Single dose oral lornoxicam for acute postoperative pain in adults
- PMID: 19821419
- PMCID: PMC6485324
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007441.pub2
Single dose oral lornoxicam for acute postoperative pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Lornoxicam is one of the oxicam class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), producing analgesic and antipyretic effects in part through the non-selective inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase-1 and -2. It is prescribed for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute lumbar-sciatica conditions and for postoperative pain management. Lornoxicam is available in 31 countries in Europe, the Middle East, Far East and South America, and is becoming more widely available.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy, the time to onset of analgesia, the time to use of rescue medication and any associated adverse events of single dose oral lornoxicam in acute postoperative pain.
Search strategy: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE and PubMed to June 2009.
Selection criteria: Single oral dose, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of lornoxicam for relief of established moderate to severe postoperative pain in adults.
Data collection and analysis: Studies were assessed for methodological quality and the data extracted by two review authors independently. Summed total pain relief over 6 hours (TOTPAR 6) was used to calculate the number of participants achieving at least 50% pain relief. These derived results were used to calculate, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), the relative benefit compared to placebo, and the number needed to treat (NNT) for one participant to experience at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours. Numbers of participants using rescue medication over specified time periods, and time to use of rescue medication, were sought as additional measures of efficacy. Information on adverse events and withdrawals was collected.
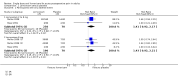
Main results: Three studies, with 628 participants, met the inclusion criteria; 434 participants were treated with various doses (2 mg to 32 mg) of lornoxicam, 118 with placebo, and 76 with other active therapies. All the participants had pain following third molar extraction, and study duration was 8 to 24 hours. The NNT for at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours after a single dose of lornoxicam 8 mg was 2.9 (2.3 to 4.0). There were insufficient data to analyse other doses or use of rescue medication. No serious adverse events or withdrawals were reported by any of the studies.
Authors' conclusions: Oral lornoxicam is effective at treating moderate to severe acute postoperative pain, based on limited data. Adverse events did not differ significantly from placebo.
Conflict of interest statement
PH, SD, RAM & HJM have received research support from charities, government and industry sources at various times, but no such support was received for this work. RAM and HJM have consulted for various pharmaceutical companies. RAM, and HJM have received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies related to analgesics and other healthcare interventions.
Figures


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Moller 2008 {published data only}
-
- Moller PL, Norholt SE. Analgesic efficacy of quick‐release versus standard lornoxicam for pain after third molar surgery: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, single‐dose trial. Clinical drug investigation 2008;28(12):757‐66. [PUBMED: 18991469] - PubMed
Norholt 1995 {published data only}
-
- Norholt SE, Sindet‐Pedersen S, Bugge C, Branebjerg PE, Ersboll BK, Bastian HL. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐response study of the analgesic effect of lornoxicam after surgical removal of mandibular third molars. Journal of clinical pharmacology 1995;35(6):606‐14. [PUBMED: 7665721] - PubMed
Patel 1991 {published data only}
-
- Patel A, Skelly AM, Kohn H, Preiskel HW. Double‐blind placebo‐controlled comparison of the analgesic effects of single doses of lornoxicam and aspirin in patients with postoperative dental pain. British Dental Journal 1991;170(8):295‐9. [PUBMED: 2036277] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cooper 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cooper SA, Fielding AF, Lucyk D, Hersh EV, Quinn PD, Betts N, et al. Lornoxicam: Analgesic efficacy and safety of a new oxicam derivative. Advances in Therapy 1996;13(1):67‐77.
Additional references
Barden 2004
-
- Barden J, Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Wiffen PJ. Relative efficacy of oral analgesics after third molar extraction. British Dental Journal 2004;197(7):407‐11. - PubMed
Barden 2006
Berg 1999
-
- Berg J, Fellier H, Christoph T, Grarup J, Stimmeder D. The analgesic NSAID lornoxicam inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX)‐1/‐2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the formation of interleukin (IL)‐6 in vitro. Inflammation Research 1999;48:369‐79. - PubMed
Berry 1992
Clarke 2009
Collins 1997
-
- Collins SL, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. The visual analogue pain intensity scale: what is moderate pain in millimetres?. Pain 1997;72:95‐7. - PubMed
Collins 2001
-
- Collins SL, Edwards J, Moore RA, Smith LA, McQuay HJ. Seeking a simple measure of analgesia for mega‐trials: is a single global assessment good enough?. Pain 2001;91(1‐2):189‐94. - PubMed
Cook 1995
Cooper 1991
-
- Cooper SA. Single‐dose analgesic studies: the upside and downside of assay sensitivity. The Design of Analgesic Clinical Trials. Advances in Pain Research Therapy 1991;18:117‐24.
