Sequential phase II Southwest Oncology Group studies (S0112 and S0301) of daunorubicin and cytarabine by continuous infusion, without and with ciclosporin, in older patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukaemia
- PMID: 19821823
- PMCID: PMC2967366
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07919.x
Sequential phase II Southwest Oncology Group studies (S0112 and S0301) of daunorubicin and cytarabine by continuous infusion, without and with ciclosporin, in older patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukaemia
Abstract
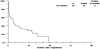
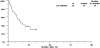
Attempts to overcome multi-drug resistance in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) have been limited by toxicities. To investigate the effect of reducing peak drug levels, we performed sequential phase II studies using continuous infusion daunorubicin and cytarabine without (AD) and then with ciclosporin (ADC) in older patients with AML. Untreated patients (age 56+ years) received daunorubicin (45 mg/m2 per day for 3 d) and cytarabine (200 mg/m2 per day for 7 d), both by continuous infusion, without (S0112, 60 patients) and then with (S0301, 50 patients) the addition of ciclosporin. Complete response (CR) rates were 38% on S0112 and 44% on S0301. Fatal induction toxicities occurred in 17% and 12% respectively, arising primarily from infection and haemorrhage. Median overall and relapse-free survival was 7 and 8 months for AD respectively, and 6 and 14 months for ADC. Patients with phenotypic or functional P-glycoprotein had somewhat higher CR rates with ADC than AD, although confidence intervals overlapped. In these sequential trials, continuous infusion AD produced CR rates comparable to those with bolus daunorubicin. The addition of ciclosporin did not cause undue toxicities, produced a similar CR rate, and possibly improved relapse-free survival. Further correlate analyses did not identify a subpopulation specifically benefitting from the addition of ciclosporin.
Figures
References
-
- Advani R, Visani G, Milligan D, Saba H, Tallman M, Rowe JM, Wiernik PH, Ramek J, Dugan K, Lum B, Villena J, Davis E, Paietta E, Litchman M, Covelli A, Sikic B, Greenberg P. Treatment of poor prognosis AML patients using PSC833 (valspodar) plus mitoxantrone, etoposide, and cytarabine (PSC-MEC) Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;457:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JE, Kopecky KJ, Willman CL, Head D, O’Donnell MR, Luthardt FW, Norwood TH, Chen IM, Balcerzak SP, Johnson DB, Appelbaum FR. Outcome after induction chemotherapy for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia is not improved with mitoxantrone and etoposide compared to cytarabine and daunorubicin: a Southwest Oncology Group study. Blood. 2002;100:3869–76. - PubMed
-
- Baer MR, George SL, Dodge RK, O’Loughlin KL, Minderman H, Caligiuri MA, Anastasi J, Powell BL, Kolitz JE, Schiffer CA, Bloomfield CD, Larson RA. Phase 3 study of the multidrug resistance modulator PSC-833 in previously untreated patients 60 years of age and older with acute myeloid leukemia: Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study 9720. Blood. 2002;100:1224–32. - PubMed
-
- Becton D, Dahl GV, Ravindranath Y, Chang MN, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Head DR, Stine KC, Lacayo NJ, Sikic BI, Arceci RJ, Weinstein H, Pediatric Oncology Group Randomized use of cyclosporin A (CsA) to modulate P-glycoprotein in children with AML in remission: Pediatric Oncology Group Study 9421. Blood. 2006;107:1315–24. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA74647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States