Delusional infestation
- PMID: 19822895
- PMCID: PMC2772366
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00018-09
Delusional infestation
Abstract
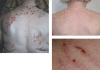
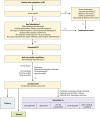
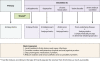
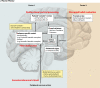
This papers aims at familiarizing psychiatric and nonpsychiatric readers with delusional infestation (DI), also known as delusional parasitosis. It is characterized by the fixed belief of being infested with pathogens against all medical evidence. DI is no single disorder but can occur as a delusional disorder of the somatic type (primary DI) or secondary to numerous other conditions. A set of minimal diagnostic criteria and a classification are provided. Patients with DI pose a truly interdisciplinary problem to the medical system. They avoid psychiatrists and consult dermatologists, microbiologists, or general practitioners but often lose faith in professional medicine. Epidemiology and history suggest that the imaginary pathogens change constantly, while the delusional theme "infestation" is stable and ubiquitous. Patients with self-diagnosed "Morgellons disease" can be seen as a variation of this delusional theme. For clinicians, clinical pathways for efficient diagnostics and etiology-specific treatment are provided. Specialized outpatient clinics in dermatology with a liaison psychiatrist are theoretically best placed to provide care. The most intricate problem is to engage patients in psychiatric therapy. In primary DI, antipsychotics are the treatment of choice, according to limited but sufficient evidence. Pimozide is no longer the treatment of choice for reasons of drug safety. Future research should focus on pathophysiology and the neural basis of DI, as well as on conclusive clinical trials, which are widely lacking. Innovative approaches will be needed, since otherwise patients are unlikely to adhere to any study protocol.
Figures

References
-
- Accordino, R. E., D. Engler, I. H. Ginsburg, and J. Koo. 2008. Morgellons disease? Dermatol. Ther. 21:8-12. - PubMed
-
- Adunsky, A. 1997. Early post-stroke parasitic delusions. Age Ageing 26:238-239. - PubMed
-
- Aftab, A., and K. M. Ranjha. 2005. Ekboms disease (delusional disorder, somatic type): a case report. J. Pak. Assoc. Dermatol. 15:96-98.
-
- Agency for Health Care Policy and Research. 1992. AHCPR publication 92-0032. Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, Rockville, MD.
-
- Aguirre, A. J., R. Apiquian, A. Fresan, and C. Cruz-Fuentes. 2007. Association analysis of exon III and exon I polymorphisms of the dopamine D4 receptor locus in Mexican psychotic patients. Psychiatry Res. 153:209-215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

