Atrial natriuretic peptide for preventing and treating acute kidney injury
- PMID: 19821351
- PMCID: PMC12369934
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006028.pub2
Atrial natriuretic peptide for preventing and treating acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common in hospitalised patients and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Despite recent advances, outcomes have not substantially changed in the last four decades. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) has shown promise in animal studies, however randomised controlled trials (RCTs) have shown inconsistent clinical benefits.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of ANP for preventing and treating AKI.
Search strategy: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE and reference lists of retrieved articles.
Selection criteria: RCTs that investigated all forms of ANP versus any other treatment in adult hospitalised patients with or "at risk" of AKI.
Data collection and analysis: Results were expressed as risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) or mean difference (MD). Outcomes were analysed separately for low and high dose ANP for preventing or treating AKI.
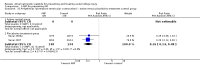
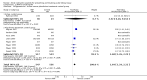
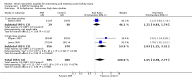
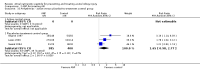
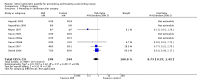
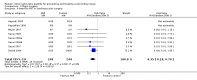
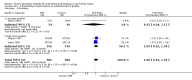
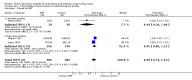
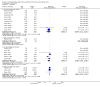
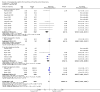
Main results: Nineteen studies (11 prevention, 8 treatment; 1,861 participants) were included. There was no difference in mortality between ANP and control in either the low or high dose prevention studies. Low (but not high) dose ANP was associated with a reduced need for RRT in the prevention studies (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.71). Length of hospital and ICU stay were significantly shorter in the low dose ANP group. For established AKI, there was no difference in mortality with either low or high dose ANP. Low (but not high) dose ANP was associated with a reduction in the need for RRT (RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.98). High dose ANP was associated with more adverse events (hypotension, arrhythmias). After major surgery there was a significant reduction in RRT requirement with ANP in the prevention studies (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.99), but not in the treatment studies. There was no difference in mortality between ANP and control in either the prevention or treatment studies. There was a reduced need for RRT with low dose ANP in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery (RR 0.35, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.70). ANP was not associated with outcome improvement in either radiocontrast nephropathy or oliguric AKI.
Authors' conclusions: ANP may be associated with improved outcomes when used in low doses for preventing AKI and in managing postsurgery AKI and should be further explored in these two settings. There were no significant adverse events in the prevention studies, however in the high dose ANP treatment studies there were significant increases hypotension and arrhythmias.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures


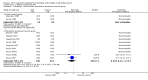




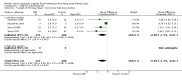






















Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Akamatsu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Akamatsu N, Sugawara Y, Tamura S, Kaneko J, Togashi J, Kishi Y, et al. Prevention of renal impairment by continuous infusion of human atrial natriuretic peptide after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2005;80(8):1093‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Allgren 1997 {published data only}
-
- Allgren RL, Marbury TC, Rahman SN, Weisberg LS, Fenves AZ, Lafayette RA, et al. Anaritide in acute tubular necrosis. Auriculin Anaritide Acute Renal Failure Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;336(12):828‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brenner 1995 {published data only}
-
- Brenner P, Meyer M, Reichenspurner H, Meiser B, Muller R, Mentz P, et al. Significance of prophylactic urodilatin (INN: ularitide) infusion for the prevention of acute renal failure in patients after heart transplantation. European Journal of Medical Research 1995;1(3):137‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hayashi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hayashi Y, Ohtani M, Sawa Y, Hiraishi T, Akedo H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Synthetic human alpha‐atrial natriuretic peptide improves the management of postoperative hypertension and renal dysfunction after the repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2003;42(5):636‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hayashida 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hayashida N, Chihara S, Kashikie H, Tayama E, Yokose S, Akasu K, et al. Effects of intraoperative administration of atrial natriuretic peptide. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2000;70(4):1319‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Herbert 1999 {published data only}
-
