Pentoxifylline for alcoholic hepatitis
- PMID: 19821406
- PMCID: PMC6769169
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007339.pub2
Pentoxifylline for alcoholic hepatitis
Abstract
Background: Alcoholic hepatitis is a life-threatening disease, with an average mortality of approximately 40%. There is no widely accepted, effective treatment for alcoholic hepatitis. Pentoxifylline is used to treat alcoholic hepatitis, but there has been no systematic review to assess its effects.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of pentoxifylline in alcoholic hepatitis.
Search strategy: The Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index Expanded, LILACS, clinicaltrials.gov, and full text searches were conducted until August 2009. Manufacturers and authors were contacted.
Selection criteria: All randomised clinical trials of pentoxifylline in participants with alcoholic hepatitis compared to control were selected for inclusion.
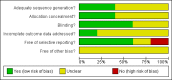
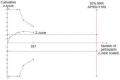
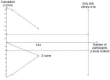
Data collection and analysis: Two authors extracted data and evaluated the risk of bias. RevMan Analysis was used for statistical analysis of dichotomous data with risk ratio (RR) and of continuous data with mean difference (MD), both with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Trial sequential analysis (TSA) was also used for statistical analysis of dichotomous and continuous data in order to control for random error. Where data were only available from one trial, we used Fisher's exact test or Student's t-test.
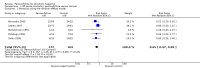
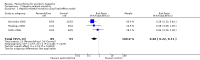
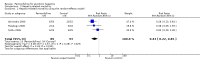
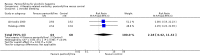
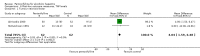
Main results: Five trials, with a total of 336 randomised participants, were included. A total of 105 participants (31%) died. Of the five included trials, four (80%) had a high risk of bias. Meta-analysis using all five trials showed that pentoxifylline reduced mortality compared with control (RR 0.64; 95% CI 0.46 to 0.89). However, this result was not supported by trial sequential analysis, which adjusts for multiple testing on accumulating data. Furthermore, four of the five trials were judged to have a high risk of bias, thus risking an overestimated intervention effect. Meta-analysis showed that pentoxifylline reduced the hepatic-related mortality due to hepatorenal syndrome (RR 0.40; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.71), but trial sequential analysis did not support this result. Data from one trial suggests that pentoxifylline may increase the occurrence of serious and non-serious adverse events compared to control.
Authors' conclusions: The current available data may indicate a possible positive intervention effect of pentoxifylline on all-cause mortality and mortality due to hepatorenal syndrome, and conversely, an increase in serious and non-serious adverse events. However, the evidence is not firm; no conclusions can be drawn regarding whether pentoxifylline has a positive, negative, or neutral effect on participants with alcoholic hepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures









Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Akriviadis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Akriviadis E, Botla R, Briggs W, Han S, Reynolds T, Shakil O. Improved short‐term survival with pentoxifylline treatment in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1997;26(4 (Pt 2)):250A. - PubMed
-
- Akriviadis E, Botla R, Briggs W, Han S, Reynolds T, Shakil O. Pentoxifylline improves short‐term survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000;119(6):1637‐48. - PubMed
-
- Karnam US, Reddy KR. A toast to pentoxifylline. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 2001;96(5):1635‐7. - PubMed
Lebrec 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lebrec D, Thabut D, Oberti F, Perarnau J‐M, Condat B, Barraud H, et al. Pentoxifylline for the treatment of patients with advanced cirrhosis. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind trial. Hepatology 2007;46(4 Suppl 1):249A.
McHutchison 1991 {published data only}
-
- McHutchison JG, Runyon BA, Draguesku JO, Comineelli F, Person JL, Castracane J. Pentoxifylline may prevent renal impairment (hepatorenal syndrome) in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1991;14(4 (Pt 2)):96A.
