Blood pressure lowering efficacy of diuretics as second-line therapy for primary hypertension
- PMID: 19821398
- PMCID: PMC12410055
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007187.pub2
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of diuretics as second-line therapy for primary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Diuretics are widely prescribed for hypertension not only as a first-line drug but also as a second-line drug. Therefore, it is essential to determine the effects of diuretics on blood pressure (BP), heart rate and withdrawals due to adverse effects (WDAEs) when given as a second-line drug.
Objectives: To quantify the additional reduction in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of diuretic therapy as a second-line drug in patients with primary hypertension
Search strategy: CENTRAL (The Cochrane Library 2008, Issue 2), MEDLINE (1966-July 2008), EMBASE (1988-July 2008) and bibliographic citations of articles and reviews were searched.
Selection criteria: Double-blind, randomized, controlled trials evaluating the BP lowering efficacy of a diuretic in combination therapy with another class of anti-hypertensive drugs compared with the respective monotherapy (without a diuretic) for a duration of 3 to 12 weeks in patients with primary hypertension.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted the data and assessed trial quality.
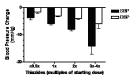
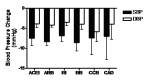
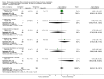
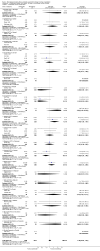
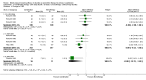
Main results: Fifty-three double-blind RCTs evaluating a thiazide in 15129 hypertensive patients (baseline BP of 156/101 mmHg) were included. Hydrochlorothiazide was the thiazide used in 49/53 (92%) of the included studies. The additional BP reduction caused by the thiazide as a second drug was estimated by comparing the difference in BP reduction between the combination and monotherapy groups. Thiazides as a second-line drug reduced BP by 6/3 and 8/4 mmHg at doses of 1 and 2 times the manufacturer's recommended starting dose respectively. The BP lowering effect was dose related. The effect was similar to that obtained when thiazides are used as a single agent. Only 3 double-blind RCTs evaluating loop diuretics were identified. These RCTs showed a BP lowering effect of a starting dose of about 6/3 mmHg.
Authors' conclusions: Thiazides when given as a second-line drug have a dose related effect to lower blood pressure that is similar to when they are added as a first-line drug. This means that the BP lowering effect of thiazides is additive. Loop diuretics appear to have a similar blood pressure lowering effect as thiazides at 1 times the recommended starting dose. Because of the short duration of the trials and lack of reporting of adverse events, this review does not provide a good estimate of the incidence of adverse effects of diuretics given as a second-line drug.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures











Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Asplund 1981 {published data only}
-
- Asplund J. A fixed‐ratio combination of metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide (Co‐betaloc(TM)) in essential hypertension: A comparison between the individual drugs. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1981;29(3):387‐394. [EMBASE1981130462]
Benz 1998 {published data only}
-
- Benz JR, Black HR, Graff A, Reed A, Fitzsimmons S, Shi Y. Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. A multiple dose, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial comparing combination therapy with monotherapy. Journal of Human Hypertension 1998;12:861‐6. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00158693] - PubMed
Bermudez 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bermudez J.A. Kornhauser Araujo C. Parra Carrillo J.Z. Paz Barahona M. Management of essential arterial hypertension with a single daily dose of a fixed combination of slow‐release oxprenolol and chlorthalidone [MANEJO DE LA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL ESENCIAL CON LA COMBINACION FIJA DE OXPRENOLOL DE LIBERACION LENTA MAS CLORFTALIDONA, EN UNA DOSIS AL DIA. ENSAYO COMPARATIVO Y MULTICENTRICO]. Investigacion Medica Internacional 1982;9(2):156‐163.
Brown 1990 {published data only}
-
- Brown CL, Backhouse CI, Grippat JC, Santoni JP. The effect of perindopril and hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination on blood pressure and on the renin‐angiotensin system in hypertensive subjects.. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1990;39(4):327‐32. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00073926] - PubMed
Camera 1995 {published data only}
-
- Camera MI, Waisman GD, Galarza CR, Alfie J, Arahabety A, Saggese O, Magi MI, Mayorga LM. Multi‐centre study of the antihypertensive effect of lisinopril (20 mg) and a fixed combination of lisinopril (20 mg) and hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg) once daily in mild to moderate essential hypertension.. Drug Development Research. 1995;34(suppl. 2):20‐23. [EMBASE 1995095667; CN‐00169283]
-
- Waisman GD, Galarza CR, Alfie J, Mayorga LM, et al. Comparison of the Haemodynamic Effects of Lisinopril and Lisinopril Plus Hydrochlorothiazide During Rest and Orthostatic Stress. Drug Development Research 1995;Suppl 2:24‐29.
