Resolving the composition of protein complexes using a MALDI LTQ Orbitrap
- PMID: 19822444
- PMCID: PMC2820827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jasms.2009.08.026
Resolving the composition of protein complexes using a MALDI LTQ Orbitrap
Abstract
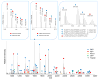
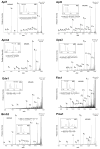
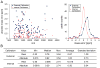
Current biological studies have been advanced by the continuous development of robust, accurate, and sensitive mass spectrometric technologies. The MALDI LTQ Orbitrap is a new addition to the Orbitrap configurations, known for their high resolving power and accuracy. This configuration provides features inherent to the MALDI source, such as reduced spectra complexity, forgiveness to contaminants, and sample retention for follow-up analyses with targeted or hypothesis-driven questions. Here we investigate its performance for characterizing the composition of isolated protein complexes. To facilitate the assessment, we selected two well characterized complexes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Apl1 and Nup84. Manual and automatic MS and MS/MS analyses readily resolved their compositions, with increased confidence of protein identification compared with our previous reports using MALDI QqTOF and MALDI IT. CID fragmentation of singly-charged peptides provided sufficient information for conclusive identification of the isolated proteins. We then assessed the resolution, accuracy, and sensitivity provided by this instrument in the context of analyzing the isolated protein assemblies. Our analysis of complex mixtures of singly-charged ions up to m/z 4000 showed that (1) the resolving power, inversely proportional to the square root of m/z, had over four orders of magnitude dynamic range; (2) internal calibration led to improved accuracy, with an average absolute mass error of 0.5 ppm and a distribution centered at 0 ppm; and (3) subfemtomole sensitivity was achieved using both CHCA and DHB matrices. Additionally, our analyses of a synthetic phosphorylated peptide in mixtures showed subfemtomole level of detection using neutral loss scanning.
2010 American Society for Mass Spectrometry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, Rout MP, Sali A. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature. 2007;450(7170):683–94. - PubMed
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, Sali A, Rout MP. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007;450(7170):695–701. - PubMed
-
- Karas M, Hillenkamp F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal Chem. 1988;60(20):2299–301. - PubMed
-
- Hillenkamp F, Karas M, Beavis RC, Chait BT. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of biopolymers. Anal Chem. 1991;63(24):1193A–1203A. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

