Protopia: a protein-protein interaction tool
- PMID: 19828077
- PMCID: PMC2762066
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S12-S17
Protopia: a protein-protein interaction tool
Abstract
Background: Protein-protein interactions can be considered the basic skeleton for living organism self-organization and homeostasis. Impressive quantities of experimental data are being obtained and computational tools are essential to integrate and to organize this information. This paper presents Protopia, a biological tool that offers a way of searching for proteins and their interactions in different Protein Interaction Web Databases, as a part of a multidisciplinary initiative of our institution for the integration of biological data http://asp.uma.es.
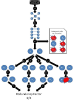
Results: The tool accesses the different Databases (at present, the free version of Transfac, DIP, Hprd, Int-Act and iHop), and results are expressed with biological protein names or databases codes and can be depicted as a vector or a matrix. They can be represented and handled interactively as an organic graph. Comparison among databases is carried out using the Uniprot codes annotated for each protein.
Conclusion: The tool locates and integrates the current information stored in the aforementioned databases, and redundancies among them are detected. Results are compatible with the most important network analysers, so that they can be compared and analysed by other world-wide known tools and platforms. The visualization possibilities help to attain this goal and they are especially interesting for handling multiple-step or complex networks.
Figures





References
-
- Rodríguez-Caso C, Sole R. Networks in cell biology. In: Dubitzky W, Granzow M, Berrar D, editor. Fundamentals of Data Mining in Genomics and Proteomics. Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2006.
-
- Palotai R, Szalay MS, Csermely P. Chaperones as integrators of cellular networks: changes of cellular integrity in stress and diseases. IUBMB Life. 2008;60:10–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