Paladugu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Paladugu H, Sawant P, Dalvi L, Kudalkar J. Role of pentoxifylline in treatment of severe acute alcoholic hepatitis ‐ a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2006;21:A459.
Sidhu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sidhu S, Singla M, Bhatia KL. Pentoxifylline reduces disease severity and prevents renal impairment in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double blind, placebo controlled trial. Hepatology 2006;44(4 (Suppl 1)):373A‐374A.
References to studies excluded from this review
Austin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Austin AS, Mahida YR, Clarke D, Ryder SD, Freeman JG. A pilot study to investigate the use of oxpentifylline (pentoxifylline) and thalidomide in portal hypertension secondary to alcoholic cirrhosis. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;19(1):79‐88. - PubMed
Cholongitas 2001 {published data only}
-
- Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV. Pentoxifylline improves short‐term survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Annals of Gastroenterology 2001;14(4):333‐5. - PubMed
Fernández‐Rodríguez 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fernández‐Rodríguez CM, Lledó JL, López‐Serrano P, Gutiérrez ML, Alonso S, Pérez‐Fernández MT, et al. Effect of pentoxifylline on survival, cardiac function and both portal and systemic hemodynamics in advanced alcoholic cirrhosis: a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas 2008;100(8):481‐9. - PubMed
Lee 2006 {published data only}
Louvet 2008 {published data only}
-
- Louvet A, Diaz E, Dharancy S, Coevoet H, Texier F, Thévenot T, et al. Early switch to pentoxifylline in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis is inefficient in non‐responders to corticosteroids. Journal of Hepatology 2008;48:465‐70. - PubMed
-
- Louvet A, Diaz E, Texier F, Coevoet H, Dharancy S, Plane C, et al. Evaluation of pentoxifylline in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis non‐responders to corticosteriods: a pilot controlled study. Hepatology 2005;42(4 (Suppl 1)):754A. - PubMed
Verma 2006 {published data only}
-
- Verma S, Ajudia K, Mendler M, Redeker A. Prevalence of septic events, type 1 hepatorenal syndrome, and mortality in severe alcoholic hepatitis and utility of discriminant function and MELD score in predicting these adverse events. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2006;51(9):1637‐43. - PubMed
Watson 2008 {published data only}
-
- Watson E, Lafferty H, Forrest EH. When corticosteroids fail: rescue treatment with pentoxifylline for alcoholic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 2008;48(S2):S366.
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT00205049 {published data only}
-
- Pentoxifylline for acute alcoholic hepatitis. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00205049 (accessed 14 August 2009).
References to ongoing studies
NCT00388323 {published data only}
-
- Adipose tissue involvement in alcohol‐induced liver inflammation in human: study of pro‐ and anti‐inflammatory cytokines and adipokines. http://ClincalTrials.gov/show/NCT00388323.
Additional references
Akriviadis 2000
-
- Akriviadis E, Botla R, Briggs W, Han S, Reynolds T, Shakil O. Pentoxifylline improves short‐term survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000;199:1637‐48. - PubMed
Altman 2003
Begg 1994
-
- Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994;50:1088‐101. - PubMed
Brok 2008
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Gluud C, Wetterslev J. Trial sequential analysis reveals insufficient information size and potentially false positive results in many meta‐analyses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(8):763‐9. - PubMed
Brok 2008a
-
- Brok, J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses maybe inconclusive ‐ Trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data inapparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. - PubMed
Ceccanti 2006
-
- Ceccanti M, Attili A, Balducci G, Attilia F, Giacomelli S, Rotondo C, et al. Acute alcoholic hepatitis. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2006;40:833‐41. - PubMed
Christensen 1995
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Fisher 1922
-
- Fisher RA. On the interpretation of χ2 from contingency tables, and the calculation of P. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 1922;85(1):87‐94.
Gluud 2001
-
- Gluud C. Alcoholic hepatitis: no glucocorticosteroids?. FALK Symposium 121. Steatohepatitis (NASH and ASH). 2001; Vol. 121:400.
