Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501
- PMID: 19826110
- PMCID: PMC2793043
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7545
Phase II study of cisplatin plus etoposide and bevacizumab for previously untreated, extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3501
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the efficacy and safety of bevacizumab plus cisplatin and etoposide in patients with extensive-stage disease, small-cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC).
Patients and methods: In this phase II trial, 63 patients were treated with bevacizumab 15 mg/kg plus cisplatin 60 mg/m(2) and etoposide 120 mg/m(2), which was followed by bevacizumab alone until death or disease progression occurred. The primary end point was the proportion of patients alive at 6 months without disease progression (ie, progression-free survival [PFS]). Secondary end points included overall survival (OS), objective response rate, and toxicity. Correlative studies were performed to explore the relationship between baseline and changes in plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), soluble cell adhesion molecules (ie, vascular cell adhesion molecule [VCAM], intercellular cell adhesion molecule [ICAM], and E-selectin) and basic fibroblast growth factor and outcome.
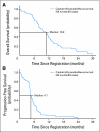
Results: The 6-month PFS was 30.2%, the median PFS was 4.7 months, and OS was 10.9 months. The response rate was 63.5%. The most common adverse event was neutropenia (57.8%). Only one patient had grade 3 pulmonary hemorrhage. Patients who had high baseline VCAM had a higher risk of progression or death compared with those who had low baseline VCAM levels. No relationships between outcome and any other biomarkers were seen.
Conclusion: The addition of bevacizumab to cisplatin and etoposide in patients with ED-SCLC results in improved PFS and OS relative to historical controls who received this chemotherapy regimen without bevacizumab. This regimen appears to be well tolerated and has minimal increase in toxicities compared with chemotherapy alone. Baseline VCAM levels predicted survival, but no other relationships among treatment, biomarkers, and outcome were identified.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized phase II study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: results from the SALUTE trial.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun 1;29(16):2215-22. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.29.3423. Epub 2011 Apr 18. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21502556 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase II-III study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive small-cell lung cancer: results from the IFCT-0802 trial†.Ann Oncol. 2015 May;26(5):908-914. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv065. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Ann Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25688059 Clinical Trial.
-
Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Bevacizumab Regimen Followed by Oral Etoposide and Bevacizumab Maintenance Treatment in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience.Clin Lung Cancer. 2015 Nov;16(6):e229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 18. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26072097
-
Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Jan;22(1):51-65. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30539-8. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33285097 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of small cell lung cancer; advances and future prospects.Respir Investig. 2025 Jul;63(4):680-685. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2025.05.013. Epub 2025 May 29. Respir Investig. 2025. PMID: 40446464 Review.
Cited by
-
[The molecular pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;13(11):C46-57. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.11.18. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21081036 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Cisplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 30306, a phase II study.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Nov 20;29(33):4436-41. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.6923. Epub 2011 Oct 3. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21969504 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and safety of bevacizumab in extensive-disease small cell lung cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Aug;9(16):1285. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-963. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34532422 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of angiogenesis inhibitors in small-cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):1141-1155. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13588. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27901478 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Sinus Bradycardia: A Narrative Review of a Forgotten Adverse Effect of Cardiotoxicity.Drug Saf. 2022 Feb;45(2):101-126. doi: 10.1007/s40264-021-01132-5. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Drug Saf. 2022. PMID: 35025085 Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Simon GR, Turrisi A. Management of small cell lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. (ed 2) 2007;132:324S–339S. - PubMed
-
- Clark R, Ihde DC. Small-cell lung cancer: Treatment progress and prospects. Oncology (Williston Park) 1998;12:647–658. discussion 661–663. - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Furuse K, Saijo N, et al. Randomized trial of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine versus cisplatin and etoposide versus alternation of these regimens in small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991;83:855–861. - PubMed
-
- Wolf M, Havemann K, Holle R, et al. Cisplatin/etoposide versus ifosfamide/etoposide combination chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter German randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1987;5:1880–1889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA07190/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA66636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA066636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA49957/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA049957/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA023318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA007190/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA23318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical