Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of Cochrane reviews
- PMID: 19821440
- PMCID: PMC10636593
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007848.pub2
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of Cochrane reviews
Abstract
Background: The biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are very effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA), however there is a lack of head-to-head comparison studies.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and safety of abatacept, adalimumab, anakinra, etanercept, infliximab, and rituximab in patients with RA.
Methods: This 'Overview of Reviews' was done by including all Cochrane Reviews on Biologics for RA available in The Cochrane Library. We included only data on standard dosing regimens for these biologic DMARDs from placebo-controlled trials. The primary efficacy and safety outcomes were ACR50 and withdrawals due to adverse events. We calculated Risk Ratios (RR) for efficacy, Odds Ratio (OR) for safety and combined estimates of events across the placebo groups as the expected Control Event Rate (CER). Indirect comparisons of biologics were performed for efficacy and safety using a hierarchical linear mixed model incorporating the most important study-level characteristic (i.e. type of biologic) as a fixed factor and study as a random factor; reducing the between study heterogeneity by adjusting for the interaction between the proportion of patients responding on placebo and the duration of the trial.
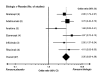
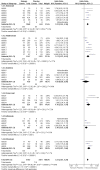
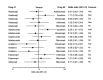
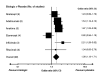
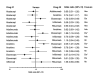
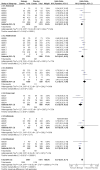
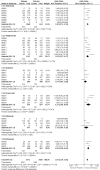
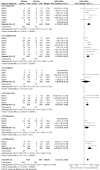
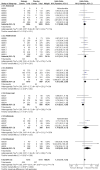
Main results: From the six available Cochrane reviews, we obtained data from seven studies on abatacept, eight on adalimumab, five on anakinra, four on etanercept, four on infliximab, and three on rituximab.The indirect comparison estimates showed similar efficacy for the primary efficacy outcome for all biologics with three exceptions. Anakinra was less efficacious than etanercept with a ratio of RRs (95% CI; P value) of 0.44 (0.23 to 0.85; P = 0.014); anakinra was less efficacious than rituximab, 0.45 (0.22 to 0.90; P = 0.023); and likewise adalimumab was more efficacious than anakinra, 2.34 (1.32 to 4.13; P = 0.003).In terms of safety, adalimumab was more likely to lead to withdrawals compared to etanercept, with a ratio of ORs of 1.89 (1.18 to 3.04; P = 0.009); anakinra more likely than etanercept, 2.05 (1.27 to 3.29; P = 0.003); and likewise etanercept less likely than infliximab, 0.37 (0.19 to 0.70; P = 0.002).
Authors' conclusions: Based upon indirect comparisons, anakinra seemed less efficacious than etanercept, adalimumab and rituximab and etanercept seemed to cause fewer withdrawals due to adverse events than adalimumab, anakinra and infliximab. Significant heterogeneity in characteristics of trial populations imply that these finding must be interpreted with caution. These findings can inform physicians and patients regarding their choice of biologic for treatment of RA.
Conflict of interest statement
JS ‐ speaker honoraria from Abbott; research grants from AMGEN, Allergan, Takeda, Savient; consultant fee from Savient, URL pharma
RC ‐ research grant and consultant fee from Bristol‐Myers Squibb and Abbott
GW ‐ research grant and consultant fee from Bristol‐Myers Squibb
MS ‐ speaker honoraria from Bristol‐Myers Squibb and Roche and consultant fee from Amgen
RB ‐ none
ML ‐ none
ETG ‐ none
PT ‐ grants/honoraria from Bristol Myers, Chiltern International, and UCB
Figures
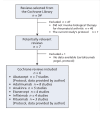
Update of
References
References to included reviews
Blumenauer 2003
Lethaby 2003
Lopez‐Olivo 2008
Maxwell 2008
Mertens 2008
Additional references
Alonso‐Ruiz 2008
Arnett 1988
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31(3):315‐24. - PubMed
Atkins 2004
Barlow 1999
-
- Barlow JH, Cullen LA, Rowe IF. Comparison of knowledge and psychological well‐being between patients with a short disease duration (< or = 1 year) and patients with more established rheumatoid arthritis (> or = 10 years duration). Patient Education and Counseling 1999;38:195‐203. - PubMed
Becker 2008
-
- Becker LA, Oxman AD. Chapter 22: Overviews of Reviews. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 (updated September 2008). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochranehandbook.org.
