BU-32: a novel proteasome inhibitor for breast cancer
- PMID: 19821999
- PMCID: PMC2790855
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2411
BU-32: a novel proteasome inhibitor for breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Proteasome inhibition provides an attractive approach to cancer therapy and may have application in the treatment of breast cancer. However, results of recent clinical trials to evaluate the effect of the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (Velcade, also called PS-341) in metastatic breast cancer patients have shown limited activity when used as a single agent. This underscores the need to find new and more efficacious proteasome inhibitors. In this study, we evaluate the efficacy of the novel proteasome inhibitor BU-32 (NSC D750499-S) using in vitro and in vivo breast cancer models.
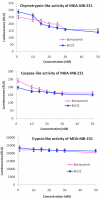
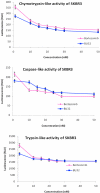
Methods: We have recently synthesized a novel proteasome inhibitor (BU-32) and tested its growth inhibitory effects in different breast cancer cells including MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and SKBR3 by in vitro cytotoxicity and proteasomal inhibition assays. The apoptotic potential of BU32 was tested using flow cytometry and analyzing cell cycle regulatory proteins. In vivo tumor xenograft studies for solid tumor as well as tumor metastasis were conducted using MDA-MB-231-GFP cells.
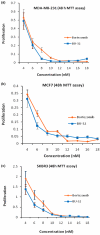
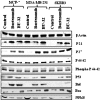
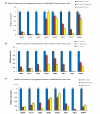
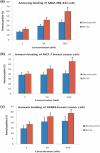
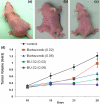
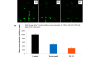
Results: We report for the first time that BU-32 exhibits strong cytotoxicity in a panel of cell lines: MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 5.8 nM), SKBR3 (IC50 = 5.7 nM) and MCF-7 cells (IC50 = 5.8 nM). It downregulates a wide array of angiogenic marker genes and upregulates apoptotic markers, including Bid and Bax. Incubation of MDA-MB-231 cells with BU-32 results in the accumulation of cell cycle inhibitor proteins p21 and p27 and stabilization of the tumor suppressor protein p53. Studies in in vivo solid tumor and metastasis models show significant effect with a 0.06 mg/kg dose of BU-32 and marked reduction in tumor burden in the skeleton.
Conclusions: We have shown that BU-32 is effective in cultured breast cancer cells and in breast cancer xenografts. The results suggest its potential benefit in breast cancer treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Orlowski M, Cardozo C, Michaud C. Evidence for the presence of five distinct proteolytic components in the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Properties of two components cleaving bonds on the carboxyl side of branched chain and small neutral amino acids. Biochemistry. 1993;32:1563–1572. doi: 10.1021/bi00057a022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

