of Therapeutics 2002;9:89‐97. - PubMed
Haglund 2006 {published data only}
-
- Haglund B, Bültzingslöwen I. Combining paracetamol with a selective cyclooxygenase‐2 inhibitor for acute pain relief after third molar surgery: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. European Journal of Oral Sciences 2006;114(4):293‐301. - PubMed
Jackson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jackson ID, Heidemann BH, Wilson J, Power I, Brown RD. Double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial comparing rofecoxib with dexketoprofen trometamol in surgical dentistry. British Journal of Anaesthetics 2004;92(5):675‐80. - PubMed
Kellstein 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kellstein D, Ott D, Jayawardene S, Fricke J. Analgesic efficacy of a single dose of lumiracoxib compared with rofecoxib, celecoxib and placebo in the treatment of post‐operative dental pain. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2004;58(3):244‐50. - PubMed
Korn 2004 {published data only}
-
- Korn S, Vassil TC, Kotey PN, Fricke JR Jr. Comparison of rofecoxib and oxycodone plus acetaminophen in the treatment of acute pain: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study in patients with moderate to severe postoperative pain in the third molar extraction model. Clinical Therapeutics 2004;26(5):769‐78. - PubMed
Malmstrom 1999 {published data only}
-
- Malmstrom K, Daniels S, Kotey P, Seidenberg BC, Desjardins PJ. Comparison of rofecoxib and celecoxib, two cycloocygenase‐2 inhibitors, in postoperative dental pain: a randomised placebo‐ and active‐ comparator controlled clinical trial. Clinical Therapeutics 1999;21(10):1653‐63. - PubMed
Malmstrom 2002 {published data only}
-
- Malmstrom K, Fricke JR, Kotey P, Kress B, Morrison B. A comparison of rofecoxib versus celecoxib in treating pain after dental surgery: a single‐center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐comparator‐controlled, parallel‐group, single‐dose study using the dental impaction pain model. Clinical Therapeutics 2002;24(10):1549‐60. - PubMed
Michael‐Hill 2006 {published data only}
-
- Michael Hill C, Sindet‐Pederson S, Seymour RA, Hawkesford JE 2nd, Coulthard P, Lamey PJ, et al. Analgesic efficacy of the cyclooxygenase‐inhibiting nitric oxide donor AZD3582 in postoperative dental pain: Comparison with naproxen and rofecoxib in two randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled studies. Clinical Therapeutics 2006;28(9):1279‐95. - PubMed
Morrison 1999 {published data only}
-
- Morrison BW, Christensen S, Yuan W, Brown J, Amlani S, Seidenberg B. Analgesic efficacy of the cyclooxygenase‐2‐specific inhibitor of rofecoxib in post‐dental surgery pain: a randomised, controlled clinical trial. Clinical Therapeutics 1999;21(6):943‐53. - PubMed
Reicin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Reicin A, Brown J, Jove M, deAndrade JR, Bourne M, Krupa D, Walters D, Seidenberg B. Efficacy of single‐dose and multidose rofecoxib in the treatment of post‐orthopedic surgery pain. American Journal of Orthopedics 2001;30(1):40‐8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Lee 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lee YS, Kim H, Wu TX, Wang XM, Dionne RA. Genetically mediated interindividual variation in analgesic responses to cyclooxygenase inhibitory drugs. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;79(5):407‐18. - PubMed
Ong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ong KS, Seymour RA, Yeo JF, Ho KH, Lirk P. The efficacy of preoperative versus postoperative rofecoxib for preventing acute postoperative dental pain: a prospective randomized crossover study using bilateral symmetrical oral surgery. Clinical Journal of Pain 2005;21(6):536‐42. - PubMed
Reuben 2000 {published data only}
-
- Reuben SS, Bhopatkar S, Maciolek H, Joshi W, Sklar J. The preemptive analgesic effect of rofecoxib after ambulatory arthroscopic knee surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2002;94(1):55‐5. - PubMed
Reuben 2002 {published data only}
-
- Reuben SS, Conelly NR. Postoperative analgesic effects of celecoxib or rofecoxib after spinal fusion surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2000;91(5):1221‐5. - PubMed
Riest 2006 {published data only}
-
- Riest G, Peters J, Weiss M, Pospiech J, Hoffmann O, Neuhäuser M, et al. Does perioperative administration of rofecoxib improve analgesia after spine, breast and orthopaedic surgery. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2006;23(3):219‐26. - PubMed
Zacharias 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zacharias M, Silva RK, Herbison P, Templer P. A randomized crossover trial of tenoxicam compared with rofecoxib for postoperative dental pain control. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 2004;32(6):770‐4. - PubMed
Additional references
Barden 2004
-
- Barden J, Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA. Relative efficacy of oral analgesics after third molar extraction. British Dental Journal 2004;197(7):407‐11. - PubMed
BNF 2001
-
- BMJ. British National Formulary. 42. London: British Medical Association, September 2001.