Chadha 1983 {published data only}
Chrysant 1994 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG. Antihypertensive effectiveness of low‐dose lisinopril‐hydrochlorothiazide combination. A large multicenter study. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(7):737‐43. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 1994117160, CN‐00100251] - PubMed
Chrysant 1996 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Fagan T, Glazer R, Kriegman A. Effects of benazepril and hydrochlorothiazide, given alone and in low‐ and high‐dose combinations, on blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Archives of Family Medicine 1996;5(1):17‐24; discussion 25. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00122483] - PubMed
Chrysant 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Weber MA, Wang AC, Hinman DJ. Evaluation of antihypertensive therapy with the combination of olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide.. American journal of hypertension : journal of the American Society of Hypertension 2004;17(3):252‐9. - PubMed
Drayer 1995 {published data only}
-
- Drayer JI, Stimpel M, Fox A, Weber M. The Antihypertensive Properties of the Angiotensin‐Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Moexipril Given Alone or in Combination with a Low Dose of a Diuretic [Am J Ther]. 1995 2;8:525‐531. - PubMed
Fernandez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez M, Madero R, Gonzalez D, Camacho P, Villalpando J, Arriaga J. Combined versus single effect of fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1994;23(1 Suppl):I207‐10. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00098271, EMBASE 1994025969] - PubMed
Frei 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frei M, Küster L, Gardosch von Krosigk PP, Koch HF, Küppers H. Moxonidine and hydrochlorothiazide in combination: a synergistic antihypertensive effect.. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1994;24 Suppl 1:S25‐8. - PubMed
Frishman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frishman WH, Bryzinski BS, Coulson LR, DeQuattro VL, Vlachakis ND, Mroczek WJ, Dukart G, Goldberg JD, Alemayehu D, Koury K. A multifactorial trial design to assess combination therapy in hypertension. Treatment with bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(13):1461‐8. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00102520, EMBASE 1994210883] - PubMed
Frishman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Frishman WH, Burris JF, Mroczek WJ, Weir MR, Alemayehu D, Simon JS, Chen SY, Bryzinski BS. First‐line therapy option with low‐dose bisoprolol fumarate and low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide in patients with stage I and stage II systemic hypertension. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1995;35(2):182‐8. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 1995055004, CN‐00114120] - PubMed
Genthon 1994 {published data only}
-
- Genthon R, Andrieux LA, Arnaud J, Ballade M, Billou J, Bosredon A, Boutges B, Dubon T, Goigoux B, Lalanne G, Laurentjoye F, Lion A, Lorans P, Maurat X, Moulinet P, Ricard L, Roche A, Sdrigotti D, Rangoonwala B, et al. Study of the efficacy and safety of the combination ramipril 2.5 mg plus hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg in patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. INT J CLIN PHARMACOL RES 1994;14(1):1‐9. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 1994205899; CN‐00170369] - PubMed
Hart 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hart W. Lisinopril‐hydrochlorothiazide combination compared with the monocomponents in elderly hypertensive patients. Journal of Human Hypertension 1991;5 Suppl 2:85‐9. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00081965; EMBASE1992032801] - PubMed
Homuth 1993 {published data only}
-
- Homuth V, Faulhaber HD, Loose U, Loffler K, Luft FC. Usefulness of piretanide plus ramipril for systemic hypertension: a multicenter trial. American Journal of Cardiology 1993;72(9):666‐71. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00097410; EMBASE1993273569] - PubMed
Kayanakis 1987 {published data only}
Kellaway 1993 {published data only}
-
- Kellaway GS. A comparison of the efficacy of cilazapril versus cilazapril plus hydrochlorothiazide in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Inhibace General Practice Study Group.. European journal of clinical pharmacology 1993;44(4):377‐9. - PubMed
Kochar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kochar M, Guthrie R, Triscari J, Kassler‐Taub K, Reeves RA. Matrix study of irbesartan with hydrochlorothiazide in mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(8 Pt 1):797‐805. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00167270] - PubMed
Lacourciere 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lacourcière Y, Arnott W. Placebo‐controlled comparison of the effects of nebivolol and low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide as monotherapies and in combination on blood pressure and lipid profile in hypertensive patients.. Journal of human hypertension 1994 Apr;8(4):283‐8. - PubMed
Lacourciere 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lacourcière Y, Poirier L, Hebert D, Assouline L, Stolt P, Rehel B, Khder Y. Antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of two fixed‐dose combinations of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide compared with valsartan monotherapy in patients with stage 2 or 3 systolic hypertension: an 8‐week, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group trial.. Clinical therapeutics 2005;27(7):1013‐21. - PubMed
Lenz 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lenz T, Schulte KL, Wagner B, Lilienthal J, Gotzen R. Quinapril, hydrochlorothiazide, and combination in patients with moderate to severe hypertension.. European Heart Journal 1994;15(7):940‐6. [CN‐00104892; EMBASE 1994237184] - PubMed
Li 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li Y, Liu G, Jiang B, Gao R, Chen L, Su L, Li J. A comparison of initial treatment with losartan/HCTZ versus losartan monotherapy in chinese patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension.. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2003;58(7):673‐7. [CN‐00459020] - PubMed
MacKay 1996 {published data only}
-
- MacKay JH, Arcuri KE, Goldberg AI, Snapinn SM, Sweet CS. Losartan and low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of concomitant administration compared with individual components.. Archives of Internal Medicine 1996;156(3):278‐85. [EMBASE 1996062529; CN‐00123252] - PubMed
-
- Schoenberger JA, Bauer J, Barden LP, Brown R, Byyny R, Cohen J, Davis A, Davis P, Popli S, Guthrie G, Herman T, Hotltzman J, Kelly D, Marbury TC, Lewis G, Littlejohn T, MacKay JH, Mulrow P, O CD, et al. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of hypertension.. Journal of Hypertension, Supplement. 1995;13(1):S43‐S47. [EMBASE 1995266978] - PubMed
Manning 1996 {published data only}
-
- Manning G, Joy A, Mathias CJ, McDonald CJ, Millar‐Craig MW. Double‐blind, parallel, comparative multicentre study of a new combination of diltiazem and hydrochlorothiazide with individual components in patients with mild or moderate hypertension. Journal of human hypertension 1996 Jul;10(7):443‐8. - PubMed
McGill 2001 {published data only}
-
- McGill JB. Angiotensin II receptor antagonist plus a thiazide diuretic is more efficacious for treating hypertension than either drug alone.. Blood Pressure Monitoring 2001;6(SUPPL. 1):S3‐S13.