- Herbert MK, Ginzel S, Muhlschlegel S, Weis KH. Concomitant treatment with urodilatin (ularitide) does not improve renal function in patients with acute renal failure after major abdominal surgery‐‐a randomized controlled trial. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 1999;111(4):141‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kurnik 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kurnik BR, Weisberg LS, Cuttler IM, Kurnik PB. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide versus mannitol on renal blood flow during radiocontrast infusion in chronic renal failure. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 1990;116(1):27‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kurnik 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kurnik BR, Allgren RL, Genter FC, Solomon RJ, Bates ER, Weisberg LS. Prospective study of atrial natriuretic peptide for the prevention of radiocontrast‐induced nephropathy. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1998;31(4):674‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kuse 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kuse ER, Meyer M, Constantin R, Oldhafer K, Schlitt HJ, Schulz‐Knappe P, et al. Urodilatin (INN: ularitide). A new peptide in the treatment of acute kidney failure following liver transplantation. Anaesthesist 1996;45(4):351‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Langrehr 1997 {published data only}
-
- Langrehr JM, Kahl A, Meyer M, Neumann U, Knoop M, Jonas S, et al. Prophylactic use of low‐dose urodilatin for prevention of renal impairment following liver transplantation: a randomized placebo‐controlled study. Clinical Transplantation 1997;11(6):593‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lewis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lewis J, Salem MM, Chertow GM, Weisberg LS, McGrew F, Marbury TC, et al. Atrial natriuretic factor in oliguric acute renal failure. Anaritide Acute Renal Failure Study Group. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2000;36(4):767‐74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meyer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Meyer M, Wiebe K, Wahlers T, Zenker D, Schulze FP, Michels P, et al. Urodilatin (INN:ularitide) as a new drug for the therapy of acute renal failure following cardiac surgery. Clinical & Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 1997;24(5):374‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meyer 1999 {published data only}
-
- Meyer M, Pfarr E, Schirmer G, Uberbacher HJ, Schope K, Bohm E, et al. Therapeutic use of the natriuretic peptide ularitide in acute renal failure. Renal Failure 1999;21(1):85‐100. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rahman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rahman SN, Kim GE, Mathew AS, Goldberg CA, Allgren R, Schrier RW, et al. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in clinical acute renal failure. Kidney International 1994;45(6):1731‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sezai 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sezai A, Shiono M, Orime Y, Hata H, Hata M, Negishi N, et al. Low‐dose continuous infusion of human atrial natriuretic peptide during and after cardiac surgery. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2000;69(3):732‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sezai 2006a {published data only}
-
- Sezai A, Hata M, Wakui S, Shiono M, Negishi N, Kasamaki Y, et al. Efficacy of low‐dose continuous infusion of alpha‐human atrial natriuretic peptide (hANP) during cardiac surgery: possibility of postoperative left ventricular remodeling effect. Circulation Journal 2006;70(1):1426‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sezai 2006b {published data only}
-
- Sezai A, Shiono M, Hata M, Iida M, Wakui S, Soeda M, et al. Efficacy of continuous low‐dose human atrial natriuretic peptide given from the beginning of cardiopulmonary bypass for thoracic aortic surgery. Surgery Today 2006;36(6):508‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sezai 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sezai A, Hata M, Wakui S, Niino T, Takayama T, Hirayama A, et al. Efficacy of continuous low‐dose hANP administration in patients undergoing emergent coronary artery bypass grafting for acute coronary syndrome. Circulation Journal 2007;71(19):1401‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Swärd 2004 {published data only}
-
- Swärd K, Valsson F, Odencrants P, Samuelsson O, Ricksten SE. Recombinant human atrial natriuretic peptide in ischemic acute renal failure: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32(6):1310‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cedidi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Cedidi C, Meyer M, Kuse ER, Schulz‐Knappe P, Ringe B, Frei U, et al. Urodilatin: a new approach for the treatment of therapy‐resistant acute renal failure after liver transplantation. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 1994;24(9):632‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gianello 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gianello P, Carlier M, Jamart J, Hulhoven R, Bernheim J, Bernard A, et al. Effect of 1‐28 alpha‐h atrial natriuretic peptide on acute renal failure in cadaveric renal transplantation. Clinical Transplantation 1995;9(6):481‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hummel 1992 {published data only}
-
- Hummel M, Kuhn M, Bub A, Bittner H, Kleefeld D, Marxen P, et al. Urodilatin: a new peptide with beneficial effects in the postoperative therapy of cardiac transplant recipients. Clinical Investigator 1992;70(8):674‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lang 1992 {published data only}
-
- Lang CC, Henderson IS, Mactier R, Stewart WK, Struthers AD. Atrial natriuretic factor improves renal function and lowers systolic blood pressure in renal allograft recipients treated with cyclosporin A. Journal of Hypertension 1992;10(5):483‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCT00390624 {published data only}
-
- Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers. Prevention of nephrotoxicity following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation using Urodilatin (Ularitide, Atrial Natriuretic Peptide) and mannitol. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov accessed 23 April 2008. [NCT00390624]
