Sorafenib inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling in cholangiocarcinoma cells by activating the phosphatase shatterproof 2
- PMID: 19821497
- PMCID: PMC2891152
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23214
Sorafenib inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling in cholangiocarcinoma cells by activating the phosphatase shatterproof 2
Abstract
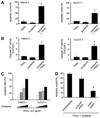
The Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway is one of the key signaling cascades in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cells, mediating their resistance to apoptosis. Our aim was to ascertain if sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, may also inhibit JAK/STAT signaling and, therefore, be efficacious for CCA. Sorafenib treatment of three human CCA cell lines resulted in Tyr(705) phospho-STAT3 dephosphorylation. Similar results were obtained with the Raf-kinase inhibitor ZM336372, suggesting sorafenib promotes Tyr(705) phospho-STAT3 dephosphorylation by inhibiting Raf-kinase activity. Sorafenib treatment enhanced an activating phosphorylation of the phosphatase SHP2. Consistent with this observation, small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of phosphatase shatterproof 2 (SHP2) inhibited sorafenib-induced Tyr(705) phospho-STAT3 dephosphorylation. Sorafenib treatment also decreased the expression of Mcl-1 messenger RNA and protein, a STAT3 transcriptional target, as well as sensitizing CCA cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis. In an orthotopic, syngeneic CCA model in rats, sorafenib displayed significant tumor suppression resulting in a survival benefit for treated animals. In this in vivo model, sorafenib also decreased tumor Tyr(705) STAT3 phosphorylation and increased tumor cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: Sorafenib accelerates STAT3 dephosphorylation by stimulating phosphatase SHP2 activity, sensitizes CCA cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, and is therapeutic in a syngeneic rat, orthotopic CCA model that mimics human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures






References
-
- Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA, Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T, et al. gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:91–102. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer–new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, et al. Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention and therapy of cancer: modern target but ancient solution. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1091:151–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