-
- McGill JB, Reilly PA. Telmisartan plus hydrochlorothiazide versus telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide monotherapy in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(6):833‐50. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00373202] - PubMed
Merrill 1987 {published data only}
-
- Merrill DD, Byyny RL, Carr A, Dauer AD, Kazilionis JE, Lester FM, Miller K, Gibson TP, Whipple J. Lisinopril/HCTZ in essential hypertension [abstract]. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1987; Vol. 41, issue 2:227.
Mersey 1993 {published data only}
-
- Mersey J, D'Hemecourt P, Blaze K. Once‐daily fixed combination of captopril and hydrochlorothiazide as first line therapy for mild to moderate hypertension. CURR. THER. RES. CLIN. EXP. 1993;53(5):502‐512. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00182021]
Meyer 1994 {published data only}
-
- Meyer BH, Pauly NC. Double‐blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of trandolapril 2 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg in patients with mild‐to‐moderate essential hypertension. J CARDIOVASC PHARMACOL 1994;23(SUPPL. 4):S77‐S80. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 1994264217; CN‐00172078] - PubMed
Neutel 2008 {published data only}
-
- Neutel J.M, Franklin S.S, Lapuerta P, Bhaumik A, Ptaszynska A. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of irbesartan/HCTZ combination therapy with irbesartan and HCTZ monotherapy in the treatment of moderate hypertension.. Journal of Human Hypertension 2008;22(4):266‐274. - PubMed
Oparil 1980 {published data only}
-
- Oparil S. Multiclinic double‐blind evaluation of timolol combined with hydrochlorothiazide in essential hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1980;27(4):527‐537. [CN‐00333696; EMBASE 1980132951]
Papademetriou 2000 {published data only}
-
- Papademetriou V, Reif M, Henry D, et al. Combination Therapy with Candesartan Cilexetil and Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients with Systemic Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 2000;2:372‐8.
Papademetriou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Papademetriou V, Hainer JW, Sugg J, Munzer D, ATTACH Study Group. Factorial antihypertensive study of an extended‐release metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide combination.. American journal of hypertension : journal of the American Society of Hypertension 2006 Dec;19(12):1217‐25. - PubMed
Parati 2006 {published data only}
-
- Parati G, Omboni S, Castiglioni G, Cereda U, Corradi L, Fogari R, Garavelli G, Malacco E, Pisani A, Villa G. Antihypertensive efficacy of zofenopril and hydrochlorothiazide combination on ambulatory blood pressure. Blood Pressure 2006;15(Suppl 1):7‐17.
Philipp 1997 {published data only}
-
- Philipp T, Letzel H, Arens HJ. Dose‐finding study of candesartan cilexetil plus hydrochlorothiazide in patients with mild to moderate hypertension.. Journal of human hypertension 1997 Sep;11 Suppl 2:S67‐8. - PubMed
Pool 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Gennari J, Goldstein R, Kochar MS, Lewin AJ, Maxwell MH, McChesney JA, Mehta J, Nash DT, Nelson EB, et al. Controlled multicenter study of the antihypertensive effects of lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, and lisinopril plus hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of 394 patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1987;9 Suppl 3:S36‐42. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00254084; EMBASE1987181938] - PubMed
Pool 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pool PE, Applegate WB, Woehler T, Sandall P, Cady WJ. A randomized, controlled trial comparing diltiazem, hydrochlorothiazide, and their combination in the therapy of essential hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 1993;13(5):487‐93. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00097378] - PubMed
Pool 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Cushman WC, Saini RK, Nwachuku CE, Battikha JP. Use of the factorial design and quadratic response surface models to evaluate the fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1997;10(1):117‐23. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00136040] - PubMed
Pool 2007a {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Schmieder RE, Azizi M, Aldigier JC, Januszewicz A, Zidek W, Chiang Y, Satlin A. Aliskiren, an orally effective renin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy alone and in combination with valsartan.. American journal of hypertension : journal of the American Society of Hypertension 2007 Jan;20(1):11‐20. - PubMed
Pool 2007b {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Glazer R, Weinberger M, Alvarado R, Huang J, Graff A. Comparison of valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy at doses up to 320/25 mg versus monotherapy: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study followed by long‐term combination therapy in hypertensive adults.. Clinical therapeutics 2007 Jan;29(1):61‐73. - PubMed
Prisant 2000 {published data only}
-
- Prisant LM. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Profiles in Patients Treated with Once‐Daily Diltiazem Extended‐Release or Indapamide Alone or in Combination. American Journal of Therapeutics 2000;7:177‐184. - PubMed
Romero 1995 {published data only}
-
- Romero R, Castellote E, Ocon J, Wagner B. Controlled multicenter study with quinapril, hydrochlorothiazide, and combination in patients with moderate to severe hypertension.. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1995;26(1):114‐8. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00120025] - PubMed