Sands 1991 {published data only}
-
- Sands JM, Neylan JF, Olson RA, O'Brien DP, Whelchel JD, Mitch WE. Atrial natriuretic factor does not improve the outcome of cadaveric renal transplantation. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1991;1(9):1081‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Seta 1998 {published data only}
-
- Seta K, Hayashi T, Sugawara A, Kasuno K, Watanabe S, Sumi Y, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide as a preload depressor in acute renal failure secondary to congestive heart failure. Renal Failure 1998;20(5):717‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Swärd 2001 {published data only}
-
- Swärd K, Valson F, Ricksten SE. Long‐term infusion of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) improves renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate in clinical acute renal failure. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2001;45(5):536‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Swärd 2005 {published data only}
-
- Swärd K, Valsson F, Sellgren J, Ricksten SE. Differential effects of human atrial natriuretic peptide and furosemide on glomerular filtration rate and renal oxygen consumption in humans. Intensive Care Medicine 2005;31(1):79‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Valsson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Valsson F, Ricksten SE, Hedner T, Zall S, William‐Olsson EB, Lundin S. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide on renal function after cardiac surgery and in cyclosporine‐treated heart transplant recipients. Journal of Cardiothoracic & Vascular Anesthesia 1994;8(4):425‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Valsson 1996 {published data only}
-
- Valsson F, Ricksten SE, Hedner T, Lundin S. Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide on acute renal impairment in patients with heart failure after cardiac surgery. Intensive Care Medicine 1996;22(3):230‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Brivet 1996
-
- Brivet FG, Kleinknecht DJ, Loirat P, Landais PJ. Acute renal failure in intensive care units‐‐causes, outcome, and prognostic factors of hospital mortality; a prospective, multicenter study. French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Critical Care Medicine 1996;24(2):192‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chertow 1998
-
- Chertow GM, Lazarus JM, Paganini EP, Allgren RL, Lafayette RA, Sayegh MH. Predictors of mortality and the provision of dialysis in patients with acute tubular necrosis. The Auriculin Anaritide Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(4):692‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chertow 2006
-
- Chertow GM, Palevsky PM, Greene T. Studying the prevention of acute kidney injury: lessons from an 18th‐century mathematician. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2006;1(5):1124‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coca 2008
-
- Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney International 2008;73(9):1008‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Conger 1991
-
- Conger JD, Falk SA, Hammond WS. Atrial natriuretic peptide and dopamine in established acute renal failure in the rat. Kidney International 1991;40(1):21‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dickersin 1994
Dorner 1998
-
- Dorner GT, Selenko N, Kral T, Schmetterer L, Eichler HG, Wolzt M. Hemodynamic effects of continuous urodilatin infusion: a dose‐finding study. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1998;64(3):322‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Edelstein 1997
-
- Edelstein CL, Ling H, Wangsiripaisan A, Schrier RW. Emerging therapies for acute renal failure. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1997;30(5 Suppl 4):89‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Egger 1997
Forssmann 2001
-
- Forssmann W, Meyer M, Forssmann K. The renal urodilatin system: clinical implications. Cardiovascular Research 2001;51(3):450‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gianello 1990
-
- Gianello P, Squifflet JP, Carlier M, Lambotte L, Ketelslegers JM, Alexandre GP. Atrial natriuretic factor: a protective role after acute renal ischemia? Is there room for it in kidney transplantation?. Transplant International 1990;3(1):41‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Guerin 2000
-
- Guerin C, Girard R, Selli JM, Perdrix JP, Ayzac L. Initial versus delayed acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: A multicenter prospective epidemiological study. Rhone‐Alpes Area Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 2000;161(3 Pt 1):872‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Hou 1983
-
- Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT. Hospital‐acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. American Journal of Medicine 1983;74(2):243‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jo 2007
-
- Jo SK, Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Pharmacologic treatment of acute kidney injury: Why drugs havent worked and what is on the horizon. Clinical Journal of The American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2007;2(2):356‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kaufman 1991
-
- Kaufman J, Dhakal M, Patel B, Hamburger R. Community‐acquired acute renal failure. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1991;17(2):191‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kinsey 2008
Lameire 2005
-
- Lameire N, Biesen W, Vanholder R. Acute renal failure. Lancet 2005;365(9457):417‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lefebvre 1996
-
- Lefebvre C, McDonald S. Development of a sensitive search strategy for reports of randomized controlled trials in EMBASE. Fourth International Cochrane Colloquium; 1996 Oct 20‐24; Adelaide (Australia). 1996.
