Massive gliosis induced by interleukin-6 suppresses Abeta deposition in vivo: evidence against inflammation as a driving force for amyloid deposition
- PMID: 19825975
- PMCID: PMC3083918
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-141754
Massive gliosis induced by interleukin-6 suppresses Abeta deposition in vivo: evidence against inflammation as a driving force for amyloid deposition
Abstract
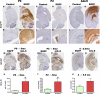
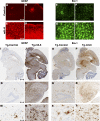
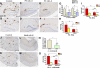
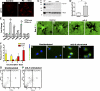
Proinflammatory stimuli, after amyloid beta (Abeta) deposition, have been hypothesized to create a self-reinforcing positive feedback loop that increases amyloidogenic processing of the Abeta precursor protein (APP), promoting further Abeta accumulation and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a proinflammatory cytokine, has been shown to be increased in AD patients implying a pathological interaction. To assess the effects of IL-6 on Abeta deposition and APP processing in vivo, we overexpressed murine IL-6 (mIL-6) in the brains of APP transgenic TgCRND8 and TG2576 mice. mIL-6 expression resulted in extensive gliosis and concurrently attenuated Abeta deposition in TgCRND8 mouse brains. This was accompanied by up-regulation of glial phagocytic markers in vivo and resulted in enhanced microglia-mediated phagocytosis of Abeta aggregates in vitro. Further, mIL-6-induced neuroinflammation had no effect on APP processing in TgCRND8 and had no effect on APP processing or steady-state levels of Abeta in young Tg2576 mice. These results indicate that mIL-6-mediated reactive gliosis may be beneficial early in the disease process by potentially enhancing Abeta plaque clearance rather than mediating a neurotoxic feedback loop that exacerbates amyloid pathology. This is the first study that methodically dissects the contribution of mIL-6 with regard to its potential role in modulating Abeta deposition in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation in Alzheimer disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response? Nat Med. 2006;12:1005–1015. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole G M, Cooper N R, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich B L, Finch C E, Frautschy S, Griffin W S, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie I R, McGeer P L, O'Banion M K, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel F L, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ringheim G E, Szczepanik A M, Petko W, Burgher K L, Zhu S Z, Chao C C. Enhancement of beta-amyloid precursor protein transcription and expression by the soluble interleukin-6 receptor/interleukin-6 complex. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;55:35–44. - PubMed
-
- Gao H M, Jiang J, Wilson B, Zhang W, Hong J S, Liu B. Microglial activation-mediated delayed and progressive degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2002;81:1285–1297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