Rosenthal 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rosenthal T, Grossman E, Rathaus M, Bernheim J, Zevin D, Levi J, Weinstein J, Rogel S. Treatment of hypertension by enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide separately and together: a multicenter study. Israel Journal of Medical Sciences 1990;26(2):63‐6. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00066622; EMBASE1990104829] - PubMed
Safar 1973 {published data only}
-
- Safar M, Maiz HB, Weiss Y, Lagrue G, Milliez P. [Antihypertensive action of a beta‐blocker: value of a controlled therapeutic trial] [Action anti‐hypertensive d'un bêta‐bloqueur: intérêt d'un essai thérapeutique contrôlé.]. Therapeutique (La Semaine des hôpitaux) 1973 Sep‐Oct;49(7):459‐62. - PubMed
-
- Safar M, Weiss Y, Sobel A, Lagrue G, Milliez P. [Antihypertensive properties of a beta blocking agent, pindolol] [Action anti‐hypertensive d'un bêta‐bloqueur, le pindolol.]. La Nouvelle presse médicale 1973 Nov;2(40):2685‐8. - PubMed
Safar 1994 {published data only}
-
- Safar M, Zanchetti A, Sever PS, et al. Perindopril and Indapamide as a Combination in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension ‐ A Double‐Blind Randomized Placebo‐Controlled European Multicenter Study [POSTER]. AJH 1994; Vol. 7, issue 4:43A.
Saruta 2007 {published data only}
-
- Saruta T, Ogihara T, Matsuoka H, et al. Antihypertensive Efficacy and Safety of Fixied‐Dose Combination Therapy with Losartan Plus Hydrochlorothiazide in Japanese Patients with Essential Hypertension. Hypertens Res 2007;30:729‐739. - PubMed
Saul 1995 {published data only}
-
- Saul P. Efficacy and tolerability of a once‐daily low‐dose lisinopril /hydrochlorothiazide preparation: Comparison with its monocomponents. Drug Development Research. 1995;34(suppl. 2):8‐13. [EMBASE 1995095665; CN‐00173176]
Schoenberger 1986 {published data only}
-
- Schoenberger JA, Wilson DJ. Once‐daily treatment of essential hypertension with captopril.. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 1986;2(4):379‐87. [CN‐00046328] - PubMed
Thijs 1995 {published data only}
-
- Thijs L, Celis H, Kiowski W, Loffler K, Middeke M, Schulz W, Staessen J, Amery A. Double‐blind comparison of antihypertensive treatment with ramipril and piretanide, given alone or in combination. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1995;26(1):33‐8. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 1995198201; CN‐00120021] - PubMed
Vaicaitis 1980 {published data only}
-
- Vaicaitis JS. VVaicaitis JS. Evaluation of a beta‐blocker, timolol maleate, combined with hydrochlorothiazide in essential hypertension.. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1980;27(3):365‐373. [EMBASE1980107978 EMBASE1980107978]
Villamil 2007 {published data only}
-
- Villamil A, Chrysant Sg, Calhoun D, et al. Renin Inhibition with Aliskiren Provides Additive Antihypertensive Efficacy When Used in Combination with Hydrochlorothiazide. Journal of Hypertension 2007;25:217‐226. - PubMed
von Manteuffel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Manteuffel GE, Rakette S, Woll EM, Reinfrank J, Schiemann J. Effectiveness and tolerance of combined verapamil retard and hydrochlorothiazide. Results of a double‐blind, randomized study [Wirksamkeit und Vertraglichkeit der Kombination Verapamil retard und Hydrochlorothiazid. Ergebnisse einer doppelblinden, randomisierten Studie.]. Fortschritte der Medizin 1995;113(26):374‐8. - PubMed
Weinberger 1982 {published data only}
Weir 1992 {published data only}
-
- Weir MR, Weber MA, Punzi HA, Serfer HM, Rosenblatt S, Cady WJ. A dose escalation trial comparing the combination of diltiazem SR and hydrochlorothiazide with the monotherapies in patients with essential hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1992;6(2):133‐8. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00084591; EMBASE1992151099] - PubMed
Yodfat 1994 {published data only}
-
- Yodfat Y, Zimilchman R. Dose‐finding and dose justification of once‐daily cilazapril in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in non‐obese patients with mild‐to‐moderate essential hypertension. J. DRUG DEV. 1993;6(3):117‐121. [EMBASE 1994092035; CN‐00179498]
References to studies excluded from this review
Agrawal 1979 {published data only}
Agrawal 1987 {published data only}
-
- Agrawal RL. Double‐blind comparison of Inderal LA (160mg), Half‐Inderal LA (80 mg), and Half‐Inderal LA plus bendrofluazide (2.5mg) in the treatment of elderly hypertensive patients. The British Journal of Clinical Practice 1987;41:916‐920. - PubMed
Anderton 1988 {published data only}
-
- Anderton JL, Vallance BD, Stanley NN, Crowe PF, Mittra B, Perks WH. Atenolol and Sustained Release Nifedipine Alone and in Combination in Hypertension. Drugs 1988;35 (suppl. 4):22‐26. - PubMed
Bainbridge 1993 {published data only}
Bateman 1979 {published data only}
Bauer 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bauer JH, Gaddy P. Effects of Enalapril Alone, and in Combination with Hydrochlorothiazide, on Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone, Renal Function, Salt and Water Excretion, and Body Fluid Composition. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1985;6(4):222‐32. - PubMed
-
- Comparative studies: enalapril versus hydrochlorothiazide as first‐step therapy for the treatment of primary hypertension. Bauer JH, Jones LB. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1984;4(1):55‐62. - PubMed
Bertrand 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bertrand Ed, Dienot B, Ravinet L. Study of treatment of arterial hypertension with oxprenolol (compared with placebo) and chlortalidone [Etude du traitement de l'hypertension artérielle par Oxprénolol (comparé à un placebo) et par Chlortalidone]. Médecine d'Afrique Noire 1982;29(4):271‐274.
