Photostimulation of channelrhodopsin-2 expressing ventrolateral medullary neurons increases sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in rats
- PMID: 19822543
- PMCID: PMC2805374
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.177535
Photostimulation of channelrhodopsin-2 expressing ventrolateral medullary neurons increases sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in rats
Abstract
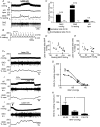
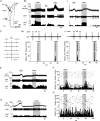
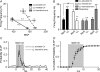
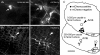
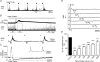
To explore the specific contribution of the C1 neurons to blood pressure (BP) control, we used an optogenetic approach to activate these cells in vivo. A lentivirus that expresses channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) under the control of the catecholaminergic neuron-preferring promoter PRSx8 was introduced into the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). After 2-3 weeks, ChR2 was largely confined to Phox2b-expressing neurons (89%). The ChR2-expressing neurons were non-GABAergic, non-glycinergic and predominantly catecholaminergic (54%). Photostimulation of ChR2-transfected RVLM neurons (473 nm, 20 Hz, 10 ms, 9 mW) increased BP (15 mmHg) and sympathetic nerve discharge (SND; 64%). Light pulses at 0.2-0.5 Hz evoked a large sympathetic nerve response (16 x baseline) followed by a silent period (1-2 s) during which another stimulus evoked a reduced response. Photostimulation activated most (75%) RVLM baroinhibited neurons sampled with 1/1 action potential entrainment to the light pulses and without accommodation during 20 Hz trains. RVLM neurons unaffected by either CO(2) or BP were light-insensitive. Bötzinger respiratory neurons were activated but their action potentials were not synchronized to the light pulses. Juxtacellular labelling of recorded neurons revealed that, of these three cell types, only the cardiovascular neurons expressed the transgene. In conclusion, ChR2 expression had no discernable effect on the putative vasomotor neurons at rest and was high enough to allow precise temporal control of their action potentials with light pulses. Photostimulation of RVLM neurons caused a sizable sympathoactivation and rise in blood pressure. These results provide the most direct evidence yet that the C1 neurons have a sympathoexcitatory function.
Figures


References
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL. Axonal projection patterns of ventrolateral medullospinal sympathoexcitatory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985;53:1551–1566. - PubMed
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Brown DL, Guyenet PG. Cardiovascular neurons of brain stem with projections to spinal cord. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1984;247:R1009–R1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