Liano 1989
-
- Liano F, Garcia‐Martin F, Gallego A, Orte L, Teruel JL, Marcen R, et al. Easy and early prognosis in acute tubular necrosis: a forward analysis of 228 cases. Nephron 1989;51(3):307‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Liano 1996
-
- Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community‐based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney International 1996;50(3):811‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2002
-
- Mehta RL, Pascual MT, Soroko S, Chertow GM PICARD Study Group. Diuretics, mortality, and nonrecovery of renal function in acute renal failure. JAMA 2002;288(20):2547‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2004
-
- Mehta RL, Pascual MT, Soroko S, Savage BR, Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA, et al. Spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: The PICARD experience. Kidney International 2004;66(4):1613‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2007
Moore 1984
-
- Moore RD, Smith CR, Lipsky JJ, Mellits ED, Lietman PS. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity in patients treated with aminoglycosides. Annals of Internal Medicine 1984;100(3):352‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Parikh 2006
-
- Parikh CR, Mishra J, Thiessen‐Philbrook H, Dursun B, Ma Q, Kelly C, et al. Urinary IL‐18 is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney International 2006;70(1):199‐203. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pascual 1990
-
- Pascual J, Orofino L, Liano F, Marcen R, Naya MT, Orte L, et al. Incidence and prognosis of acute renal failure in older patients. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1990;38(1):25‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Renal Group 2009
-
- Willis NS, Mitchell R, Higgins GY, Webster AC, Craig JC. Cochrane Renal Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2009, Issue 3. Art. No.: RENAL (accessed July 2009).
Roson 2006
-
- Rosón MI, Toblli JE, Della Penna SL, Gorzalczany S, Pandolfo M, Cavallero S, et al. Renal protective role of atrial natriuretic peptide in acute sodium overload‐induced inflammatory response. American Journal of Nephrology 2006;26(6):590‐601. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Roy 1986
-
- Roy DR. Effect of synthetic ANP on renal and loop of Henle functions in the young rat. American Journal of Physiology 1986;251(2 Pt 2):220‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Solomon 1994
-
- Solomon R, Werner C, Mann D, D'Elia J, Silva P. Effects of saline, mannitol, and furosemide to prevent acute decreases in renal function induced by radiocontrast agents. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;331(21):1416‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Spurney 1991
-
- Spurney RF, Fulkerson WJ, Schwab SJ. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: prognosis for recovery of kidney function after prolonged dialysis support. Critical Care Medicine 1991;19(1):8‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Uchino 2005
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005;294(7):813‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vesely 2003
-
- Vesely DL. Natriuretic peptides and acute renal failure. American Journal of Physiology ‐ Renal Fluid & Electrolyte Physiology 2003;285(2):167‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Waikar 2006
-
- Waikar SS, Curhan GC, Wald R, McCarthy EP, Chertow GM. Declining mortality in patients with acute renal failure, 1988 to 2002. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(4):1143‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xue 2006
-
- Xue JL, Daniels F, Star RA, Kimmel PL, Eggers PW, Molitoris BA, et al. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(4):1135‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zacharias 2005
Zanardo 1994
-
- Zanardo G, Michielon P, Paccagnella A, Rosi P, Calo M, Salandin V, et al. Acute renal failure in the patient undergoing cardiac operation: prevalence, mortality rate, and main risk factors. Journal of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery 1994;107(6):1489‐95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

