Identification of Plasmodium malariae, a human malaria parasite, in imported chimpanzees
- PMID: 19823579
- PMCID: PMC2756624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007412
Identification of Plasmodium malariae, a human malaria parasite, in imported chimpanzees
Abstract
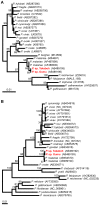
It is widely believed that human malaria parasites infect only man as a natural host. However, earlier morphological observations suggest that great apes are likely to be natural reservoirs as well. To identify malaria parasites in great apes, we screened 60 chimpanzees imported into Japan. Using the sequences of small subunit rRNA and the mitochondrial genome, we identified infection of Plasmodium malariae, a human malaria parasite, in two chimpanzees that were imported about thirty years ago. The chimpanzees have been asymptomatic to the present. In Japan, indigenous malaria disappeared more than fifty years ago; and thus, it is most likely inferred that the chimpanzees were infected in Africa, and P. malariae isolates were brought into Japan from Africa with their hosts, suggesting persistence of parasites at low level for thirty years. Such a long term latent infection is a unique feature of P. malariae infection in humans. To our knowledge, this is the first to report P. malariae infection in chimpanzees and a human malaria parasite from nonhuman primates imported to a nonendemic country.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Levine ND. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press; 1988. The protozoan phylum Apicomplexa.
-
- Reichenow E. Ueber das vorkommen der malariaparasiten des menschen bei den afrikanischen menschenaffen. Centralbl f Bakt I Abt Orig. 1920;85:207–216.
-
- Coatney GR, Collins WE, Warren M, Contacos PG. Atlanta, GA: CDC; 2003. CD-ROM. The primate malarias [original book published 1971]
-
- Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, Radhakrishnan A, Shamsul SS, et al. A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet. 2004;363:1017–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases