A genetic variation of the noradrenergic system is related to differential amygdala activation during encoding of emotional memories
- PMID: 19826083
- PMCID: PMC2761241
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907425106
A genetic variation of the noradrenergic system is related to differential amygdala activation during encoding of emotional memories
Abstract
Emotionally arousing events are typically well remembered, but there is a large interindividual variability for this phenomenon. We have recently shown that a functional deletion variant of ADRA2B, the gene encoding the alpha2b-adrenergic receptor, is related to enhanced emotional memory in healthy humans and enhanced traumatic memory in war victims. Here, we investigated the neural mechanisms of this effect in healthy participants by using fMRI. Carriers of the ADRA2B deletion variant exhibited increased activation of the amygdala during encoding of photographs with negative emotional valence compared with noncarriers of the deletion. Additionally, functional connectivity between amygdala and insula was significantly stronger in deletion carriers. The present findings indicate that the ADRA2B deletion variant is related to increased responsivity and connectivity of brain regions implicated in emotional memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

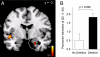
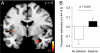
Comment in
-
The neurogenetics of remembering emotions past.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 10;106(45):18881-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910755106. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19889977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- McGaugh JL. Memory and Emotion: The Making of Lasting Memories. New York: Columbia Univ Press; 2003.
-
- Phelps EA, LeDoux JE. Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: From animal models to human behavior. Neuron. 2005;48:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Pitman RK. Post-traumatic stress disorder, hormones, and memory. Biol Psychiatry. 1989;26:221–223. - PubMed
-
- Labar KS, Cabeza R. Cognitive neuroscience of emotional memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:54–64. - PubMed
-
- Phelps EA. Human emotion and memory: Interactions of the amygdala and hippocampal complex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14:198–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

