Cholesteryl ester transfer protein: at the heart of the action of lipid-modulating therapy with statins, fibrates, niacin, and cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors
- PMID: 19825813
- PMCID: PMC2806550
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp399
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein: at the heart of the action of lipid-modulating therapy with statins, fibrates, niacin, and cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors
Abstract
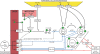
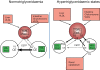
Subnormal plasma levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) constitute a major cardiovascular risk factor; raising low HDL-C levels may therefore reduce the residual cardiovascular risk that frequently presents in dyslipidaemic subjects despite statin therapy. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), a key modulator not only of the intravascular metabolism of HDL and apolipoprotein (apo) A-I but also of triglyceride (TG)-rich particles and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), mediates the transfer of cholesteryl esters from HDL to pro-atherogenic apoB-lipoproteins, with heterotransfer of TG mainly from very low-density lipoprotein to HDL. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity is elevated in the dyslipidaemias of metabolic disease involving insulin resistance and moderate to marked hypertriglyceridaemia, and is intimately associated with premature atherosclerosis and high cardiovascular risk. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition therefore presents a preferential target for elevation of HDL-C and reduction in atherosclerosis. This review appraises recent evidence for a central role of CETP in the action of current lipid-modulating agents with HDL-raising potential, i.e. statins, fibrates, and niacin, and compares their mechanisms of action with those of pharmacological agents under development which directly inhibit CETP. New CETP inhibitors, such as dalcetrapib and anacetrapib, are targeted to normalize HDL/apoA-I levels and anti-atherogenic activities of HDL particles. Further studies of these CETP inhibitors, in particular in long-term, large-scale outcome trials, will provide essential information on their safety and efficacy in reducing residual cardiovascular risk.
Figures

References
-
- Libby P. The forgotten majority: unfinished business in cardiovascular risk reduction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:1225–1228. - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, Kirby A, Sourjina T, Peto R, Collins R, Simes R Cholesterol Treatment Trialists' (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005;366:1267–1278. - PubMed
-
- Chapman MJ. Therapeutic elevation of HDL-cholesterol to prevent atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;111:893–908. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ JUPITER Study Group. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2195–2207. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Rader DJ, Rouleau JL, Belder R, Joyal SV, Hill KA, Pfeffer MA, Skene AM Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation Infection Therapy-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 22 Investigators. Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1495–1504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