Boers 2001
-
- Boers M. Treatment of early disease. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 2001;27:405‐14, x. - PubMed
Bongartz 2006
-
- Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, Buchan I, Matteson EL, Montori V. Anti‐TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta‐analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2006;295(19):2275‐85. - PubMed
Bongartz 2009
-
- Bongartz T, Warren FC, Mines D, Matteson EL, Abrams KR, Sutton AJ. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of malignancies: a systematic review and individual patient data meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2009;68(7):1177‐83. - PubMed
Bradburn 2007
-
- Bradburn MJ, Deeks JJ, Berlin JA, Russell Localio A. Much ado about nothing: A comparison of the performance of meta‐analytical methods with rare events. Statistics in Medicine 2007;26:53‐77. - PubMed
Brennan 2008
Cash 1994
-
- Cash JM, Klippel JH. Second‐line drug therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330(19):1368‐75. - PubMed
Cates 2009 [Computer program]
-
- Dr Chris Cates' EBM web site. Available from http://www.Nntonline.Net/visualrx/. Visual Rx NNT Calculator version 3. Dr Chris Cates' EBM web site. Available from http://www.Nntonline.Net/visualrx/, Accessed 13 February 2009.
Choy 2001
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(12):907‐16. - PubMed
Chung 2006
-
- Chung CP, Thompson JL, Koch GG, Amara I, Strand V, Pincus T. Are American College of Rheumatology 50% response criteria superior to 20% criteria in distinguishing active aggressive treatment in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials reported since 1997? A meta‐analysis of discriminant capacities. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2006;65(12):1602‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Connell 2006
-
- Connell L, McInnes IB. New cytokine targets in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Best Practice and Research Clinical Rheumatology 2006;20(5):865‐78. - PubMed
Cope 2008
Dersimonian 2007
-
- DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random‐effects model for meta‐analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2007;28(2):105‐14. - PubMed
Donahue 2008
-
- Donahue KE, Gartlehner G, Jonas DE, Lux LJ, Thieda P, Jonas BL, et al. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and harms of disease‐modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008;148(2):124‐34. - PubMed
Drugs 2006
-
- Drug Information Online. Drugs.com. FDA Approves First Rheumatoid Arthritis Indication for Rituxan. http://www.drugs.com/news/fda‐approves‐first‐rheumatoid‐arthritis‐indica... 03/01/2006.
EMEA 2001
-
- EMEA. EMEA Public Statement on Infliximab (Remicade): Increased incidence of mortality and hospitalization for worsening Congestive Heart Failure. http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/press/pus/325701en.pdf.
EMEA 2003
-
- EMEA. EMEA public statement: Increased risk of serious infection and neutropenia in patients treated concurrently with Kineret (anakinra) and Enbrel (etanercept). http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/kineret/3163102en.pdf.
EMEA 2004
-
- European Medicines Agency. EPARs for authorized medicinal products for human use: Anakinra: European Public Assessment Report. http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/kineret/kineret.htm Revision 11, published 27/01/09.
EMEA 2009a
-
- EMEA. Remicade (inflixmab). http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/Remicade/H‐240‐PI‐en.pdf.
EMEA 2009b
-
- European Medicines Agency. EPARs for authorized medicinal products for human use: Humira: European Public Assessment Report. http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/humira/humira.htm Revision 15, Published 11/05/09.
FDA 1998
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Etanercept Product Approval Information‐ Licensing Action 12/2/1998. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped... 1998.
FDA 1999
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Remicade® (infliximab) for IV Injection. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsar... 1999.
FDA 2001
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Kineret® (anakinra) Physician packet insert: Kineret® (anakinra) prescribing information. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped... 2001.
FDA 2002
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Package Insert. HUMIRA® (adalimumab). Abbott Laboratories. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped... 2002.
FDA 2005
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Patient Information Sheet. Abatacept (marketed as Orencia®). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped... 2005.
FDA 2006b
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Rituxan® (rituximab). http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHuma....
FDA 2007
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Drug details: Orencia. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseacti....
FDA 2008
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Humira (adalimumab): Highlights of prescribing information. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/125057s114lbl.pdf.