Gluud 2009
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL, Whitfield K, Alexakis N, Als‐Nielsen B, et al. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2009, Issue 3. Art. No.: LIVER.
Hardison 1966
-
- Hardison WG, Lee FI. Prognosis in acute liver disease of alcoholic patients. New England Journal of Medicine 1966;275:61‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.0 [updated February 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
ICH‐GCP 1996
-
- International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. Guideline for Good Clinical Practice. E6 (R1). ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline 1996.
Imperiale 1990
-
- Imperiale F, McCullough AJ. Do corticosteroids reduce mortality from alcoholic hepatitis?. Annals of Internal Medicine 1990;113:299‐307. - PubMed
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaerdard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135:982‐9. - PubMed
Lebrec 2007
-
- Lebrec D, Thabut D, Oberti F, Perarnau JM, Condat B, Barraud H, et al. Pentoxifylline for the treatment of patients with advanced cirrhosis. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind trial. Hepatology 2007;46(4 (Suppl 1)):249A‐250A.
Levistsky 2004
-
- Levistsky J, Mailliard ME. Diagnosis and therapy of alcoholic liver disease. Seminars in Liver Disease 2004;24(3):233‐46. - PubMed
Lucey 2009
-
- Lucey MR, Mathurin P, Morgan TRM. Alcholic hepatitis. The New England Journal of Meidicine 2009;360:2758‐69. - PubMed
Maddrey 1978
-
- Maddrey WC, Boitnott JK, Bedine MS, Weber FL Jr, Mezey E, White RI Jr. Corticosteroid therapy of alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1978;75:193‐9. - PubMed
Madhotra 2003
-
- Madhotra R, Gilmore IT. Recent developments in the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis. Oxford Journal of Medicine 2003;96:391‐400. - PubMed
McClain 1989
-
- McClain CJ, Cohen DA. Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1989;9:349‐51. - PubMed
McCullough 1998
-
- McCullough AJ, O'Connor JF. Alcoholic liver disease: proposed recommendations for the American College of Gastroenterology. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 1998;93(11):2022‐36. - PubMed
McHutchison 1991
-
- McHutchison JG, Runyon BA, Draguesku JO, Cominelli F, Person JL, Castracance J. Pentoxifylline may prevent renal impairment (hepatorenal syndrome) in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1991;14(4 Pt 2):96A.
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. The Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. - PubMed
Patient 2008
-
- Patient.uk. Pentoxifylline. http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/30003859/ (Accessed 30 January 2009).
Poynard 1991
-
- Poynard T, Ramond MJ, Reuff B, Mathurin P, Theodore C, et al. Corticosteroid therapy reduces mortality from alcoholic hepatitis in patients without encephalopathy. A meta‐analysis of randomized trials (RCTs) including French trials. Hepatology 1991;14:234A.
Rambaldi 2009
RevMan 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.0. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Rongey 2006
Royle 2003
-
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591‐603. - PubMed
Rücker 2008
-
- Rücker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter J. Arcsine test for publication bias in meta‐analyses with binary outcomes. Statistics in Medicine 2008;27(5):746‐63. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schultz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Sidhu 2006
-
- Sidhu S, Singla M, Bhatia KL. Pentoxifylline reduces disease severity and prevents renal impairment in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double blind, placebo controlled trial. Hepatology 2006;44 Suppl 4(1):373A.
Strieter 1988
-
- Strieter R, Remick D, Ward P, Spengler RN, Lynch JP 3rd, Larrick J. Cellular and molecular regulation of tumor necrosis factor‐alpha production by pentoxifylline. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 1988;155:1230‐6. - PubMed
Student 1908
-
- Student. The probable error of a mean. Biometrika 1908;6(1):1–25.
Thorlund 2008
-
- Thorlund K, Devereaux PJ, Wetterslev J, Gyuatt G, Ioannidis JPA, Thabane L, et al. Can trial sequential monitoring boundaries reduce spurious inferences from meta‐analyses?. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38:276–86. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

