Combination of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits endothelial cell growth directly and by regulation of angiogenic factors released by tumor cells
- PMID: 19821965
- PMCID: PMC2767355
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-361
Combination of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits endothelial cell growth directly and by regulation of angiogenic factors released by tumor cells
Abstract
Background: The combination therapy of interferon (IFN)-alpha and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) improved the prognosis of the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To determine the molecular mechanisms of the anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects, we examined the direct anti-proliferative effects on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and indirect effects by regulating secretion of angiogenic factors from HCC cells.
Methods: The direct effects on HUVEC were examined by TUNEL, Annexin-V assays and cell cycles analysis. For analysis of the indirect effects, the apoptosis induced by the conditioned medium from HCC cell treated by IFN-alpha/5-FU and expression of angiogenic factors was examined.
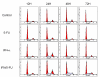
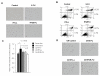
Results: IFN-alpha and 5-FU alone had anti-proliferative properties on HUVEC and their combination significantly inhibited the growth (compared with control, 5-FU or IFN alone). TUNEL and Annexin-V assays showed no apoptosis. Cell cycle analysis revealed that IFN-alpha and 5-FU delayed cell cycle progression in HUVEC with S-phase accumulation. The conditioned medium from HuH-7 cells after treatment with IFN/5-FU significantly inhibited HUVEC growth and induced apoptosis, and contained high levels of angiopoietin (Ang)-1 and low levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Ang-2. Knockdown of Ang-1 in HuH-7 cells abrogated the anti-proliferative effects on HUVEC while knockdown of Ang-2 partially rescue the cells.
Conclusion: These results suggested that IFN-alpha and 5-FU had direct growth inhibitory effects on endothelial cells, as well as anti-angiogenic effects through regulation of angiogenic factors released from HCC cells. Modulation of VEGF and Angs secretion by IFN-alpha and 5-FU may contribute to their anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects on HCC.
Figures


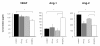

References
-
- Shen DW, Lu YG, Chin KV, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines exhibit multidrug resistance unrelated to MRD1 gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991;98:317–322. - PubMed
-
- Nagano H, Miyamoto A, Wada H, Ota H, Marubashi S, Takeda Y, Dono K, Umeshita K, Sakon M, Monden M. Interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil combination therapy after palliative hepatic resection in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, portal venous tumor thrombus in the major trunk, and multiple nodules. Cancer. 2007;110(11):1054–1058. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagano H, Sakon M, Eguchi H, Kondo M, Yamamoto T, Ota H, Nakamura M, Wada H, Damdinsuren B, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Takeda Y, Dono K, Umeshita K, Nakamori S, Monden M. Hepatic resection followed by IFN-alpha and 5-FU for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in the major portal branch. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:172–179. - PubMed
-
- Obi S, Yoshida H, Toune R, Unuma T, Kanda M, Sato S, Tateishi R, Teratani T, Shiina S, Omata M. Combination therapy of intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and systemic interferon-alpha for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous invasion. Cancer. 2006;106:1990–1997. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21832. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