Boike1982 {published data only}
-
- Boike SC, Durley Y, Cubberley RB. Atenolol and Chlorthalidone Administered Alone and in Combination for Essential Hypertension. Clinical Pharmacy 1982;1:449‐53. - PubMed
Bolzano 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bolzano K, Krempler F, Sandhofer F. [A combination of methyldopa, hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride in the treatment of essential hypertension] [Eine Kombination von Methyldopa, Hydrochlorothiazid und Amilorid bei der Behandlung der essentiellen Hypertonie.]. Acta medica Austriaca 1984;11(2):49‐53. - PubMed
Cajochen 1984 {published data only}
-
- Cajochen C, Krauchi K, Von AMA, Mori D, Graw P, Wirz‐Justice A. A multicenter comparison of the antihypertensive effects of atenolol and chlorthalidone given alone and in combination. CURR THER RES, CLIN EXP 1984;35(1):31‐39.
Canter 1994 {published data only}
-
- Canter D, Frank GJ, Knapp LE, Phelps M, Quade M, Texter M. Quinapril and hydrochlorothiazide combination for control of hypertension:assessment by factorial design. Quinapril InvestigatorGroup [see comments]. Journal of Human Hypertension 1994;8(3):155–62. - PubMed
Cappuccio 1993 {published data only}
-
- Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND, Singer DRJ, MacGregor GA. Amlodipine and Lisinopril in Combination for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: Efficacy and Predictors of Response. Journal of Hypertension 1993;11:839‐47. - PubMed
Chalmers 1982 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers JP, Wing LMH, Grygiel JJ, West MJ, Graham JR, Bune AJ. Effects of Once Daily Indapamide and Pindolol on Blood Pressure, Plasma Aldosterone Concentration and Plasma Renin Activity in a General Practice Setting. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1982;22:191‐6. - PubMed
Chalmers 1986 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers JP, Wing LMH, West MJ, Bune AJC, Elliott JM. Effects of Enalpril and Hydrochlorothiazide on Blood Pressure, Renin‐angiotensin System, and Atrial Natriuretic Factor in Essential Hypertension: A Double‐blind Factorial Cross‐over Study. Aust NZ J Med 1986;16:475‐480. - PubMed
Chrysant 1992 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Chappel C, Farnham DJ, Levin B, Lueg M, McCluskey D, Steiner C. Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of single and combined atenolol regimens. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1992;32(1):61‐5. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00081715; EMBASE1992169096] - PubMed
Crowe 1987 {published data only}
-
- Crowe PF, Finnegan OC, Rusell CJMcL, Varma MPS. A Double‐blind Study of INderex in the Treatment of Essential Hypertension. The British Journal of Clinical Practice 1987;41(10):967‐970. - PubMed
Dahlof 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dahlof B, Jonsson L, Borgholst O, Ekblad G, Engstrand C, Grundestam I, Lindh A. Improved antihypertensive efficacy of the felodipine‐metoprolol extended‐release tablet compared with each drug alone.. Blood Pressure Supplement 1993;1:37‐45. - PubMed
Dargie 1986 {published data only}
-
- Dargie H, Cleland J, Findlay I, et al. Combination of Verapamil and Beta Blockers in Systemic Hypertension. Am J Cardiol 1986;57:80D‐82D. - PubMed
-
- Dargie HJ. Verapamil and Beta‐Blockers in Hypertension: A Beneficial Drug Interaction?. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1985;39(6 SUPPL. 42):44‐47. - PubMed
De Divitiis 1981 {published data only}
-
- Divitiis O, Petitto M, Somma S, et al. Atenolol, chlorthalidone, and reserpine in mild‐moderate hypertension: Double‐blind comparison. Drugs Under Experimental & Clinical Research 1981;7(6):773‐779.
