PLAST: parallel local alignment search tool for database comparison
- PMID: 19821978
- PMCID: PMC2770072
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-329
PLAST: parallel local alignment search tool for database comparison
Abstract
Background: Sequence similarity searching is an important and challenging task in molecular biology and next-generation sequencing should further strengthen the need for faster algorithms to process such vast amounts of data. At the same time, the internal architecture of current microprocessors is tending towards more parallelism, leading to the use of chips with two, four and more cores integrated on the same die. The main purpose of this work was to design an effective algorithm to fit with the parallel capabilities of modern microprocessors.
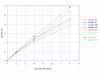
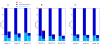
Results: A parallel algorithm for comparing large genomic banks and targeting middle-range computers has been developed and implemented in PLAST software. The algorithm exploits two key parallel features of existing and future microprocessors: the SIMD programming model (SSE instruction set) and the multithreading concept (multicore). Compared to multithreaded BLAST software, tests performed on an 8-processor server have shown speedup ranging from 3 to 6 with a similar level of accuracy.
Conclusion: A parallel algorithmic approach driven by the knowledge of the internal microprocessor architecture allows significant speedup to be obtained while preserving standard sensitivity for similarity search problems.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