Derry 2008
Derry C 2009a
Derry C 2009b
Derry P 2009
Dittrich 1990
-
- Dittrich P, Radhofer‐Welte S, Magometschnigg D, Kukovetz WR, Mayerhofer S, Ferber HP. The effect of concomitantly administered antacids on the bioavailability of lornoxicam, a novel highly potent NSAID. Drugs Under Experimental and Clinical Research 1990;16:57‐62. - PubMed
Erdogan 2008
-
- Erdogan I, Cakan T, Ozcan A, Turkyilmaz E, Baltaci B, Dikmen B. Effect of lornoxicam on postoperative analgesia after myomectomy. Agri: Agri (Algoloji) Dernegi'nin Yayin organidir = The Journal of the Turkish Society of Algology 2008;20(1):26‐31. [PUBMED: 18338276] - PubMed
Fitzgerald 2001
-
- FitzGerald GA, Patrono C. The coxibs, selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase‐2. England Journal of Medicine 2001;345(6):433‐42. - PubMed
Gaskell 2009
Hawkey 1999
-
- Hawkey CJ. Cox‐2 inhibitors. Lancet 1999;353(9149):307‐14. - PubMed
Hitzenberger 1990
-
- Hitzenberger G, Radhofer‐Welte S, Takacs F, Rosenow D. Pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam in man. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1990;66(Suppl. 4):S22‐7. - PubMed
Jadad 1996a
-
- Jadad AR, Carroll D, Moore RA, McQuay H. Developing a database of published reports of randomised clinical trials in pain research. Pain 1996;66(2‐3):239‐46. - PubMed
Jadad 1996b
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
L'Abbé 1987
-
- L'Abbe KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107:224‐33. - PubMed
Lloyd 2009
McQuay 2005
Moore 1996
Moore 1997a
Moore 1997b
Moore 1998
Moore 2003
-
- Moore RA, Edwards J, Barden J, McQuay HJ. Bandolier's Little Book of Pain. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2003. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263247‐7]
Moore 2005
Moore 2006
-
- Moore A, McQuay H. Bandolier's Little Book of Making Sense of the Medical Evidence. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006. [ISBN: 0‐19‐856604‐2]
Morris 1995
Papadima 2007
-
- Papadima A, Lagoudianakis EE, Antonakis PT, Pattas M, Kremastinou F, Katergiannakis V, et al. Parecoxib vs. lornoxicam in the treatment of postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective randomized placebo‐controlled trial. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2007;24(2):154‐8. [PUBMED: 16938157] - PubMed
Sener 2008
-
- Sener M, Yilmazer C, Yilmaz I, Bozdogan N, Ozer C, Donmez A, et al. Efficacy of lornoxicam for acute postoperative pain relief after septoplasty: a comparison with diclofenac, ketoprofen, and dipyrone. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2008;20(2):103‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2007.09.009] - DOI - PubMed
Toms 2008
Tramèr 1997
Warrington 1990a
-
- Warrington SJ, Debbas NM, Farthing M, Horton M, Johnston A, Thillainayagam A, et al. Lornoxicam, indomethacin and placebo: comparison of effects on faecal blood loss and upper gastrointestinal endoscopic appearances in healthy men. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1990;66(778):622‐6. [PUBMED: 2217030] - PMC - PubMed
Warrington 1990b
-
- Warrington SJ, Lewis Y, Dawnay A, Johnston A, Kovacs IB, Lamb E, et al. Renal and gastrointestinal tolerability of lornoxicam, and effects on haemostasis and hepatic microsomal oxidation. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1990;66 Suppl 4:S35‐40. [PUBMED: 2284219] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