FDA 2008a
-
- Food, Drug Administration. FDA: Manufacturers of TNF‐blocker drugs must highlight risk of fungal infections. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/2008/ucm116942....
FDA 2008b
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Medication Guide: Enbrel® (etanercept). http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/103795s5359lbl.pdf.
FDA 2009
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Remicade® (infliximab) for IV Injection. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/103772s5234lbl.pdf.
Felson 1995
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, et al. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38(6):727‐35. - PubMed
Finckh 2006
-
- Finckh A, Liang MH, Herckenrode CM, Pablo P. Long‐term impact of early treatment on radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta‐analysis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;55(6):86‐72. - PubMed
Fleischman 2003
-
- Fleischmann RM, Schechtman J, Bennett R, Handel ML, Burmester GR, Tesser J, et al. Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (r‐metHuIL‐1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A large, international, multicenter, placebo‐controlled trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;48(4):927‐34. - PubMed
Fransen 2005
-
- Fransen J, Riel PL. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2005;23(5 Suppl 39):S93‐9. - PubMed
Fries 1980
-
- Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1980;23(2):137‐45. - PubMed
Furst 2008
-
- Furst DE, Keystone EC, Kirkham B, et al. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2008. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;67 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):iii2‐25. - PubMed
Gartlehner 2006
-
- Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Jonas BL, Thieda P, Lohr KN. The comparative efficacy and safety of biologics for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. The Journal of Rheumatology 2006;33(12):2398‐408. - PubMed
Genovese 2005
-
- Genovese MC, Becker JC, Schiff M, Luggen M, Sherrer Y, Kremer J, et al. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(11):1114‐23. - PubMed
Health Canada 2006
-
- Health Canada. Important Safety Information on anti‐TNFα Therapy: Enbrel (etanercept), Humira (adalimumab), and Remicade (infliximab) ‐ For Health Professionals. http://www.hc‐sc.gc.ca/dhp‐mps/medeff/advisories‐avis/prof/_2006/anti‐tnf_therap_hpc‐c....
Health Canada 2006b
-
- Health Canada. Possible association of Remicade (infliximab) with hepatosplenic T‐cell lymphoma in pediatric and young adult patients with Crohn's disease ‐ For Health Professionals. http://www.hc‐sc.gc.ca/dhp‐mps/medeff/advisories‐avis/prof/_2006/remicade_3_hpc‐cps‐en....
Health Canada 2009
-
- Health Canada. Association of Enbrel (etanercept) with histoplasmosis and other invasive fungal infections ‐ for health professionals. http://www.hc‐sc.gc.ca/dhp‐mps/medeff/advisories‐avis/prof/_2009/enbrel_hpc‐cps‐eng.php.
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Keystone 2004
-
- Keystone EC, Kavanaugh AF, Sharp JT, Tannenbaum H, Hua Y, Teoh LS, et al. Radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti‐tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy: a randomized, placebo‐controlled, 52‐week trial. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50(5):1400‐11. - PubMed
Klareskog 2004
-
- Klareskog L, Heijde D, Jager JP, Gough A, Kalden J, Malaise M, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double‐blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;363(9410):675‐81. - PubMed
Kristensen 2007
-
- Kristensen LE, Christensen R, Bliddal H, Geborek P, Danneskiold‐Samsoe B, Saxne T. The number needed to treat for adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab based on ACR50 response in three randomized controlled trials on established rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2007;36:411‐7. - PubMed
Kvien 2004
-
- Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):1‐12. - PubMed
Kvien 2005
-
- Kvien TK, Uhlig T. Quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2005;34(5):333‐41. - PubMed
Larsen 1977
-
- Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiologica: Diagnosis (Stockholm) 1977;4:481‐91. - PubMed
Lee 2001
-
- Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2001;358(9285):903‐11. - PubMed
Lee 2008
-
- Lee YH, Woo JH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Meta‐analysis of the combination of TNF inhibitors plus MTX compared to MTX monotherapy, and the adjusted indirect comparison of TNF inhibitors in patients suffering from active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology International 2008;28(6):553‐9. - PubMed
Lipsky 2000
-
- Lipsky PE, Heijde DM, Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti‐Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000;343(22):1594‐602. - PubMed
Lubeck 2004
-
