Mouse neurexin-1alpha deletion causes correlated electrophysiological and behavioral changes consistent with cognitive impairments
- PMID: 19822762
- PMCID: PMC2764944
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910297106
Mouse neurexin-1alpha deletion causes correlated electrophysiological and behavioral changes consistent with cognitive impairments
Abstract
Deletions in the neurexin-1alpha gene were identified in large-scale unbiased screens for copy-number variations in patients with autism or schizophrenia. To explore the underlying biology, we studied the electrophysiological and behavioral phenotype of mice lacking neurexin-1alpha. Hippocampal slice physiology uncovered a defect in excitatory synaptic strength in neurexin-1alpha deficient mice, as revealed by a decrease in miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) frequency and in the input-output relation of evoked postsynaptic potentials. This defect was specific for excitatory synaptic transmission, because no change in inhibitory synaptic transmission was observed in the hippocampus. Behavioral studies revealed that, compared with littermate control mice, neurexin-1alpha deficient mice displayed a decrease in prepulse inhibition, an increase in grooming behaviors, an impairment in nest-building activity, and an improvement in motor learning. However, neurexin-1alpha deficient mice did not exhibit any obvious changes in social behaviors or in spatial learning. Together, these data indicate that the neurexin-1alpha deficiency induces a discrete neural phenotype whose extent correlates, at least in part, with impairments observed in human patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


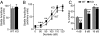
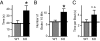
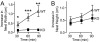
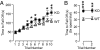
References
-
- Ushkaryov YA, Petrenko AG, Geppert M, Südhof TC. Neurexins: Synaptic cell surface proteins related to the α-latrotoxin receptor and laminin. Science. 1992;257:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Ushkaryov YA, et al. Conserved domain structure of ß-Neurexins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11987–11992. - PubMed
-
- Ichtchenko K, et al. Neuroligin 1: A splice-site specific ligand for ß-neurexins. Cell. 1995;81:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Ichtchenko K, Nguyen T, Südhof TC. Structures, alternative splicing, and neurexin binding of multiple neuroligins. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:2676–2682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

