Pegylated interferon alfa-2a yields high rates of hematologic and molecular response in patients with advanced essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera
- PMID: 19826111
- PMCID: PMC4881362
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.6075
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a yields high rates of hematologic and molecular response in patients with advanced essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera
Abstract
Purpose: We conducted a phase II study of pegylated interferon alfa-2a (PEG-IFN-alpha-2a) in patients with essential thrombocythemia (ET) and polycythemia vera (PV).
Patients and methods: Seventy-nine patients (40 with PV and 39 with ET) have been treated. Median time from diagnosis to PEG-IFN-alpha-2a was 54 months in patients with PV and 33 months in patients with ET. Eighty-one percent of patients had received prior therapy. The first three patients received PEG-IFN-alpha-2a at 450 microg weekly. As a result of poor tolerance, this dose was decreased in a stepwise manner to a current starting dose of 90 microg weekly. Seventy-seven patients are evaluable and have been observed for a median of 21 months.
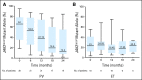
Results: The overall hematologic response rate was 80% in PV and 81% in ET (complete in 70% and 76% of patients, respectively). The JAK2(V617F) mutation was detected in 18 patients with ET and 38 patients with PV; sequential measurements by a pyrosequencing assay were available in 16 patients with ET and 35 patients with PV. The molecular response rate was 38% in ET and 54% in PV, being complete (undetectable JAK2(V617F)) in 6% and 14%, respectively. The JAK2(V617F) mutant allele burden continued to decrease with no clear evidence for a plateau. The tolerability of PEG-IFN-alpha-2a at 90 microg weekly was excellent.
Conclusion: PEG-IFN-alpha-2a resulted in remarkable clinical activity, high rates of molecular response, and acceptable toxicity in patients with advanced ET or PV. The ability of PEG-IFN-alpha-2a to induce complete molecular responses suggests selective targeting of the malignant clone.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365:1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1779–1790. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