Clarke 2009
Collins 1997
-
- Collins SL, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. The visual analogue pain intensity scale: what is moderate pain in millimetres?. Pain 1997;72(1‐2):95‐7. - PubMed
Collins 2001
-
- Collins SL, Edwards J, Moore RA, Smith LA, McQuay H J. Seeking a simple measure of analgesia for mega‐trials: is a single global assessment good enough?. Pain 2001;91:189‐94. - PubMed
Cook 1995
Cooper 1991
-
- Cooper SA. Single‐dose analgesic studies: the upside and downside of assay sensitivity. In: Max MB, Portenoy RK, Laska EM editor(s). The design of analgesic clinical trials. Advances in Pain Research and Therapy. Vol. 18, New York: Raven Press, 1991:117‐24.
Derry 2008
Derry C 2009a
Derry C 2009b
Derry P 2009
Edwards 1999
Edwards 2004
Forrest 2002
-
- Forrest JB, Camu F, Greer IA, Kehlet H, Abdalla M, Bonnet F. Ketorolac, diclofenac, and ketoprofen are equally safe for pain relief after major surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2002;88(2):227‐33. - PubMed
Garner 2002
Grahame‐Smith 2002
-
- Grahame‐Smith DG, Aronson JK. Oxford textbook of clinical pharmacology and drug therapy. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2002.
Hawkey 1999
-
- Hawkey CJ. Cox‐2 inhibitors. Lancet 1999;353(9149):307‐14. - PubMed
Hawkey 2001
-
- Hawkey CJ. Gastrointestinal safety of COX‐2 specific inhibitors. Gastroenterology Clinics of North America 2001;30(4):921‐36. - PubMed
Hawkey 2006
-
- Hawkey CJ. NSAIDs, coxibs, and the intestine. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2006;47(Suppl 1):S72‐5. - PubMed
Jadad 1996a
-
- Jadad A, Carroll D, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Developing a database of published reports of randomised clinical trials in pain research. Pain 1996;66:239‐46. - PubMed
Jadad 1996b
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Kearney 2006
-
- Kearney PM, Baigent C, Godwin J, Halls H, Emberson JR, Patrono C. Do selective cyclo‐oxygenase‐2 inhibitors and traditional non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs increase the risk of atherothrombosis? Meta‐analysis of randomised trials. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2006;3(332):1302‐8. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.332.7553.1302] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
L'Abbe 1987
-
- L'Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107:224‐33. - PubMed
Lloyd 2009
McQuay 1982
McQuay 2005
Moher 1999
-
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Lancet 1999;354:1896‐900. - PubMed
Moore 1996
Moore 1997a
Moore 1997b
Moore 1998
Moore 2003
-
- Moore RA, Edwards J, Barden J, McQuay HJ. Bandolier's Little Book of Pain. Oxfor: Oxford University Press, 2003. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263247‐7]
Moore 2005a
Moore 2005b
-
- Moore RA, Derry S, Makinson GT, McQuay HJ. Tolerability and adverse events in clinical trials of celecoxib in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review and meta‐analysis of information from company clinical trial reports. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2005;7(3):R644‐65. [DOI: 10.1186/ar1704] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2006
-
- Moore A, McQuay H. Bandolier's Little Book of Making Sense of the Medical Evidence. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006. [ISBN: 0‐19‐856604‐2]
Morris 1995
Roy 2007
Straube 2005
Toms 2008
Toms 2009
References to other published versions of this review
Barden 2002d
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