- Lubeck DP. Patient‐reported outcomes and their role in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):27‐38. - PubMed
Nixon 2007
-
- Nixon RM, Bansback N, Brennan A. Using mixed treatment comparisons and meta‐regression to perform indirect comparisons to estimate the efficacy of biologic treatments in rheumatoid arthritis. Statistics in Medicine 2007;26(6):1237‐54. - PubMed
Odegard 2005
-
- Odegard S, Finset A, Kvien TK, Mowinckel P, Uhlig T. Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis is predicted by physical and psychological health status: a 7‐year study from the Oslo RA register. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2005;34(6):441‐7. - PubMed
Osiri 2003
Pincus 1983
-
- Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA, Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1983;26(11):1346‐53. - PubMed
Pincus 2002
-
- Pincus T, Ferraccioli G, Sokka T, Larsen A, Rau R, Kushner I, et al. Evidence from clinical trials and long‐term observational studies that disease‐modifying anti‐rheumatic drugs slow radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: updating a 1983 review. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41(12):1346‐56. - PubMed
Platt 1999
-
- Platt RW, Leroux BG, Breslow N. Generalized linear mixed models for meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 1999;18(6):643‐54. - PubMed
Prevoo 1995
-
- Prevoo ML, 't Hof MA, Kuper HH, Leeuwen MA, Putte LB, Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty‐eight‐joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38(1):44‐8. - PubMed
Prevoo 1996
-
- Prevoo ML, Gestel AM, van THMA, Rijswijk MH, Putte LB, Riel PL. Remission in a prospective study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. American Rheumatism Association preliminary remission criteria in relation to the disease activity score. British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35(11):1101‐5. - PubMed
Salanti 2008
-
- Salanti G, Higgins JP, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP. Evaluation of networks of randomized trials. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 2008;17(3):279‐301. - PubMed
Schiff 2008
-
- Schiff M, Keiserman M, Codding C, Songcharoen S, Berman A, Nayiager S, et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept or infliximab vs placebo in ATTEST: a phase III, multi‐centre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;8:1096‐103. - PMC - PubMed
Scott 2006
-
- Scott DL, Kingsley GH. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(7):704‐12. - PubMed
Sharp 1971
-
- Sharp JT, Lidsky MD, Collins LC, Moreland J. Methods of scoring the progression of radiologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of radiologic, clinical and laboratory abnormalities. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1971;14(6):706‐20. - PubMed
Shea 2007
Song 2003
Strand 2008
-
- Strand V, Singh JA. Improved health‐related quality of life with effective disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs: evidence from randomized controlled trials. American Journal of Managed Care 2008;14(4)(4):234‐54. - PubMed
Sweeting 2004
-
- Sweeting MJ, Sutton AJ, Lambert PC. What to add to nothing? Use and avoidance of continuity corrections in meta‐analysis of sparse data. Statistics in Medicine 2004;23:1351‐75. - PubMed
Szekanecz 2007
-
- Szekanecz Z, Koch AE. Macrophages and their products in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2007;19(3):289‐95. - PubMed
Thompson 1999
-
- Thompson SG, Sharp SJ. Explaining heterogeneity in meta‐analysis: a comparison of methods. Statistics in Medicine 1999;18(20):2693‐708. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1989
-
- Heijde DM, Riel PL, Nuver‐Zwart IH, Gribnau FW, vad de Putte LB. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulphasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989;1(8646):1036‐8. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1993
-
- Heijde DM, 't Hof M, Riel PL, Putte LB. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20(3):579‐81. - PubMed
van Gestel 1996
-
- Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, 't Hof MA, Rijswijk MH, Putte LB, Riel PL. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1996;39:34‐40. - PubMed
Wells 1993
-
- Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, Baker PR, Groh J, Redelmeier DA. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. The Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20(3):557‐60. - PubMed
Wells 2009
-
- Wells GA, Sultan SA, Chen L, Khan M, Coyle D. Indirect evidence: indirect treatment comparisons in meta‐analysis. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Ottawa 2009.
Woolley 2003
-
- Woolley DE. The mast cell in inflammatory arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(17):1709‐11. - PubMed
Yelin 2007
-
- Yelin E. Work disability in rheumatic diseases. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2007;19(2):91‐6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

