Physical modeling of pulse artefact sources in simultaneous EEG/fMRI
- PMID: 19823981
- PMCID: PMC6870628
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20891
Physical modeling of pulse artefact sources in simultaneous EEG/fMRI
Abstract
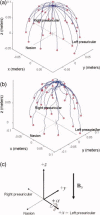
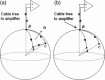
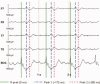
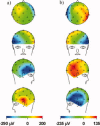
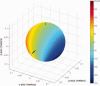
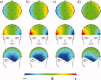
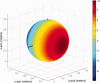
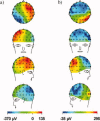
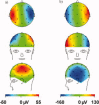
The collection of electroencephalography (EEG) data during simultaneous functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is impeded by large artefacts in the EEG recordings, with the pulse artefact (PA) being particularly challenging because of its persistence even after application of artefact correction algorithms. Despite several possible causes of the PA having been hypothesized, few studies have rigorously quantified the contributions from the different putative sources. This article presents analytic expressions and simulations describing two possible sources of the PA corresponding to different movements in the strong static field of the MR scanner: cardiac-pulse-driven head rotation and blood-flow-induced Hall voltages. Models of head rotation about a left-right axis and flow in a deep artery running in the anterior-posterior direction reproduced properties of the PA including the left/right spatial variation of polarity. Of these two sources, head rotation was shown to be the most likely source of the PA with simulated magnitudes of >200 muV being generated at 3 T, similar to the in vivo PA magnitudes, for an angular velocity of just 0.5 degrees /s. Smaller artefact voltages of less than 10 muV were calculated for flow in a model artery with physical characteristics similar to the internal carotid artery. A deeper physical understanding of the PA is a key step in working toward production of higher fidelity EEG/fMRI data: analytic expressions for the artefact voltages can guide a redesign of the wiring layout on EEG caps to minimize intrinsic artefact pickup, while simulated artefact maps could be incorporated into selective filters.
Copyright 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Allen P, Polizzi G, Krakow K, Fish D, Lemieux L ( 1998): Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: The problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. Neuroimage 8: 229–239. - PubMed
-
- Allen P, Josephs O, Turner R ( 2000): A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. Neuroimage 12: 230–239. - PubMed
-
- Anami K, Saitoh O, Yumoto M, Tanaka F, Kawagoe Y, Ohnishi T, Matsuda H ( 2002): Reduction of ballistocardiogram with a vacuum head‐fixating system during simultaneous fMRI and multi‐channel monopolar EEG recording. Int Congr Ser 1232: 427–431.
-
- Bencsik M, Bowtell R, Bowley R ( 2007): Electric fields induced in the human body by time‐varying magnetic field gradients in MRI: Numerical calculations and correlation analysis. Phys Med Biol 52: 2337–2353. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