De Divitiis 1983 {published data only}
-
- Divitiis O, Somma S, Petitto M, Fazio S, Ligouri V. Indapamide and Atenolol in the Treatment of Hypertension: Double‐blind Comparative and Combination Study. Current Medical Research Opinion 1983;8(7):493‐500. - PubMed
Durel 1992 {published data only}
-
- Durel LA, Hayashi PJ, Weidler DJ, Schneiderman N. Effectiveness of Antihypertensive Medications in Office and Ambulatory Settings: A Placebo‐Controlled Comparison of Atenolol, Metroprolol, Chlorthalidone, Verapamil, and an Atenolol‐Chlorthalidone Combination. J Clin Pharmacol 1992;32:564‐570. - PubMed
Erwteman 1984 {published data only}
Fernandez 1980 {published data only}
Forette 1979 {published data only}
-
- Forette F, Henry JF, Hervy MP, Forette B, Berthaux P. The treatment of hypertension in the elderly using a beta‐blocker: acebutolol [Traitement de l'hypertension artérielle du sujet âgé par un bêta‐bloquant: l'acébutolol.]. La Nouvelle presse médicale 1979;8(36):2881‐4. - PubMed
Frishman 1987 {published data only}
-
- Frishman WH, Goldberger J, Sherman D. Enalapril, hydrochlorothiazide, and combination therapy in patients with moderate hypertension.. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 1987;3(4):520‐7. - PubMed
Hart 1985 {published data only}
-
- Hart HC, Van dLDL, Lustermans FAT, et al. Double‐blind comparison of dytenzide, atenolol and the combination of dytenzide and atenolol in patients with essential hypertension.. CURR‐THER‐RES,‐CLIN‐EXP 1985;38(5):702‐709. [CN‐00175975; EMBASE 1986040698]
Hunter 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hunter SJ, Wiggam MI, Ennis CN, Whitehead HM, Sheridan B, Atkinson AB, Bell PM. Comparison of effects of captopril used either alone or in combination with a thiazide diuretic on insulin action in hypertensive Type 2 diabetic patients: a double‐blind crossover study.[see comment].. Diabetic Medicine 1999;16(6):482‐7. - PubMed
Jaattela 1979 {published data only}
-
- Jaattela A. The Fixed Combination of Propanolol and Bendrofluazide in the Treatment of Hypertension. Annals of Clinical Research 1979;11:80‐82. - PubMed
Jackson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Jackson G, Rowland M, Adam G, MacFarlane E, Jackson PG. Placebo Controlled Double‐blind Randomised Cross‐over Trial of Atenolol, Hydrochlorothiazide and Amiloride, and the Combination (Kalten) in Patients Over 60 Years of Age. The British Journal of Clinical Practice 1986;40(6):230‐234. - PubMed
Khalil 1982 {published data only}
-
- Khalil SI, Zein O, Mahadi Bella M. A double‐blind, crossover study of acebutolol and hydrochlorothiazide/amiloride diuretic in Sudanese patients with essential hypertension.. Current medical research and opinion 1982;1:39‐43. - PubMed
Kieso 1983 {published data only}
Koh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Koh KK, Quon MJ, Lee Y, et al. Additive Beneficial Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of Combination Therapy with Ramipril and Candesartan in Hypertensive Patients. European Heart Journal 2007;28:1440‐7. - PubMed
Kubik 1979 {published data only}
-
- Kubik M, Kendall M, Ebbutt A, John V. Metoprolol with and without chlorthalidone in hypertension. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics 1979;25(1):25‐32. - PubMed
Lang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lang H. The results of a large multicentre study comparing low‐dose lisinopril‐hydrochlorothiazide with the monocomponents.. Journal of Human Hypertension 1991;5 Suppl 2:73‐6. - PubMed
Lechi 1982 {published data only}
-
- Lechi A, Pomari S, Berto R, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Labetolol Alone and Combined with Chlorthalidone in Essential Hypertension: A Double‐blind Multicentre Controlled Study. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1982;22:289‐93. - PubMed
Leonetti 1986 {published data only}
-
- Leonetti G, Pasotti C, Capra A. Low‐dose atenolol‐chlorthalidone combination for treatment of mild hypertension.. International journal of clinical pharmacology, therapy, and toxicology 1986 Jan;24(1):43‐7. - PubMed
Magee 1986 {published data only}
-
- Magee PFA, Freis ED. Is Low‐Dose Hydrochlorothiazide Effective?. Hypertension 1986;8 (suppl II):135‐139. - PubMed
Mehta 1988 {published data only}
-
- Mehta J, Lopez LM, Thorman AD. Lisinopril Versus Lisinopril plus Phydrochlorothiazide in Essential Hypertension. Am J Cardiol 1988;61:803‐6. - PubMed
Middlemost 1994 {published data only}
-
- Middlemost SJ, Tager R, Davis J, Sareli P. Effectiveness of enalapril in combination with low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide versus enalapril alone for mild to moderate systemic hypertension in black patients.. American Journal of Cardiology 1994;73(15):1092‐7. - PubMed
Moncloa 1980 {published data only}
-
- Moncloa F, Hwang IK, Muccilli AC. Multiclinic evaluation of the antihypertensive effect of a methyldopa, hydrochlorothiazide, and amiloride combination.. Clinical Therapeutics 1980;3(3):168‐75. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00024331; EMBASE1981086995] - PubMed
Morgan 1992 {published data only}
-
- Morgan TO, Anderson A. Hemodynamic Comparisons of Enalapril and Felodipine and Their Combination. Kidney International 1992;41 (Suppl 36):S78‐81. - PubMed
-
- Morgan TO, Anderson A, Jones E. Comparison and Interaction of Low Dose Felodipine and Enalapril in the Treatmetn of Essential Hypertension in Elderly Subjects. American Journal of Hypertension 1992;5:238‐43. - PubMed
Morgan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Morgan T, Anderson A. A comparison of candesartan, felodipine, and their combination in the treatment of elderly patients with systolic hypertension.. American Journal of Hypertension 2002;15(6):544‐9. - PubMed
Muiesan 1976 {published data only}
-
- Muiesan G, Magnani B, Agabiti‐Rosei E, Alicandri C, Ambrosioni E, Miele N. Evaluation of the effect of timolol alone and in combination with hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride in the treatment of mild to moderate arterial hypertension: a double‐blind, controlled study. Clinical Science & Molecular Medicine ‐ Supplement 1976;3:529s‐531s. [MEDLINE: ; CN‐00015916] - PubMed
Neutel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Neutel JM, Smith DHG, Weber MA, et al. Efficacy of Combination Therapy With Amlodipine Besylate/Benazepril Hydrochloride for Lowering Systolic Blood Pressure in Stage 2 Hypertension. The American Journal of Geriatric Cardiology 2006;15(3):142‐50. - PubMed
Petrie 1975 {published data only}
Ricciardelli 1985 {published data only}
-
- Hemodynamic effects of the antihypertensive treatment with atenolol plus chlortalidone in fixed combination: A double‐blind crossover comparison with atenolol. Ricciardelli B, Cuocolo A, De LN, et al. Current Therapeutic Resesarch 1985;37(5):901‐11.
Rosenthal 1989 {published data only}
-
- Rosenthal J, Letzel H, Blumner E, Volger K‐D. Antihypertensive Therapy ‐ Dose‐Effect Relationship Between a Combination of Triamterene/Hydrochlorothiazide and Verapamil. Munch. med. Wschr 1989;131(16):319‐22.
Salako 1990 {published data only}
-
- Salako LA, Falase AO, Aderounmu AF, Walker O. Assessment of a Fixed‐dosage Combination of Atenolol and Chlorthalidone (Tenoretic) in Hypertensive Nigerians. Afr. J. Med. Sci 1990;19:57‐61. - PubMed
Salvetti 1987 {published data only}
-
- Salvetti A, Innocenti PF, Iardella M, Pambianco F, Saba GC, Rossetti M, Botta GF. Captopril and nifedipine interactions in the treatment of essential hypertensives: a crossover study.. Journal of Hypertension ‐ Supplement 1987;5(4):S139‐42. - PubMed
Salvetti 1989 {published data only}
-
- Salvetti A, Magagna A, Innocenti, et al. Chlorthalidone does not increase the hypotensive effect of nifedipine in essential hypertensives: a crossover multicentre study. Journal of hypertension 1989;7 (suppl 6):S250‐1. - PubMed
-
- Salvetti A, Magagna A, Innocenti, et al. The Combination of Chlorthalidone with Nifedipine Does Not Exert an Additive Antiypertensive Effect in Essential Hypertensives: A Crossover Multicenter Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1991;17:332‐335. - PubMed
Scholze 1993 {published data only}
-
- Scholze J, Breitstadt A, Cairns V, Bauer B, Bender N, Priestley C, Moreadith C, Phillips J, Vander Elst E, Koch G. Short report: ramipril and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in hypertension: a clinical trial of factorial design. The East Germany Collaborative Trial Group. Journal of hypertension 1993;11(2):217‐21. - PubMed
Singer 1987 {published data only}
-
- Singer DRJ, Markandu ND, Shore AC, MacGregor GA. Nifeidipine and Acebutolol in COmbination for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Essential Hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1987;1:31‐7. - PubMed
Tonkin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Tonkin AL, Wing LMH, Russell AE, et al. Diltiazem and atenolol in essential hypertension: additivity of effect on blood pressure and cardiac conduction with combination therapy. Journal of Hypertension 1990;8:1015‐1019. - PubMed
Topouchian 1999 {published data only}
-
- Topouchian J, Asmar R, Sayegh F, Rudnicki A, Benetos A, Bacri AM, Safar ME. Changes in arterial structure and function under trandolapril‐verapamil combination in hypertension.. Stroke 1999;5:1056‐64. - PubMed
VACSGAA 1977 {published data only}
-
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Aggents. Propanolol in the Treatment of Essential Hypertension. JAMA 1977;237(21):2303‐10. - PubMed
Van Staden 1983 {published data only}
-
- Staden DA, Gelder LW, Lingen RE. Trial of Bendrofluazide Compared to Propranolol plus Bendrofluazide (Inderetic) for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension in Blacks. Current Therapeutic Research 1983;34(4):620‐626.
Viskoper 1997 {published data only}
-
- Viskoper RJ, Compagnone D, Dies R, Zilles P. Verapamil and trandolapril alone and in fixed combination on 24‐hour ambulatory blood pressure profiles of patients with moderate essential hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research ‐ Clinical and Experimental 1997;58(6):343‐51.
Weinberger 1983 {published data only}
-
- Weinberger MH. Influence of an angiotensin converting‐enzyme inhibitor on diuretic‐induced metabolic effects in hypertension.. Hypertension 1983;5(5 Pt 2):III132‐8. - PubMed
Wing 1988 {published data only}
-
- Wing LMH, Chalmers JP, West MJ, et al. Enalapril and Atenolol in Essential Hypertension: Attenuation of Hypotensive Effects in Combination. Clin. and Exper. Hyper. ‐Theory and Practice 1988;10(1):119‐133. - PubMed
Wing 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wing LM, Russell AE, Tonkin AL, Bune AJ, West MJ, Chalmers JP. Felodipine, metoprolol and their combination compared with placebo in isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly.. Blood Pressure 1994;3(1‐2):82‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
Azizi 2000
-
- Azizi M, Linhart A, Alexander J, Goldberg A, Menten J, Sweet C, Menard J. Pilot study of combined blockade of the renin‐angiotensin system in essential hypertensive patients.. Journal of Hypertension 2000;18(8):1139‐47. - PubMed
Bucher 1997
-
- Bucher HC, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE, Walker SD. The results of direct and indirect treatment comparisons in meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1997;50(6):683‐691. - PubMed
Chan 1997
-
- Chan P, Lin CN, Tomlinson B, Lin TH, Lee YS. Additive effects of diltiazem and lisinopril in the treatment of elderly patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1997;10(7 Pt 1):743‐9. - PubMed
Chen 2008a
-
- Chen JMH, Heran BS, Perez MI, Wright JM. Blood pressure lowering efficacy of drugs inhibiting the renin‐angiotensin system as second‐line therapy for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007188] - DOI
Chen 2008b
Chen 2008c
Farsang 2001
-
- Farsang, C. Kawecka‐Jaszcz K. Langan J. Maritz F. Zannad F. Antihypertensive effects and tolerability of candesartan cilexetil alone and in combination with amlodipine. Clinical Drug Investigation 2001;21(1):17‐23.
Franklin 1999
-
- Franklin SS, Khan SA, Wong ND, Larson MG, Levy D. Is Pulse Pressure Useful in Predicting Risk for Coronary Heart Disease?: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1999;100:354‐360. - PubMed
Haider 2003
-
- Haider AW, Larson MG, FranklinSS, Levy D, FraminghamHeart Study. Systolic bloodpressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse pressure as predictors of risk for congestiveheart failure in the Framingham Heart Study. Ann Intern Med 2003;138(1):10‐16. - PubMed
Heran 2009a
Heran 2009b
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2008; Vol. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kuschnir 2004
-
- Kuschnir E, Bendersky M, Resk J, Panart MS, Guzman L, Plotquin Y, Grassi G, Mancia G, Wagener G. Effects of the combination of low‐dose Nifedipine GITS 20mg and Losartan 50mg in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 2004;43:300‐305. - PubMed
Lessem 1989
-
- Lessem JN, Barone EJ, Berl T, Detwiler J, Lewin AT, Lubash GD, Margolis R, McGowan RL, Ram CV, Vlachakis N, et al. Nicardipine and propranolol in the treatment of essential hypertension.. American Journal of Hypertension 1989;2(3 Pt 1):146‐53. - PubMed
Levine 1995
-
- Levine JH, Ferdinand KC, Cargo P, Laine H, Lefkowitz M. Additive effects of verapamil and enalapril in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1995;8(5 Pt 1):494‐9. - PubMed
Materson 1993
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, et al. Single‐drug therapy for hypertension in men: comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. N Engl J Med 1993;328:914‐21. - PubMed
Messerli 1998
-
- Messerli F, Frishman WH, Elliott WJ. Effects of verapamil and trandolapril in the treatment of hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(3 Pt 1):322‐7. - PubMed
Musini 2002
-
- Musini VM. A systematic review of the blood pressure lowering efficacy of thiazide diuretics in the treatment of adult patients with primary hypertension. MSc Thesis. The University of British Columbia. 2000.
Musini 2009
Pittrow 1997
-
- Pittrow DB. Antlsperger A. Welzel D. Wambach G. Schardt W. Weidinger G. Evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of a low‐dose combination of isradipine and spirapril in the first‐line treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. Cardiovascular Drugs & Therapy 1997;11(5):619‐627. - PubMed
Psaty 2003
-
- Psaty BM, Lumley T, Furberg CD, Schellenbaum G, Pahor M, Alderman MH, Weiss NS. Health outcomes associated with various antihypertensive therapies used as first‐line agents: A network meta‐analysis. JAMA 2003;289:2534‐2544. - PubMed
Scholze 1998
Scholze 1999
-
- Scholze J, Bauer B, Massaro J. Antihypertensive profiles with ascending dose combinations of ramipril and felodipine ER. Clinical & Experimental Hypertension (New York) 1999;21(8):1447‐62. - PubMed
Song 2003
Wong 2007
-
- Wong MMY. A systematic review of the blood pressure lowering efficacy of calcium channel blockers for primary hypertension. MSc Thesis. The Univeristy of British Columbia. 2007.
Wright 1999
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

